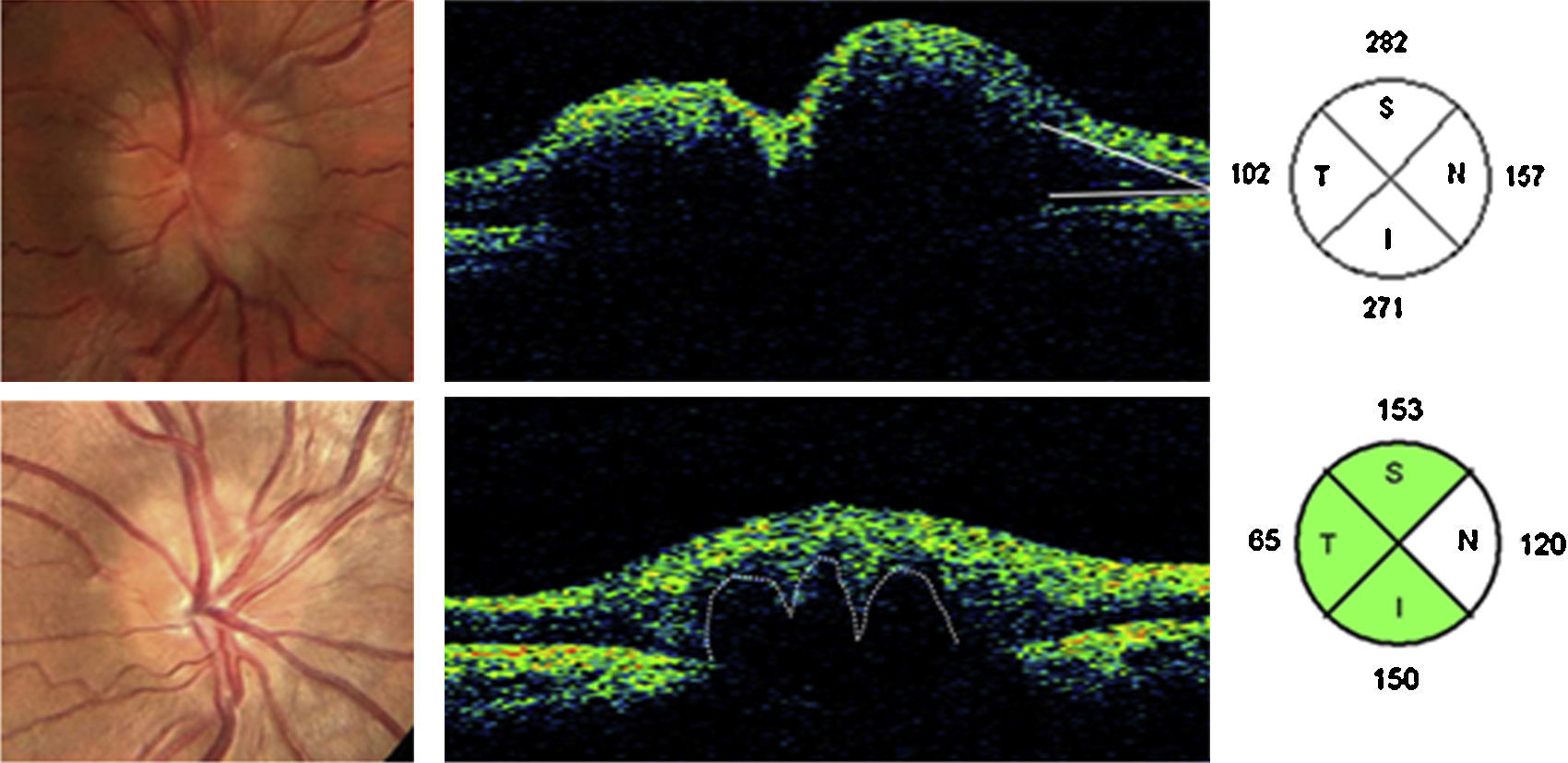
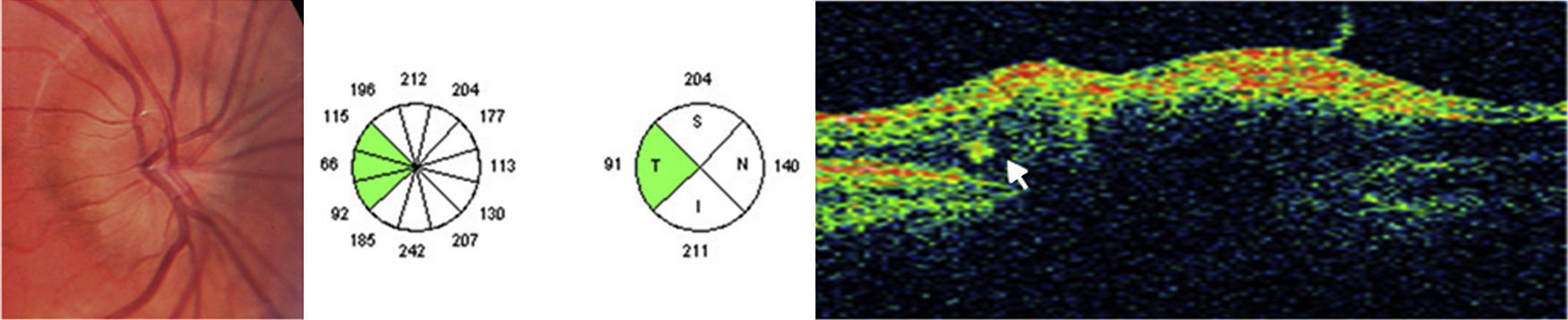
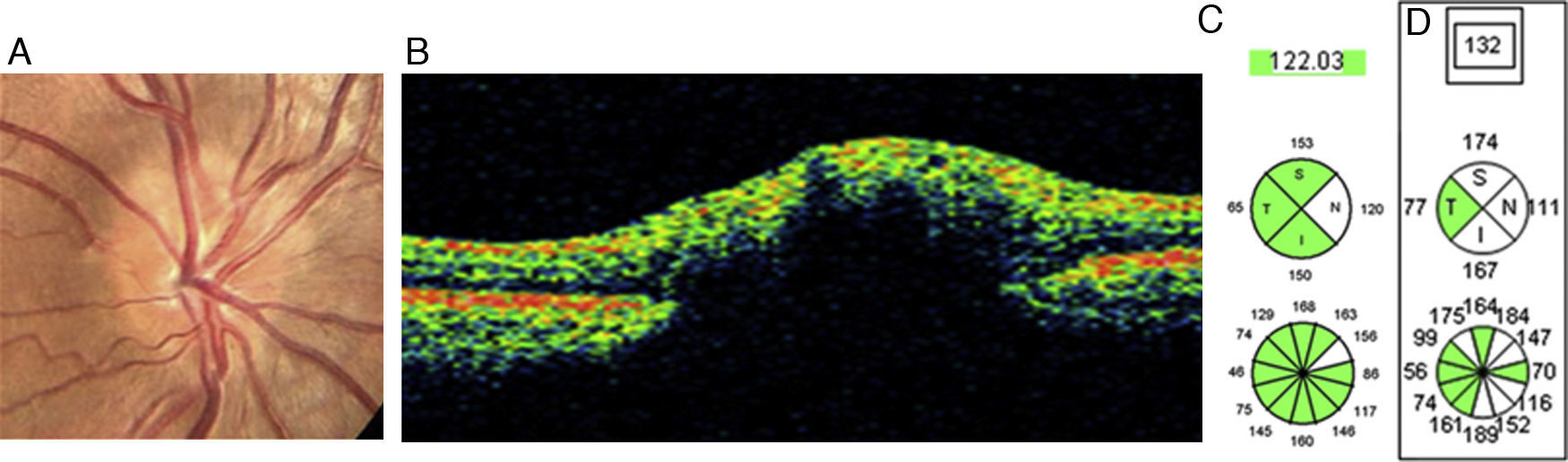
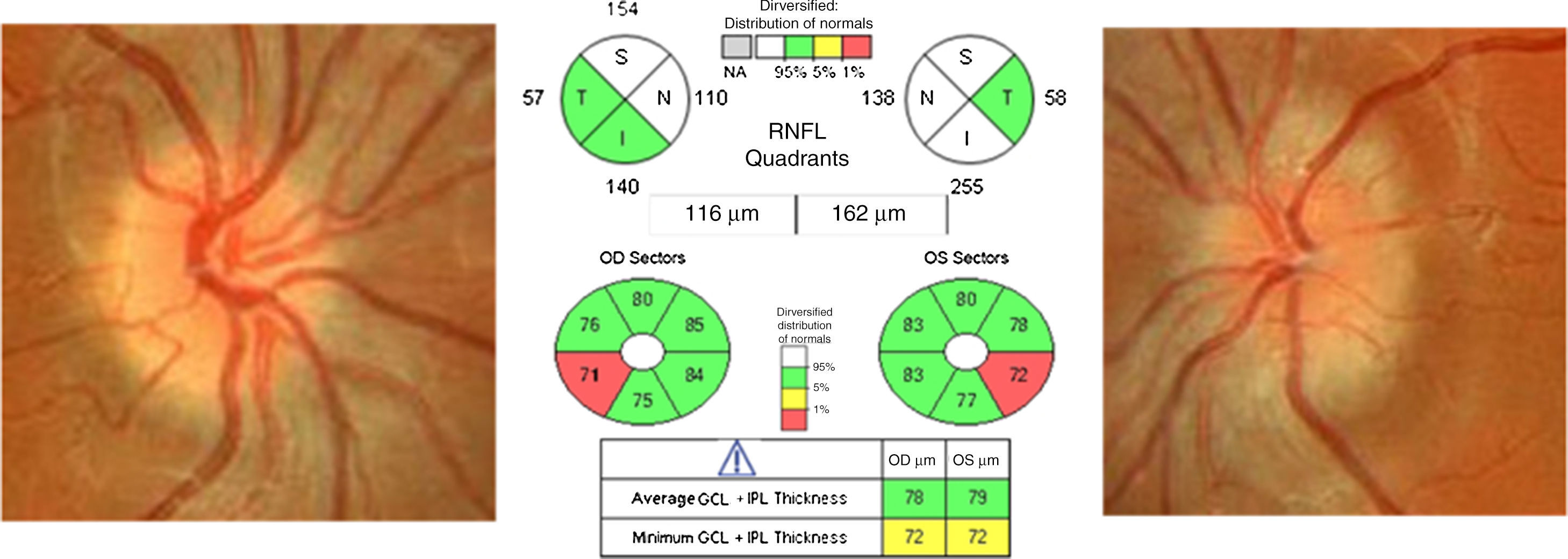
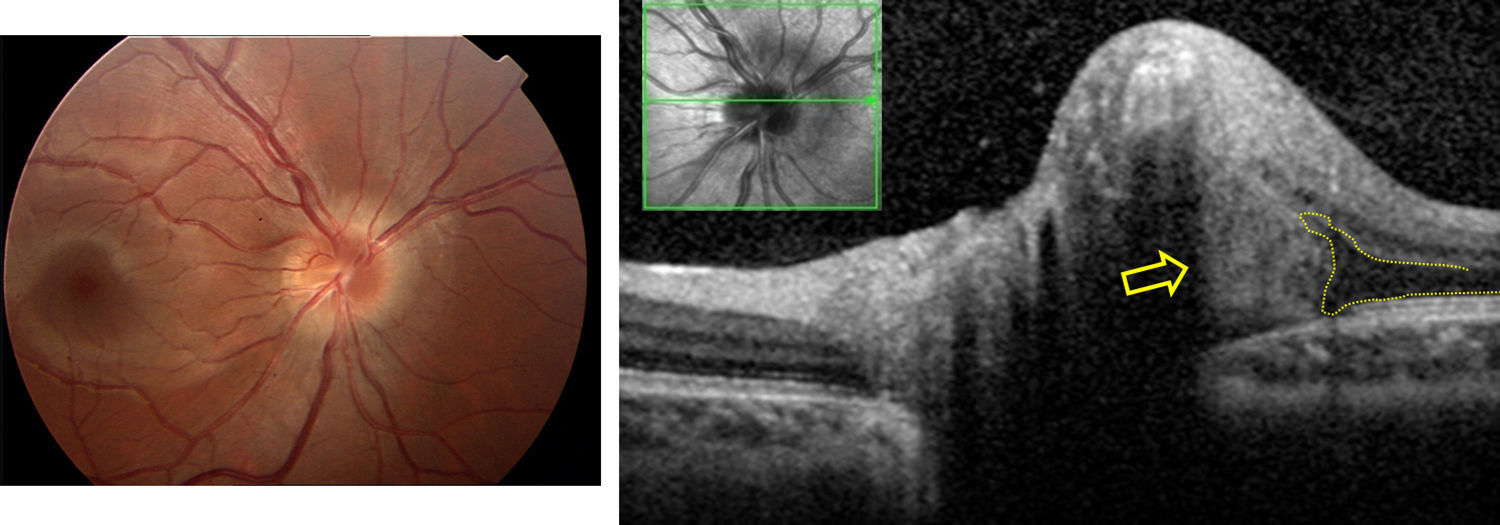
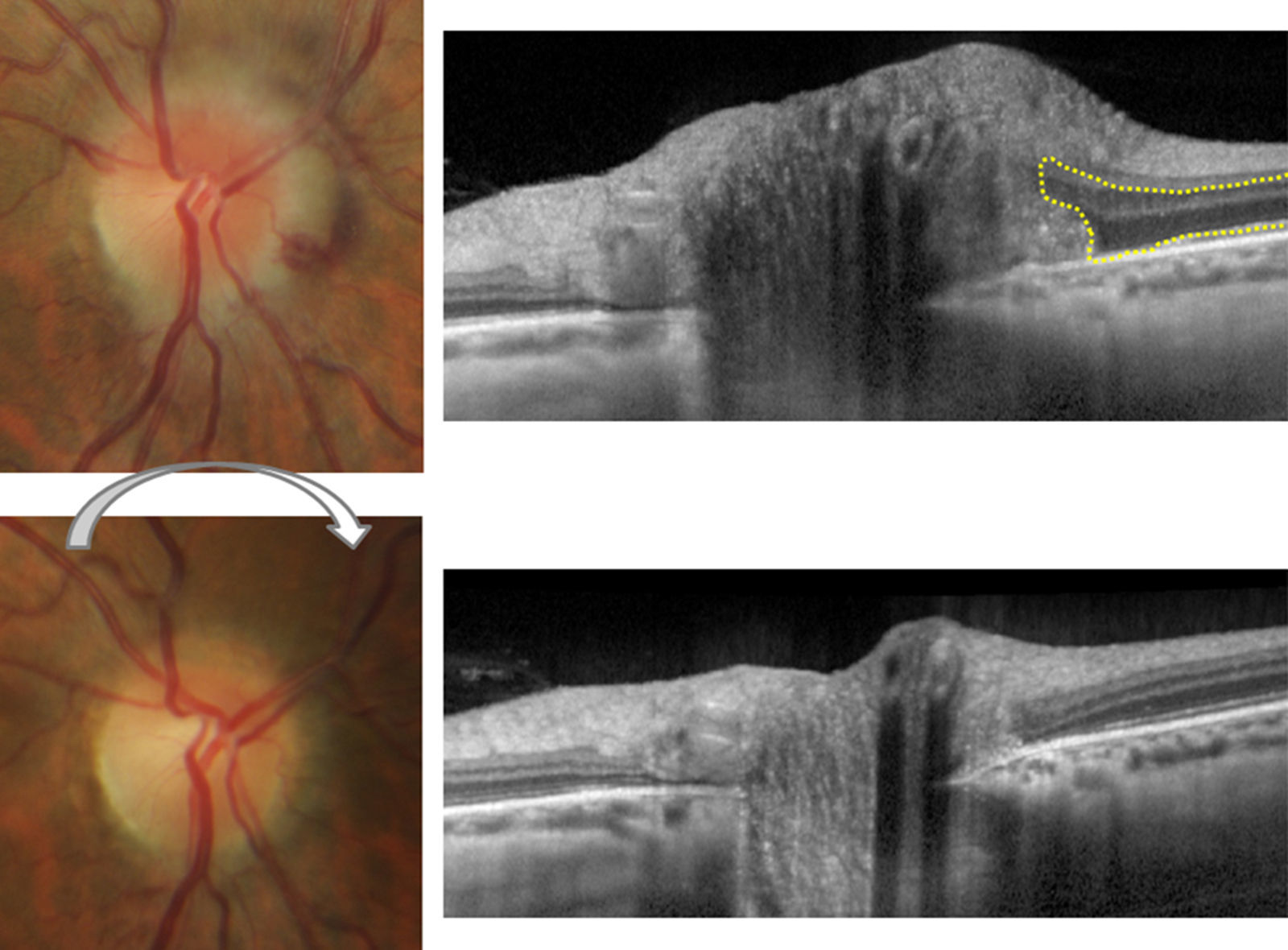
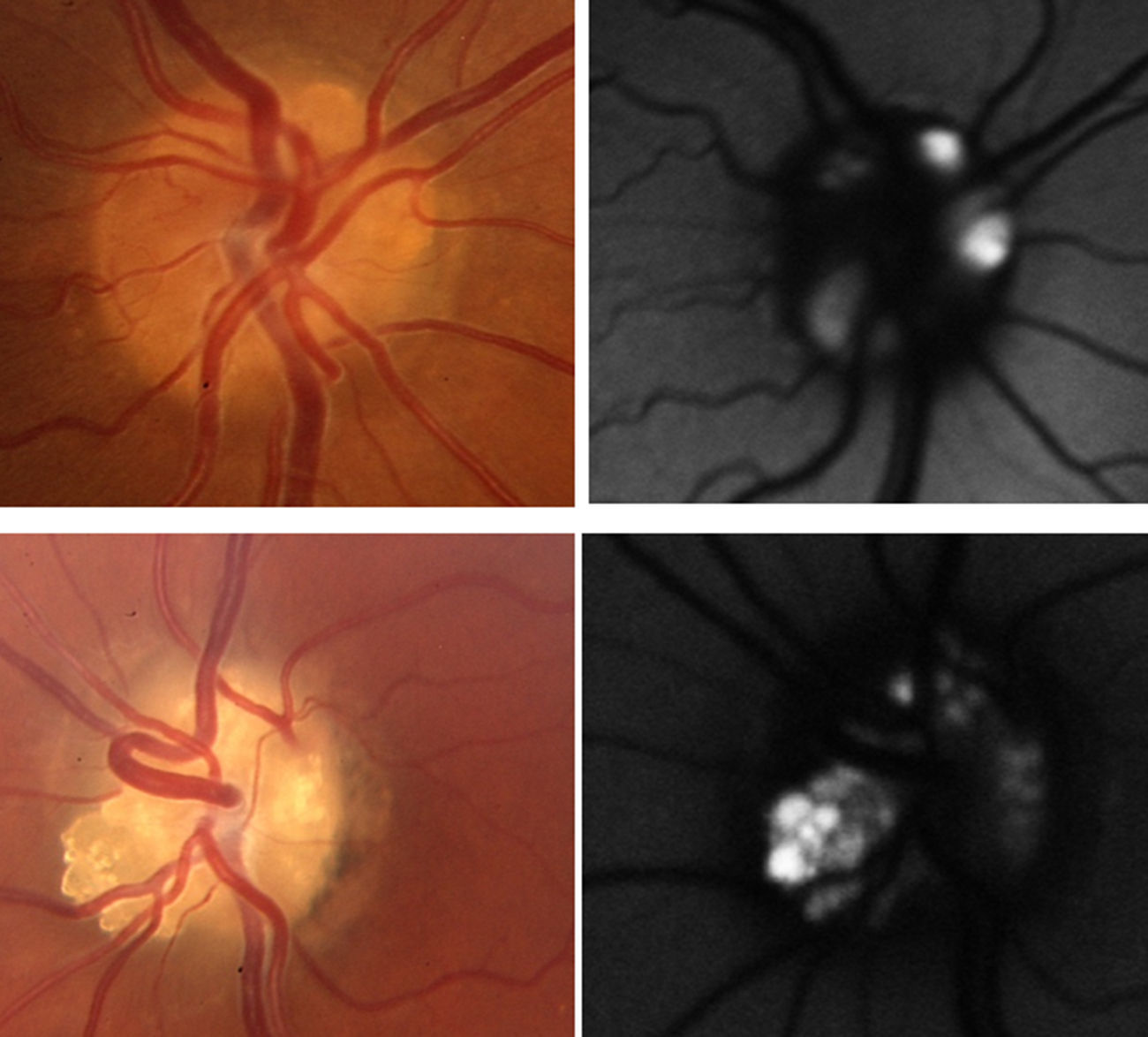
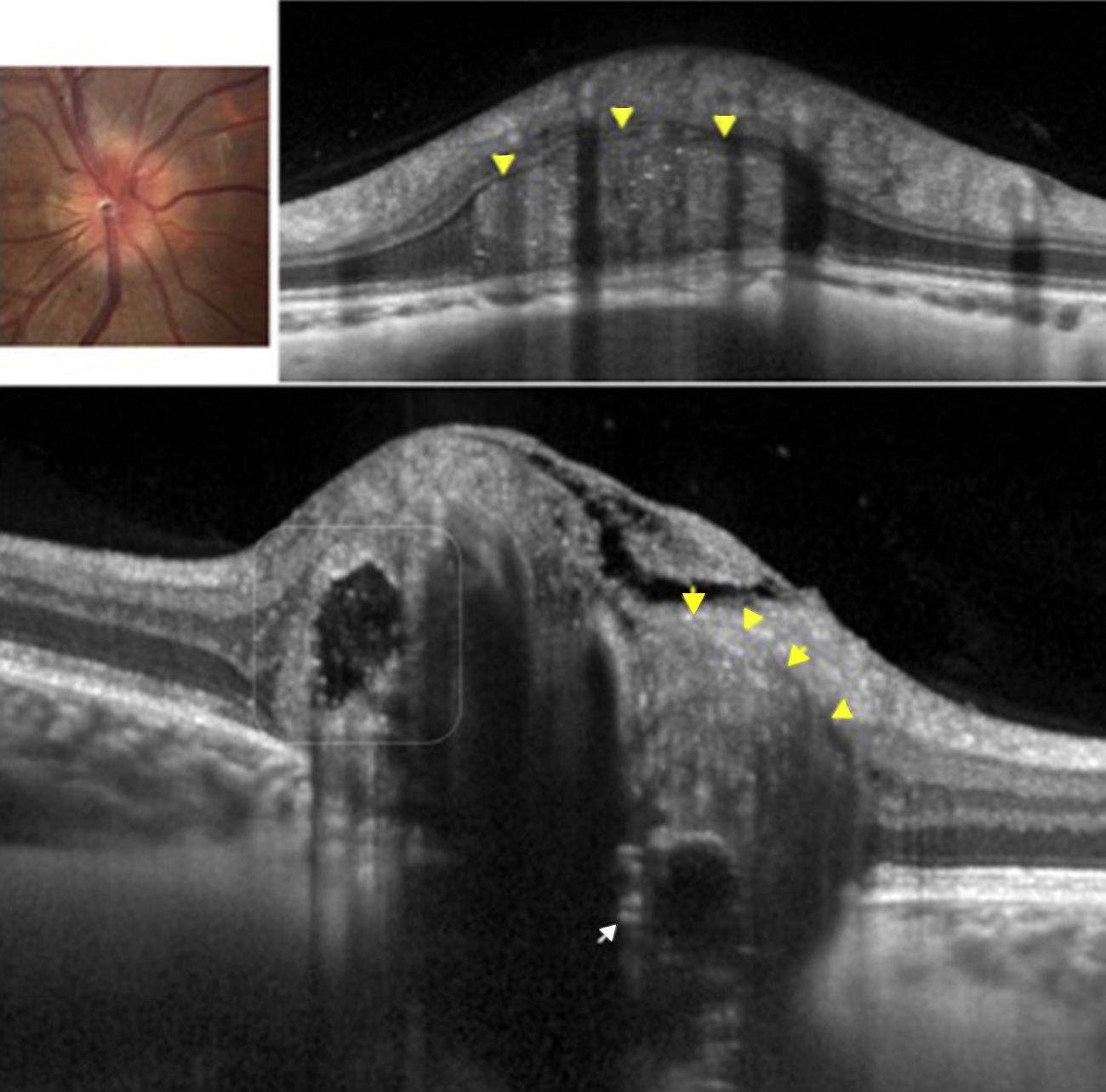
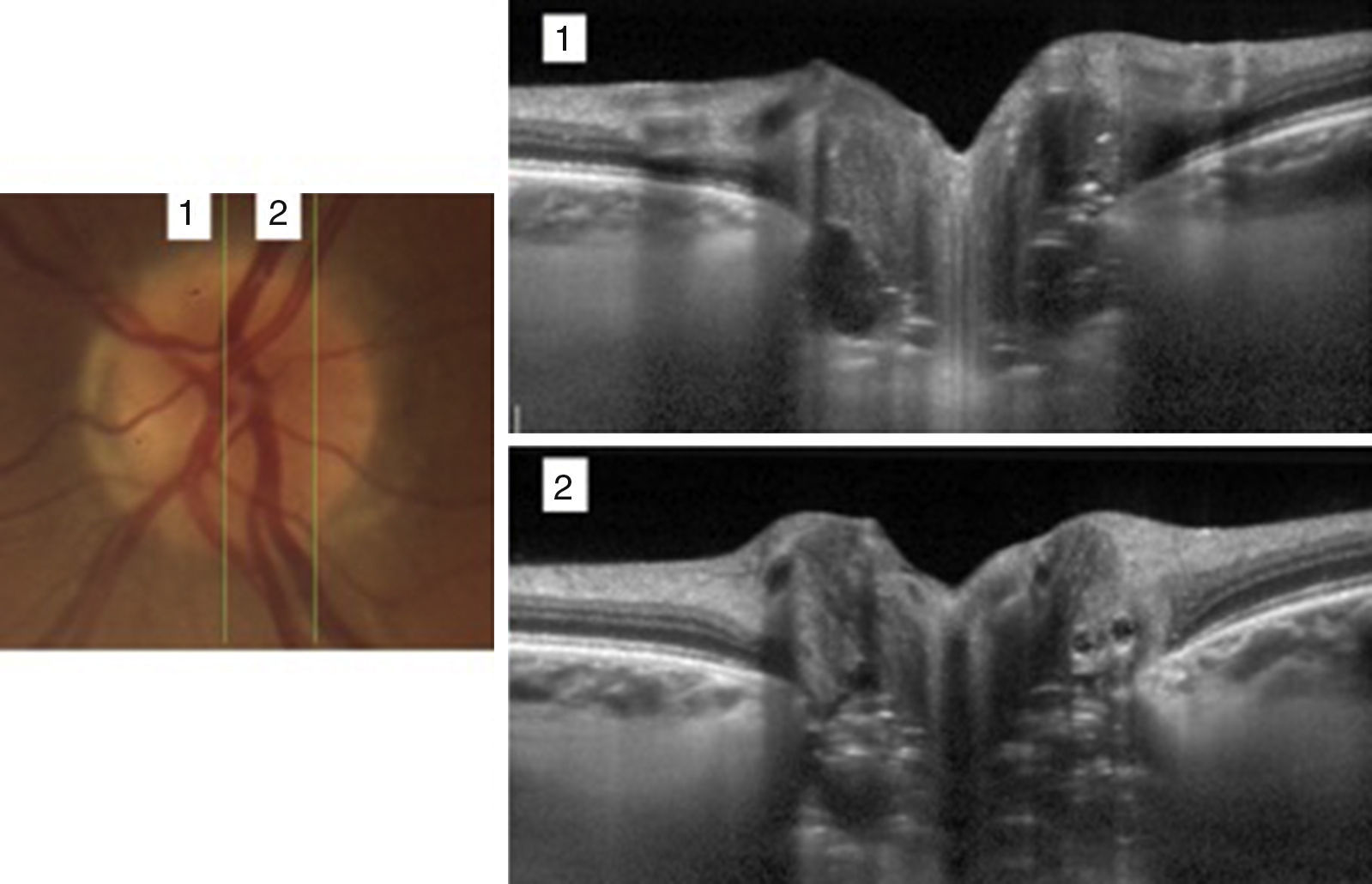
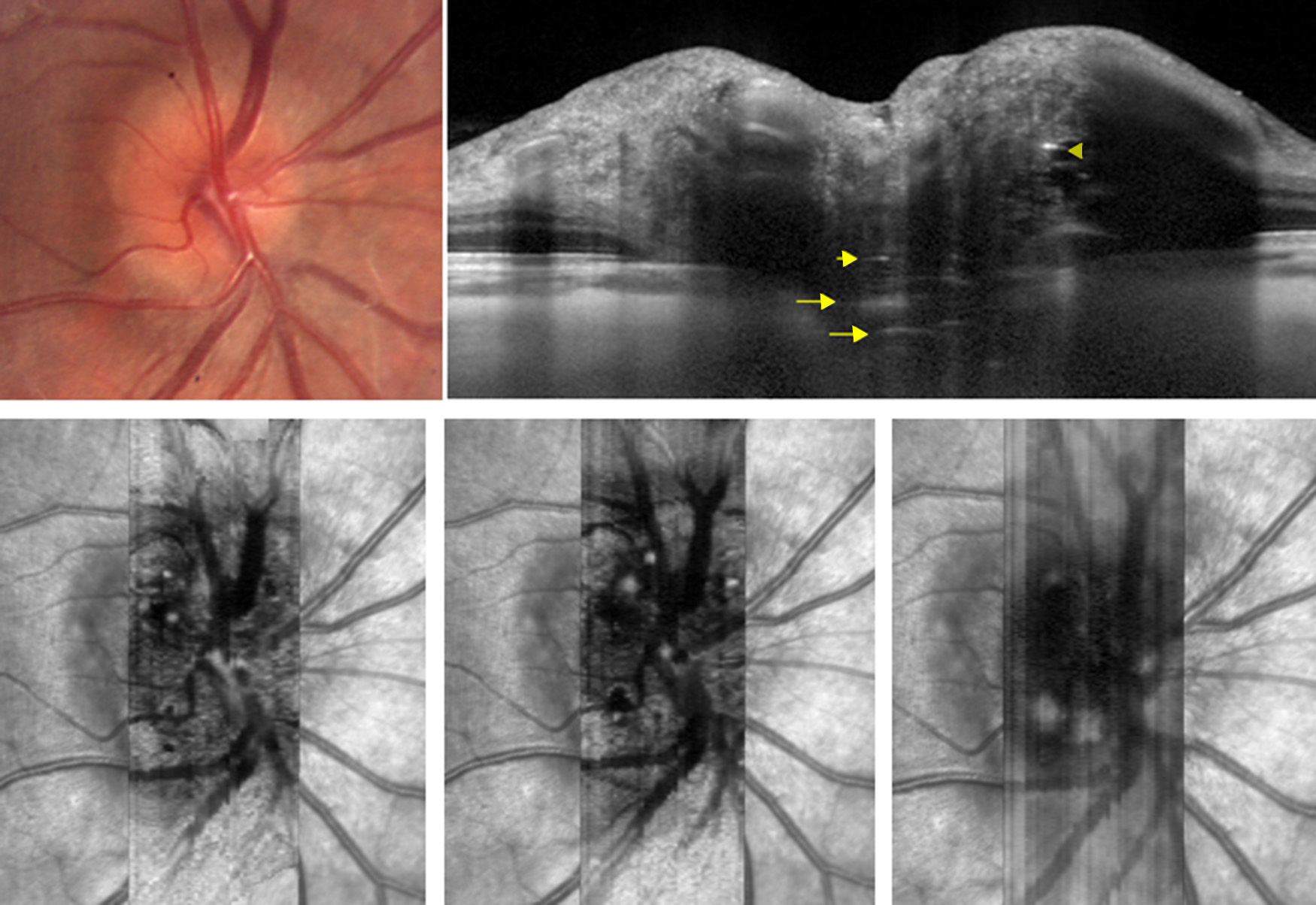
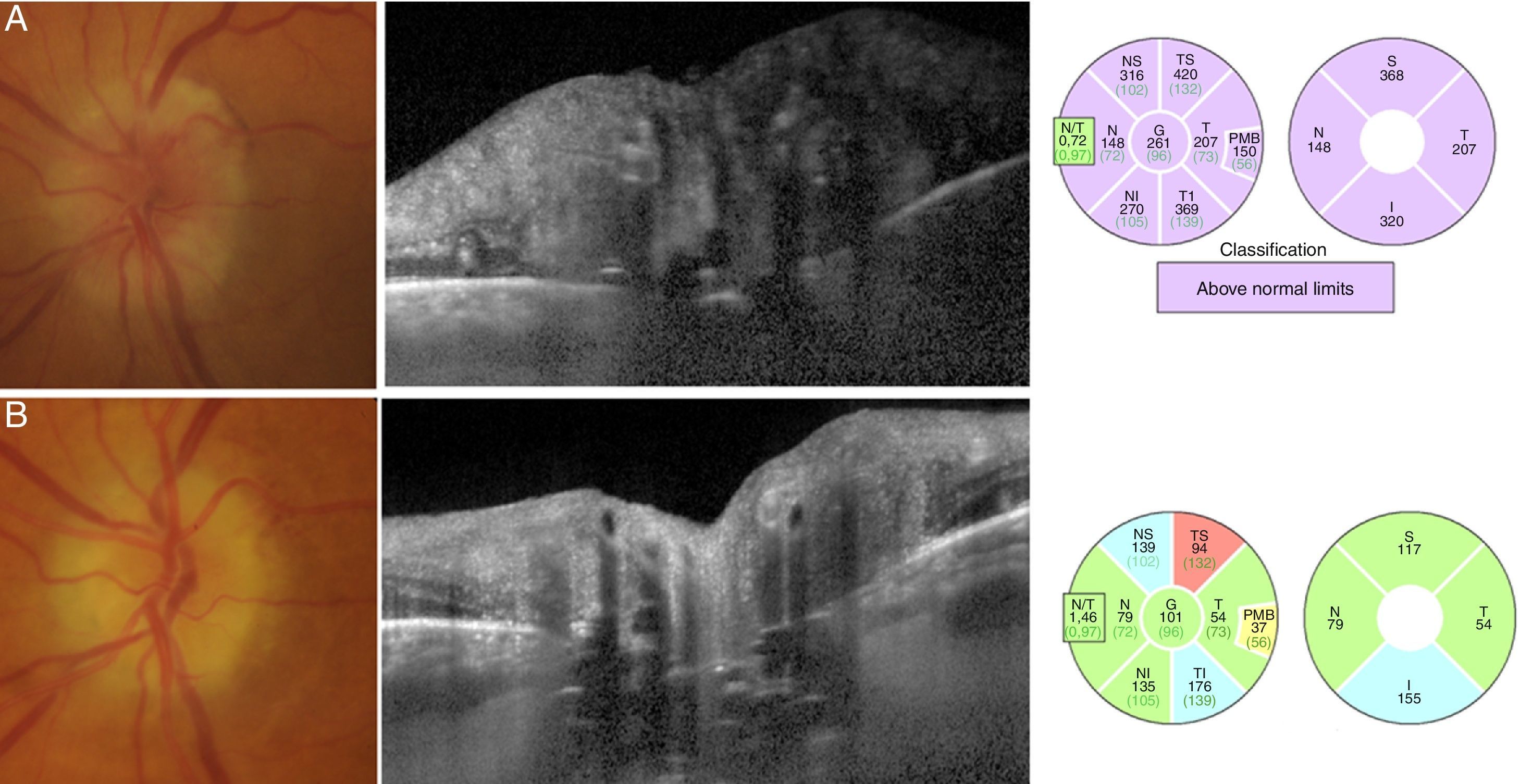
Las drusas ocultas del nervio óptico son una de las causas más frecuentes de pseudopapiledema. En esta revisión se abordan, de manera cronológica, distintos rasgos útiles en el diagnóstico diferencial con el papiledema desde el punto de vista de la tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT). La especificidad de dichos hallazgos ha aumentado paralelamente a la mejoría en la capacidad de penetración y resolución de los nuevos dispositivos de OCT. Ha sido la OCT de dominio espectral, y más concretamente la tecnología enhanced depth imaging (EDI) la que ha marcado un punto de inflexión al permitirnos visualizar directamente las drusas, cuantificar su tamaño y objetivar su repercusión sobre las estructuras vecinas en el interior de la cabeza del nervio óptico.
Buried optic nerve head drusen are one of the most common causes of pseudo-papilloedema. In this review, we have chronologically addressed several useful traits in the differential diagnosis of a true papilloedema, using the different features of optical coherence tomography (OCT). The specificity of these features has improved at the same time as the improvement in penetration capability and resolution of newer OCT devices. Spectral domain OCT, and more specifically the enhanced depth imaging (EDI) technology, represents a turning point in directly visualise drusen, to quantify their size and to recognise their impact on neighbouring structures inside the optic nerve head.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora