Abstracts of the 2021 Annual meeting of the ALEH (Asociación Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Hígado)
Más datosNon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined as a worldwide public health problem. NAFLD is a metabolic syndrome that involves: dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2), obesity, cardiovascular diseases, cirrhosis, low levels of adiponectin and hepatocarcinoma whose rate of morbidity and mortality is quite high.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the relationship between the degree of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients of both sexes, analyzing lifestyle and drugs associated with metabolic disorders that correct and influence the evolution of the disease.
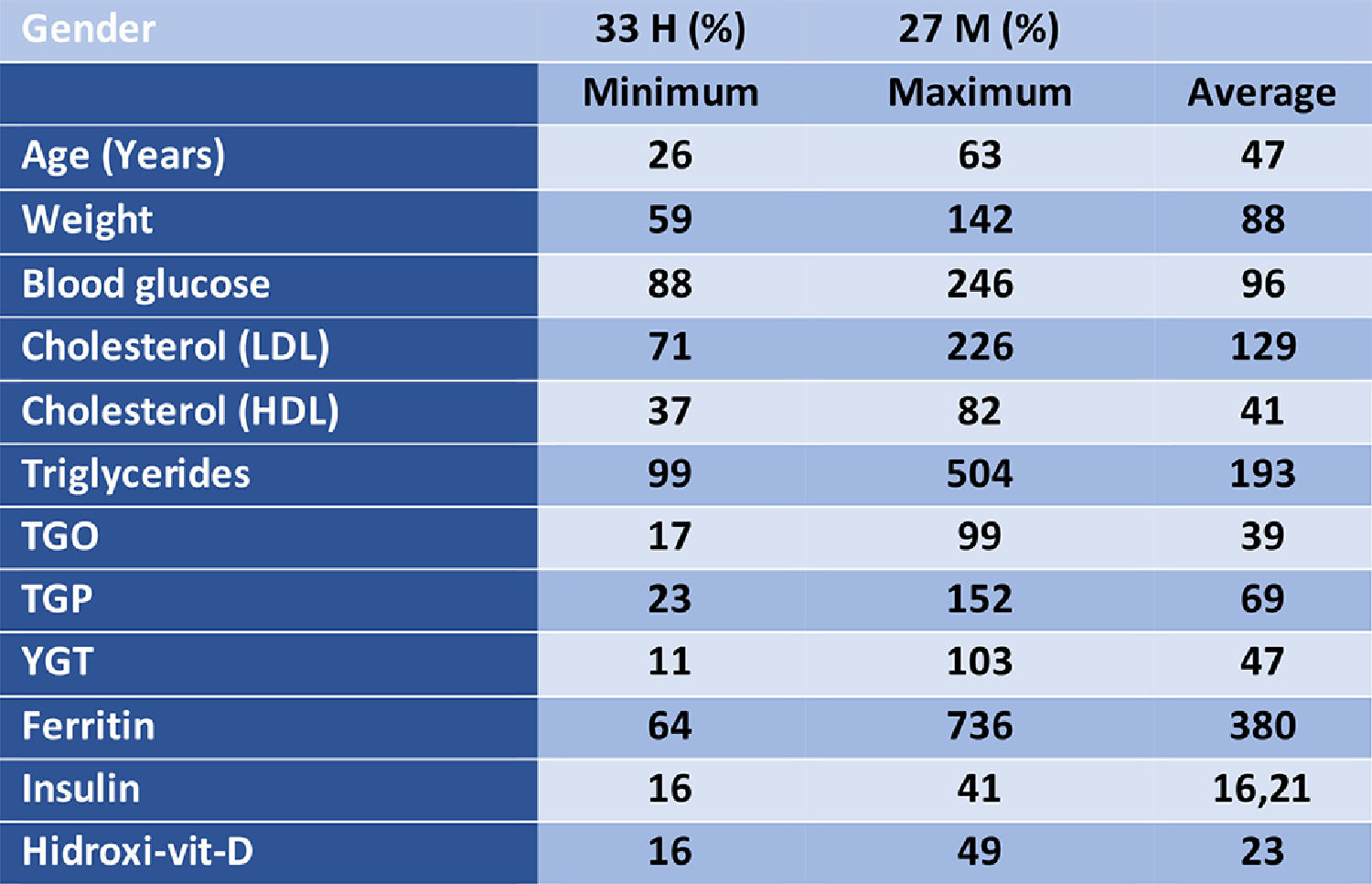
MethodsA retrospective study was conducted in patients with NAFLD treated, following the following procedures: physical and laboratory (fasting glucose, LDL and HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, TGO, TGP, gamaGT, ferritin and insulin and Hydrox-vit-D) (Table 1), ultrasound of the liver and assessment of nutrology / nutrition. Safety and efficacy were assessed over a 180-day follow-up.
Results60 patients were included with variables shown in (table 1). In the ultrasound analysis he classified: mild (8), moderate (36) accentuated (16). Hepatic elastography (Fibroscan) was performed in 1/3 of the patients in a marked way, mostly showing fibrosis <2 on the Metavir scale and in two cases: fibrosis 4. The nutritional protocol with a protein-based diet: chicken, fish and eggs, fruits, roots, vegetables and whole grains, including probiotics in 30% associating orlistat-120 mg + omega-3-1000 (EPA + DHA) + silymarin-200mg + Metformin (glyphage-XR-500mg) in two daily doses; vit supplementation. A-Z and vit. D (2,000 to 10,000 wm) and physical exercise. In the period between 90 and 180 days, weight loss, reduction in hepatic and metabolic rates and changes in the grading of liver ultrasound analysis were observed.
ConclusionThe profile of NAFLD was determined by a non-invasive method: laboratory and ultrasound and the recommendation of a nutrology / nutrition protocol, associated with drugs that correct metabolic changes, proved to be effective in controlling this pathology.