Abstracts from XVII Mexican Congress of Hepatology
Más datosSarcopenia, defined as loss of muscle mass and strength, and minimal hepatic encephalopathy (MHE), alter the quality of life and prognosis of patients with cirrhosis. Ammonia plays a key role in the pathogenesis of MHE and has been associated with decreased muscle mass and strength. However, the relationship between sarcopenia and MHE is not well defined. The objective of this study was to determine their relationship and identify predictors of MHE.
Materials and MethodsProspective study, including 96 patients with compensated cirrhosis diagnosed by transitional elastography. The presence of MHE and sarcopenia was determined by a critical flicker frequency test and standard from the European Working Group EWGSOP2. Muscle mass and strength were determined by electrical bioimpedance and a handgrip dynamometer. Functional capacity was evaluated by a Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB), performing linear logistic regression analysis to identify predictors of MHE. The trial was approved by the research ethics committee, and informed consent was obtained.
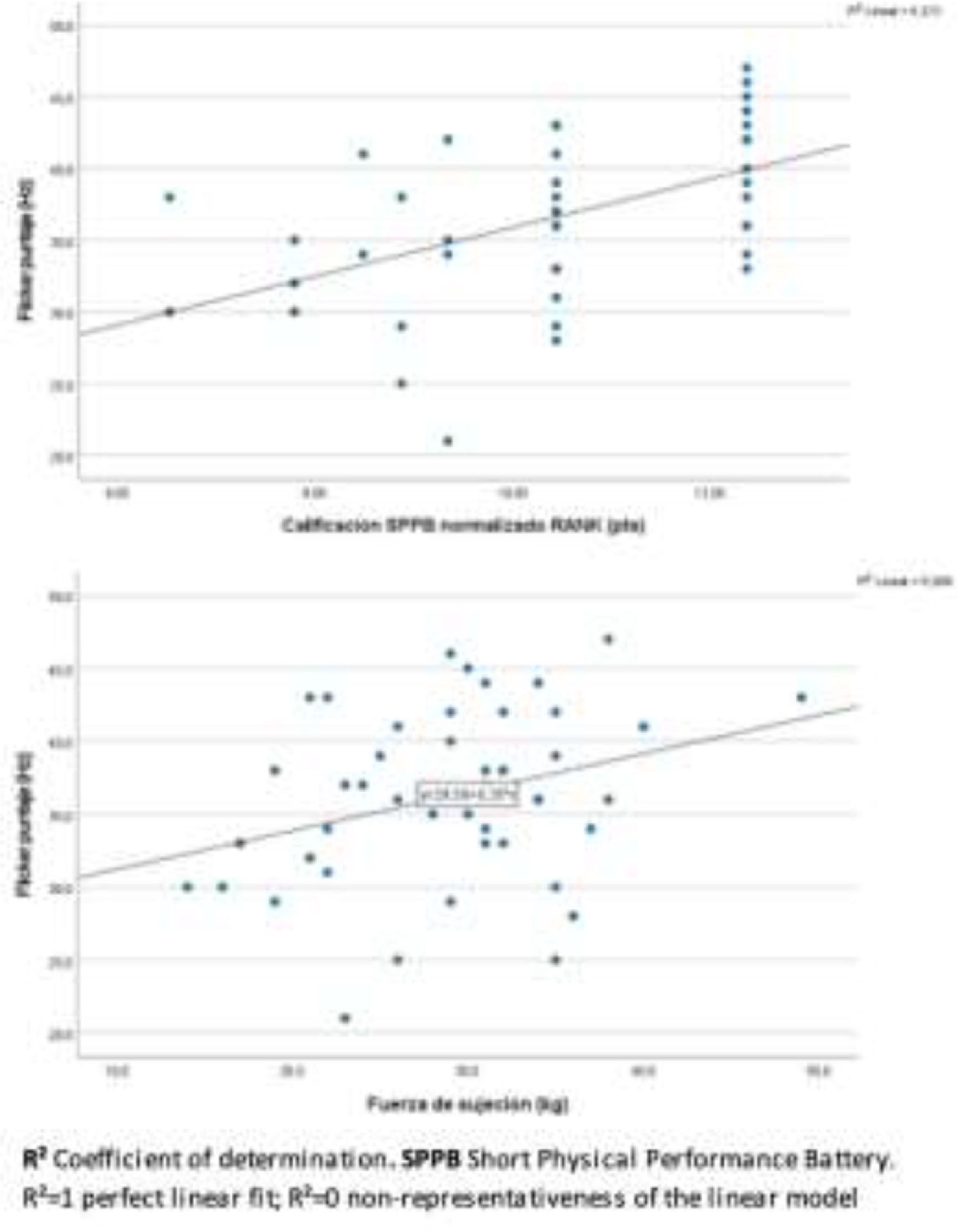
ResultsOf the ninety-six patients with cirrhosis, 61 (64%) and 35 (36.5%) were diagnosed with MHE and sarcopenia, respectively. In the multivariate analysis, the SPPB rating (R 0.521, 95% CI 0.85-2.54, p=<0.001) and grip strength (R 0.314, 95% CI 0.024-0-50, p=0.032) showed the highest predictive value for MHE. (Table 1 and Figure 1).
ConclusionsDecreased handgrip strength and SPPB score were significant predictors of MHE. Early nutritional intervention and physical rehabilitation could reduce the risk of developing EHM in patients with cirrhosis.
FundingDonation by the volunteer ladies of the Hospital General de México “Dr. Eduardo Liceaga.”
Declaration of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.