A 63 year-old-man presented with a severely itching dermatitis without other signs or symptoms. His medical history was unremarkable.
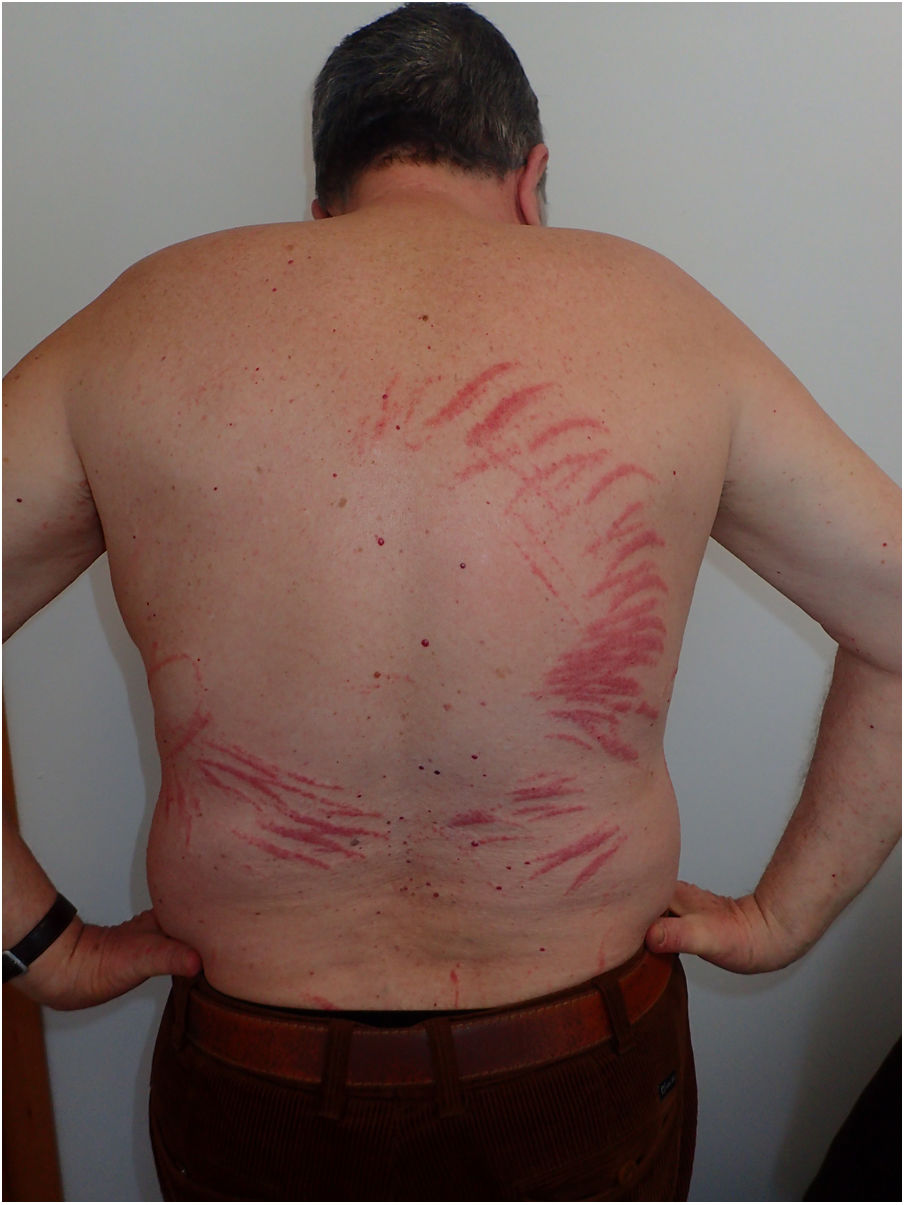
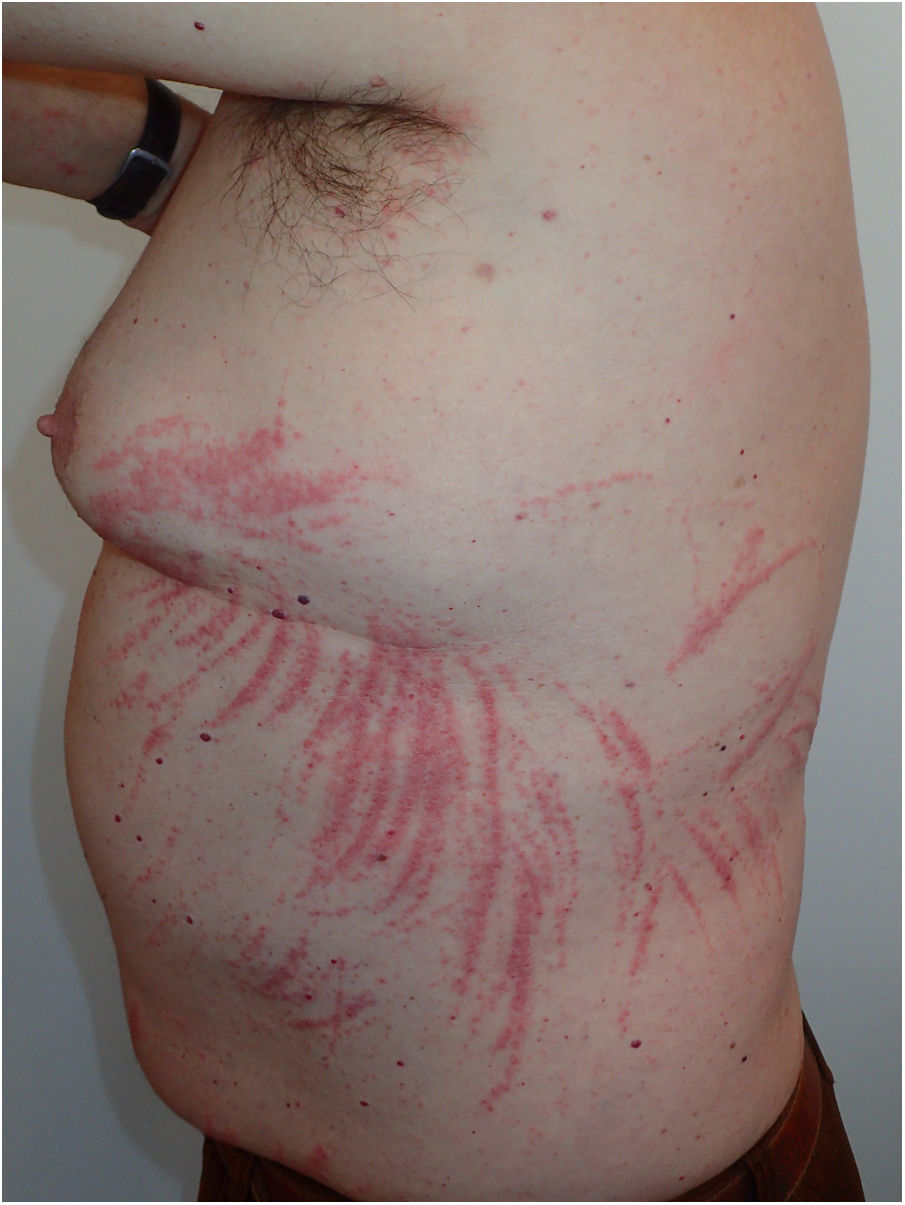
On physical examination we observed confluent erythematous micropapules in a linear and parallel pattern on the trunk, simulating a whiplash striped (Figs. 1 and 2). He denied contact with plants, and he had not received bleomycin. Two days before onset the patient ate grilled shiitake mushrooms in an Asian restaurant. After the lunch the patient go to the beach.
The laboratory studies showed eosinophilia (700cells/mcL). C-reactive protein, TSH, ferritin, creatine phosphokinase were in the normal range and negative antinuclear antibodies.
He started treatment with cetirizine 10mg/day and topical methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% for 2 weeks with good clinical response.
Flagellate dermatitis is a rare, presumedly toxic epidermal damage following consumption of raw or half-cooked Shiitake mushrooms,1 or cutaneous side effect of bleomycin2 or bendamustine. More uncommon causes of flagellate dermatitis are dermatomyosisitis, Still's disease and Chikungunya fever.
Flagellate dermatitis caused by the consumption of undercooked or raw shiitake mushrooms usually occurs 48–72h after ingestion, secondary to delayed hypersensitivity reaction.2 It presents as papular, petechial, or vesicular lesions in a crisscrossed, linear pattern, with intense itching. This dermatosis affects the trunk and extremities, less often the face or hair-covered scalp. The histology is variable and not particularly specific.
Some authors consider that the lentinan could induce a direct toxic skin reaction, other authors submitted their patients to patch and prick tests that came out positive, and they believe that the answer is a late onset hypersensitivity.3
Whether cofactors, such as medications like ACE-inhibitors or diuretics, or UV-exposure, possibly play an additional role is also under discussion.4
There was a suggestion of possibility of photodermatosis by Hanada, because the 47% of patients of a serie of 94 patients with shiitake dermatitis developed lesions after sunexposure.5 Phototoxic dermatitis is caused by contact or ingestion of some photosensitizing substance, as in the present case is shiitake ingestion.
Conflict of interestNo conflict of interest.