La pandemia COVID-19 condujo a España al decreto de estado de alarma con cese de actividades no esenciales el 14 de marzo de 2020 y a intervenciones de salud pública, como el confinamiento domiciliario y otras recomendaciones sanitarias para evitar la propagación del virus SARS-CoV-2: la higiene de manos y la obligatoriedad de portar mascarillas. Estos factores podrían haber influido en la tasa de conjuntivitis virales
MétodoEn este estudio descriptivo retrospectivo no intervencionista se compara la incidencia de conjuntivitis virales en un servicio de urgencias de un hospital nacional sobre dos periodos de tiempo: pre-COVID (13 de marzo a 30 de septiembre de 2019, un año antes del inicio de la pandemia) y COVID (13 de marzo a 30 de septiembre de 2020).
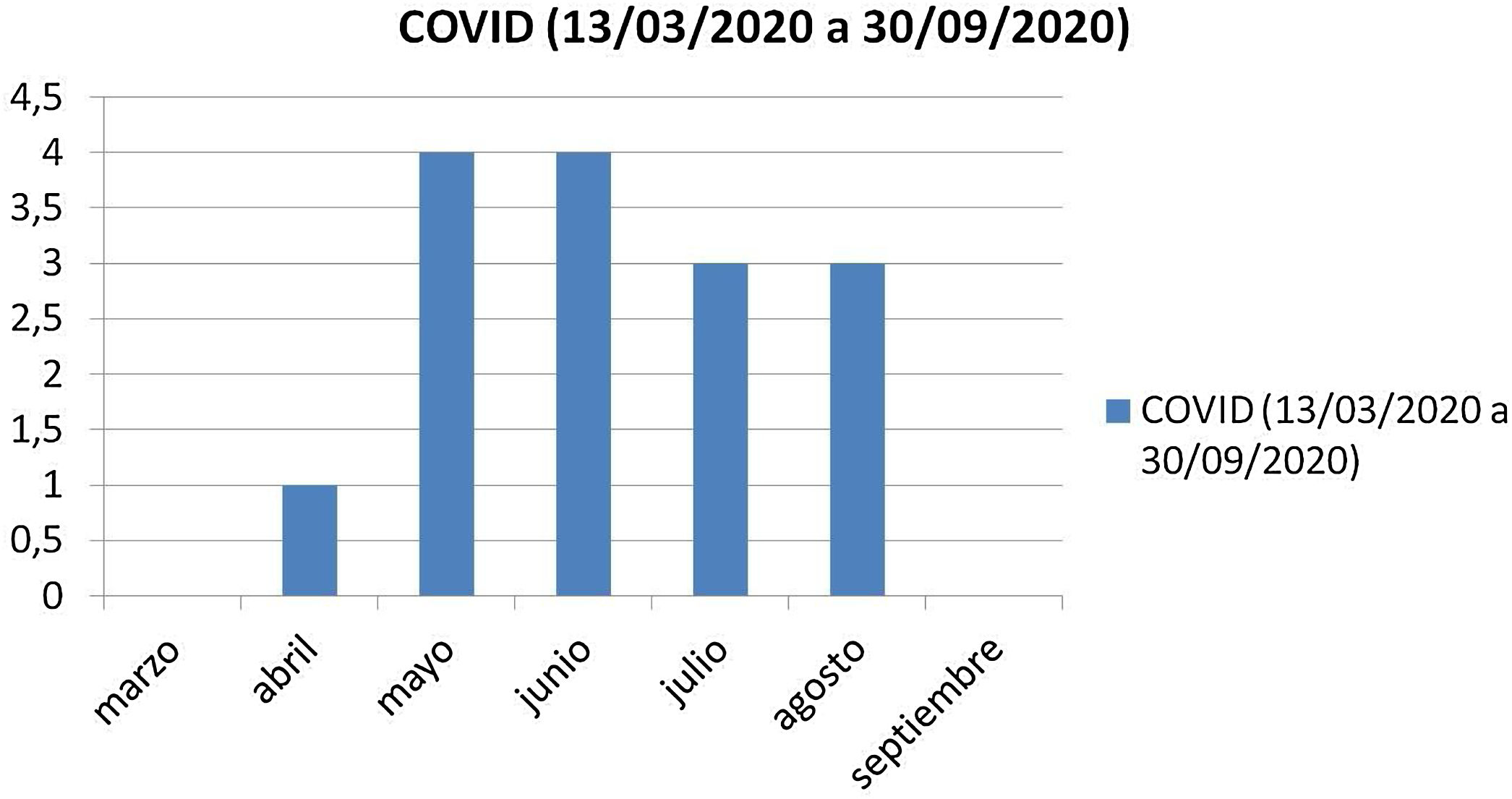
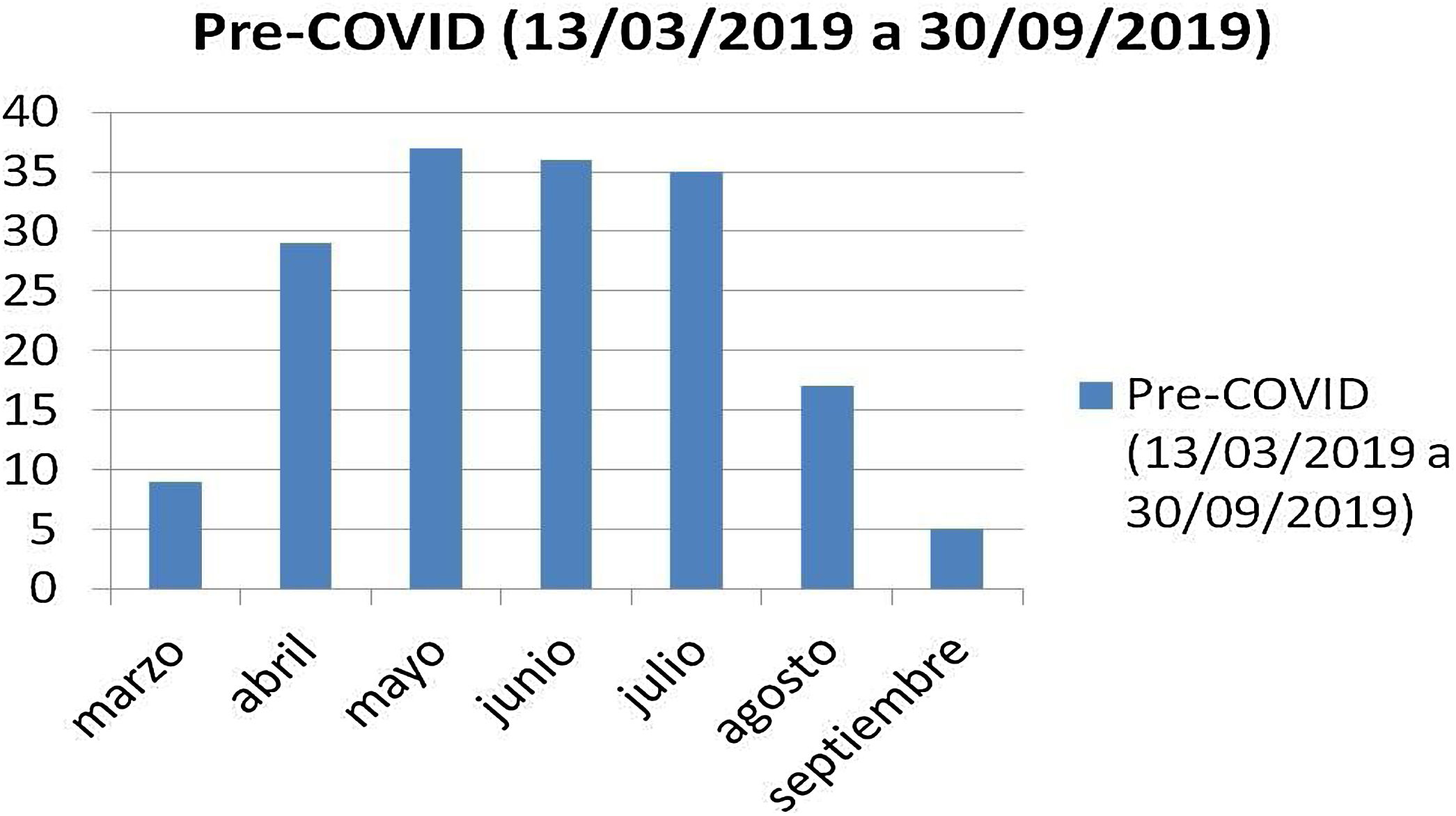
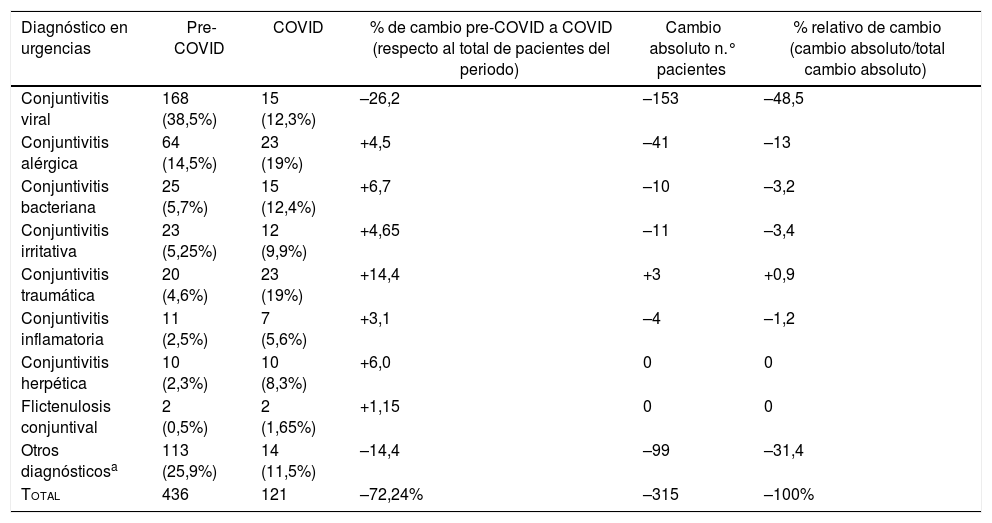
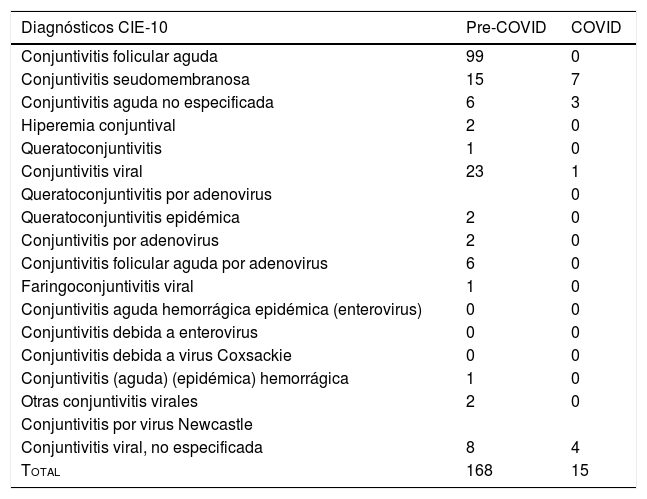
ResultadosEn el primer periodo hubo 436 conjuntivitis, de las cuales 168 (38,5%) fueron casos confirmados de conjuntivitis viral 168 (38,5%), mientras que en el segundo periodo hubo 121 registros, de los cuales los más frecuentes fueron las conjuntivitis alérgicas y las traumáticas, con 23 casos (19% cada grupo); las conjuntivitis bacterianas, con 15 casos (12,3%), y las conjuntivitis virales, con 15 casos (12,3%). El diagnóstico de conjuntivitis viral es el que experimenta una reducción relativa más importante (48,5%), mientras que otros tipos de conjuntivitis apenas cambian su frecuencia relativa entre estos dos periodos de tiempo.
ConclusionesLa conjuntivitis viral, como patología infecciosa más frecuente del ojo, tiene una transmisión similar a la del coronavirus, por lo que las medidas implantadas podrían afectar positivamente a su incidencia.
The COVID-19 pandemic led Spain to order a state of alert with the cessation of non-essential activities on 14 March 2020, and to implement public health interventions (such as home confinement) and other health recommendations to prevent the spread of the SARS-CoV-2 virus (hand washing and the obligation to wear face-masks). These factors could have influenced the rate of viral conjunctivitis.
MethodIn this retrospective, noninterventional, descriptive study, the incidence of viral conjunctivitis in an emergency department of a national hospital is compared over two distinct time periods: pre-COVID (13 March-30 September 2019, one year before the start of the pandemic) and COVID (13 March-30 September 2020).
ResultsIn the first period there were 436 cases of conjunctivitis, of which 168 (38.5%) were confirmed cases of viral conjunctivitis 168 (38.5%), while in the second period there were 121 recorded cases, of which the most frequent were allergic and traumatic (23 cases; 19% each group), bacterial (15 cases; 12.3%) and viral (15 cases; 12.3%). The diagnosis of viral conjunctivitis is the one that suffered the most significant relative reduction (48.5%), while other types of conjunctivitis hardly changed their relative frequency between these two periods of time.
ConclusionsViral conjunctivitis is the most frequent infectious disease of the eye and has a transmission rate similar to that of coronavirus, so the measures implemented could positively affect its incidence.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora