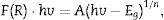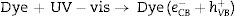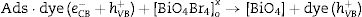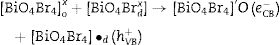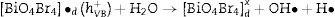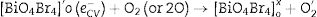Using a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method, we synthesized BiOBr powders, with and without, glycine or phenylalanine as templates. The samples were characterized by X-ray Diffraction, UV–Vis Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy, and Field Emission Gun Scanning Electron Microscopy. The XRD patterns were indexed to the tetragonal structure and presented very different intensities from each other, which is consistent with changes in the structural organization. The FEG-SEM images showed morphology alterations, from nanoplates for unmodified BiOBr to nanolamellae for BiOBr with phenylalanine (BOB-phe). The catalytic activity of BOB-phe degraded 98% of Rhodamine B dye in approximately 20min, while the other BiOBr compounds presented slower degradation kinetics, which could be explained by a higher amount of active sites on BOB-phe surface.
Utilizando un método hidrotermal asistido por microondas, sintetizamos los polvos de BiOBr, con y sin, glicina o fenilalanina como plantillas. Las muestras se caracterizaron por difracción de rayos X, espectroscopía de reflectancia difusa UV-Vis y microscopía electrónica de barrido con pistola de emisión de campo. Los patrones XRD se indexaron a la estructura tetragonal y presentaron intensidades muy diferentes entre sí, lo que es consistente con los cambios en la organización estructural. Las imágenes de FEG-SEM mostraron alteraciones de la morfología, desde nanoplacas para BiOBr no modificado hasta nanolamelas para BiOBr con fenilalanina (BOB-phe). La actividad catalítica de BOB-phe degradó el 98% del colorante de rodamina B en aproximadamente 20 minutos, mientras que los otros compuestos de BiOBr presentaron una cinética de degradación más lenta, lo que podría explicarse por una mayor cantidad de sitios activos en la superficie de BOB-phe.
Inorganic semiconductors emerged as valuable materials due to their wide range of magnetic [1,2], photocatalytic [3], optical [4], and electric [5], properties. These compounds are used for technological applications in medicine [6,7], agriculture [8], and industry [9]. Bismuth oxyhalides (BiOX, where X=F−, Cl−, Br−, or I−) and their derivatives have attracted the attention of researchers worldwide because of their optical [10,11], photocatalytic [12–14], and gas sensing properties [15]. Bismuth oxyhalides, Sillén family members, have a tetragonal structure belonging to P4/nmm space group. In this structure, XBiOBiX bilayers are stacked along the c-axis [16,17]. Also, bismuth oxyhalides can be activated by visible light due to the structural organization and low band gap value (2.0–4.8eV), which is ideal for environmental applications as pollution treatment [18], and development of renewable energy [19,20].
Considerable effort has been made to reduce oxyhalides band gap values and to improve their photocatalytic properties. Thus, the engineering of photoactivated nanomaterials has focused attention on the design of new photocatalysts with narrow band gaps and low electron-hole recombination rates [18,21]. This is achieved through structural changes, which results in marked alterations at optical and photocatalytic properties [22]. Currently, synthesis methods such as sol–gel [23], microwave [24], hydrothermal [25], solvothermal [26], template [14] and self-doping [27] have been widely explored in the obtain of BiOBr aiming to enhance the photocatalytic performance. As described above, the template method has shown to be a highly suitable option for obtaining BiOBr nanostructures with structural changes.
Zhao et al. [28] synthesized BiOBr nanosheets with [111] facets using sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) as a template in the reaction environment. This compound exhibited excellent electrochemical behavior and photocatalytic activity under visible light. Xuelei et al. [29] used ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to control the shape and size of BiOBr nanocrystals. They observed that BiOBr samples exhibited excellent photocatalytic activity due to templates used during syntheses process. Shang et al. [30] also obtained BiOBr nanostructures using CTAB as template, which presented photocatalytic activity in the photodegradation of methyl orange. Shi et al. [31] used polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a template to obtain BiOBr structures with microflower morphology. Such structure exhibited an excellent photocatalytic activity when compared with BiOBr, which were composed of square slices. All investigations described above demonstrated that the template strongly influences the morphology, hence being a determining factor in the obtains of active surface catalysts. Thus, in this paper, we synthesized BiOBr using amino acids as a template and investigated the influence of the morphology change for improving the photocatalytic activity of BiOBr nanocrystals.
Material and methodsSynthesis of BiOBr nanostructuresBiOBr samples were synthesized by the microwave-assisted hydrothermal method in the presence of amino acids as templates. In a typical procedure, 2.0mmol of potassium bromide (KBr, 99% purity, Aldrich) and bismuth nitrate (Bi(NO3)3, 99% purity, Aldrich) were added to 100mL of a 0.03molL−1 solution of the amino acid (glycine or phenylalanine). The mixture was stirred for 30min, transferred to a 150mL Teflon vessel contained in a stainless-steel autoclave reactor and heated at 180°C for 8h. The product was separated by centrifugation, washed by deionized water and dried at 60°C for 8h. The samples were denoted BiOBr-gly (produced using glycine as a template) and BiOBr-phe (produced using phenylalanine as a template). For comparison, a control sample (denoted BiOBr control) was synthesized by the same route, in the absence of amino acids.
CharacterizationX-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns were collected using a D/Max-2500PC diffractometer (Rigaku, Japan) operated at 40kV and 150mA, with Cu-Kα radiation (1.5406Å), in the 2θ range from 7–90°. The structures were refined using GSAS-II [32]. The particle size and morphology were investigated using a Field Emission Gun Scanning Electron Microscopy (FEG-SEM) Supra 35-VP (Carl Zeiss, Germany) operated at 15kV. The TEM images were obtained using FEI Tecnai F20 transmission electronic microscope (TEM) operated at acceleration voltage of 200kV. UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) was performed using a UV-2450 spectrophotometer (Varian, model Cary 5G) and BaSO4 as reference. Porosity and surface area measurements were carried out by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) curve for surface area and pore size analysis. The N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms were measured at 77K using a Gemini VII 2390A – Micrometrics. Photocurrent measurements were carried out with an electrochemical analyzer (PalmSen EIS, Compact Electrochemical Interfaces) and standard three-electrode system with the BOB-phe modified ITO electrode as working electrode, a Pt foil as the counter electrode, and Ag/AgCl (saturated KCl) as the reference electrode. The electrochemical cell was filled with 5mL volume of Na2SO4 aqueous solution at 0.5molL−1 used as the electrolyte. The photoresponse of the photocatalyst was measured at 0.00V, in presence and absence of visible light from a 30W LED lamp. All the electrochemical measurements were performed at room temperature. In the procedure, the ITO electrode was first cleaned with acetone and ethanol (1:1) mixture, followed by drying under nitrogen flow. Then, 20μL volume of BiOBr suspension (1mgmL−1) was transferred onto ITO electrode, which had area defined by a 3mm diameter circumference and left to dry at room temperature to obtain the BiOBr-modified ITO electrode.
Photocatalytic activity measurementsIn a typical experiment, 100mg of the photocatalyst was dispersed into 100mL of Rhodamine B (RhB) solution (1×10−5molL−1). The solution was allowed to achieve adsorption-desorption equilibrium for 30min with stirring in the dark before starting irradiation. The light source used was 15W Xe lamp (350–420nm, Philips Electronics). The experiment was carried out at 25°C in a temperature-controlled Pyrex photocatalytic reactor. Suspension aliquots (5mL) were removed at predetermined time intervals and immediately centrifuged. Finally, the filtrate was analyzed using a double-beam UV–vis spectrophotometer (model V-660, JASCO, USA).
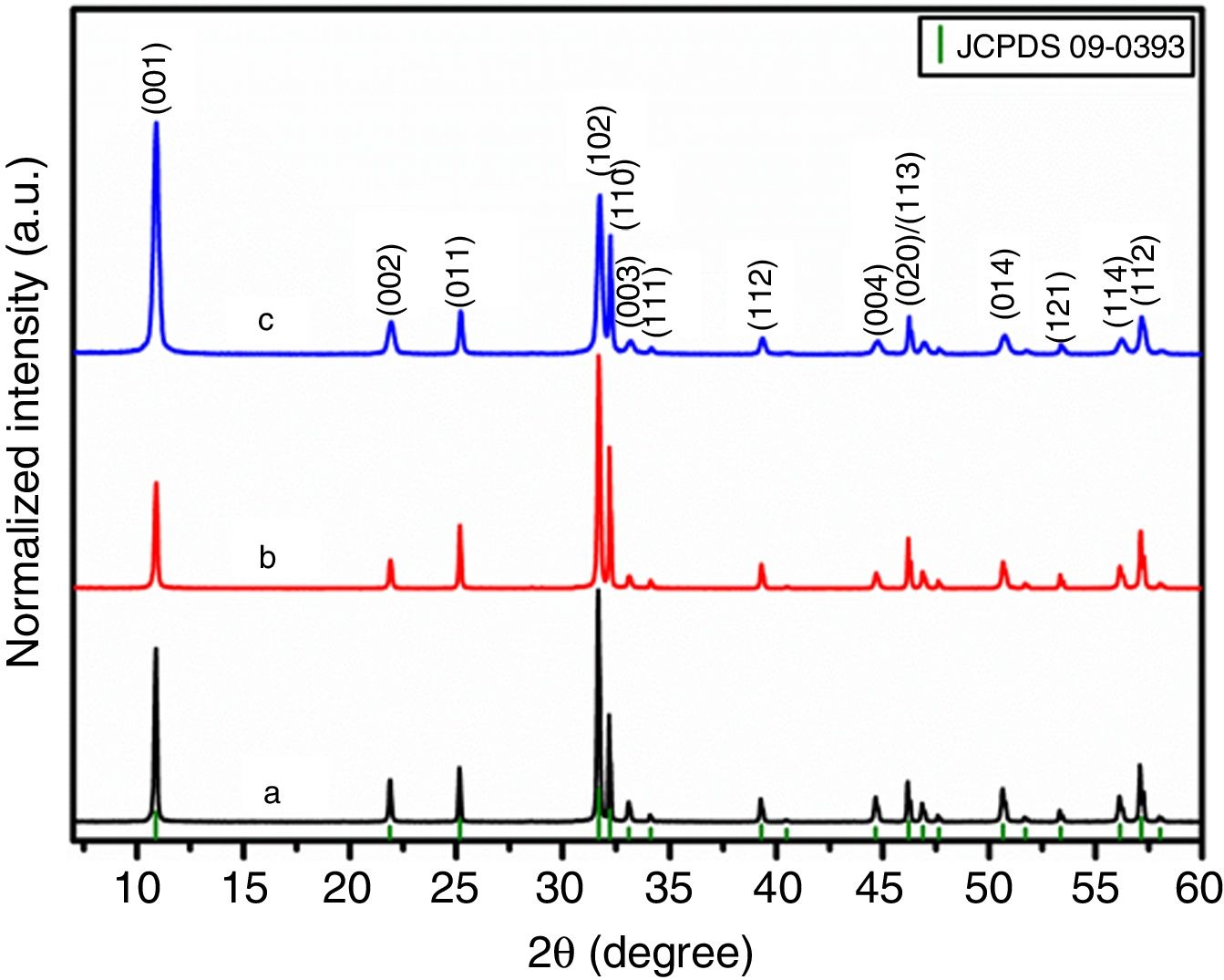
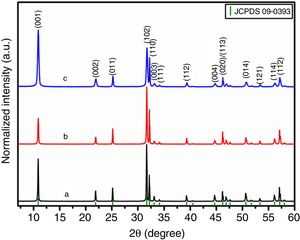
Results and discussionStructure analysisFig. 1 shows the XRD patterns for all as-prepared samples. All the peaks were indexed to the tetragonal crystal system with P4/nmm space group (JCPDS card N° 09-0393) in agreement with previous reports [28,33]. No impurities or secondary phases exceeding the limit of detection were found in any samples. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that I(102)/I(110) peak intensity ratio decreased for samples obtained using the templates (BiOBr-gly and BiOBr-phe, with values of 1.64 and 0.93, respectively), compared to the control sample (BiOBr, with a value of 2.00). This indicates that amino acid altered the formation of BiOBr crystallites leading to preferential orientation. Moreover, the BiOBr -phe sample not only showed a strong (001) preferential plane orientation but also exhibited some peak broadening, suggesting a decrease in crystallite size.
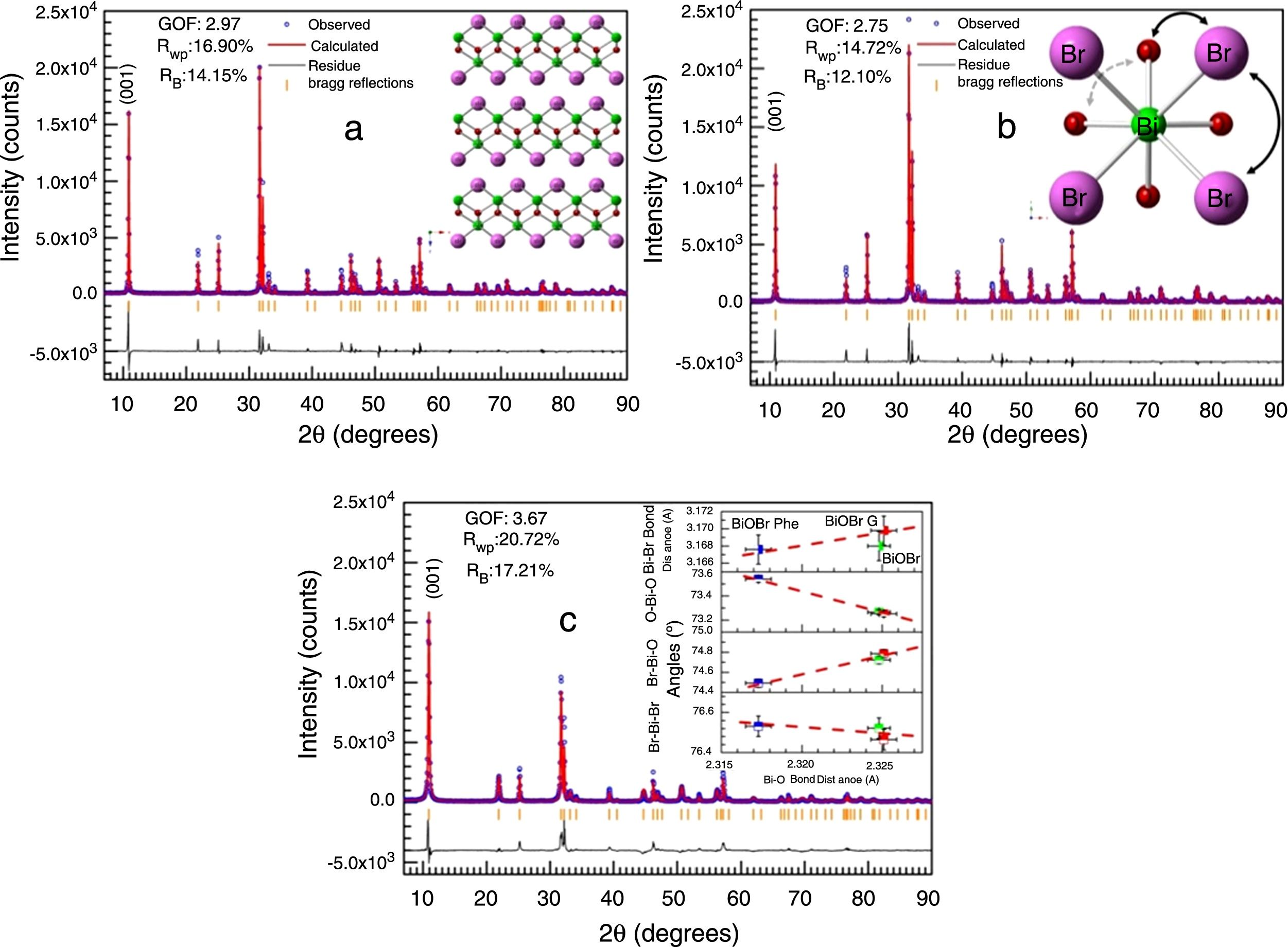
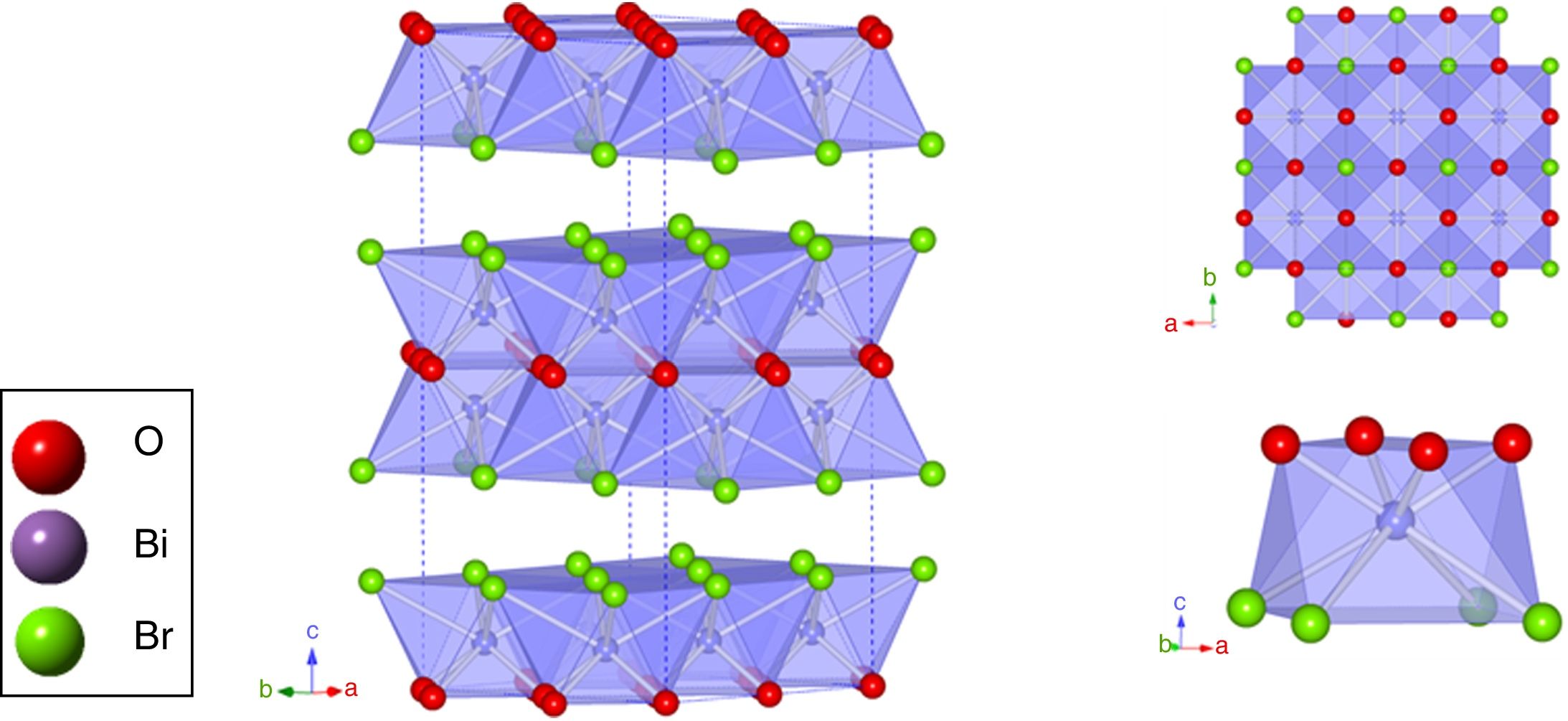
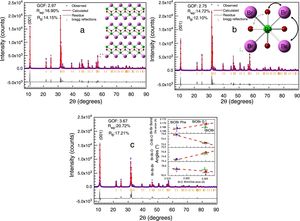
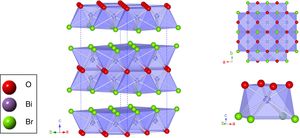
Fig. 2 illustrates the BiOBr unit cell showing that bismuth atom is coordinated by four oxygen atoms and four bromine atoms, forming a square antiprism geometry. BiOBr crystal structure can be derived from tetragonal and matlockite structure. Fig. 3 shows the refined diffractograms. The refinement procedure was performed in sequential mode, using the P4/nmm space group, which means that the same steps were executed for each diffractogram and agreed reasonably well with the literature [34].
Refined diffractograms of the BiOBr compounds: (a) BIOBR, (b) BIOBR-gly, and (c) BIOBR-phe. Insets: (a) usual structure of BiOBr for the tetragonal crystal system with space group P4/nmm; (b) selected bond angles considered; (c) BiBr bond distances and OBiO, BrBiO, and BrBiBr angles, as a function of BiO bond distance, for all samples (the dashed lines provide a guide for the eyes).
Strong preferred orientation along [001] direction was detected, as indicated by the high peak intensity at 11° in all samples. To evaluate of the bond distances and angles around the Bi cluster minimizing the error in atomic positions due to the low oxygen scattering factor, we chose the lattice origin centered at the 4d Wyckoff site, which maintains the oxygen atom at a particular position and varies the z coordinates of the heaviest atoms (Bi and Br). Table S1† shows the refined structural data for BiOBr and BiOBr-phe samples as well as calculated bond distances and angles. The bond distances and angles around the Bi cluster showed BiOBr-phe had more distorted structure compared to the other samples, indicating that reduced peak intensities were a consequence of real distortions in crystalline structure and not only due to variations in crystallite size.
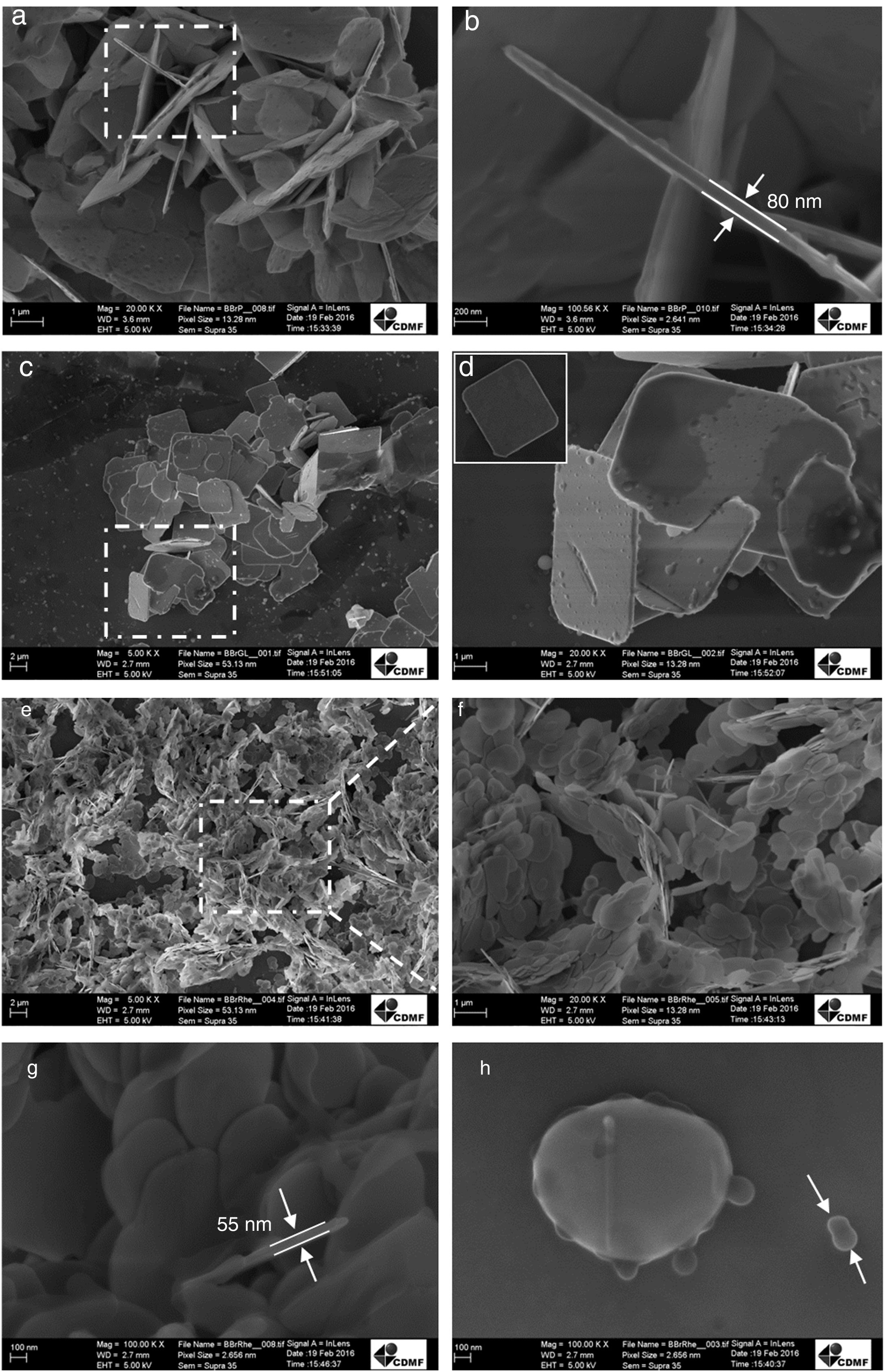
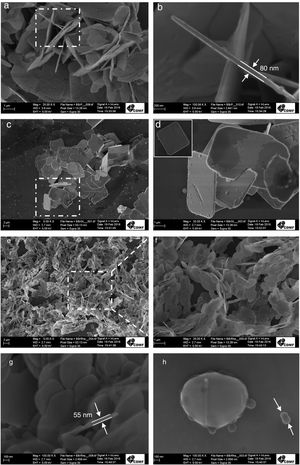
Fig. 4 shows the FEG-SEM images for as-prepared BiOBr. Presence of 3D nanoplates is the main morphological feature of BiOBr and BiOBr-gly. For BiOBr, these nanoplates have 2.5–7.5μm in length and 80nm in thickness (Fig. 4b). For BiOBr-gly, the morphological features were similar, but the size was altered, as shown in Fig. 4b and c. This sample showed greater length uniformity (3.5–5.3μm) and thickness increase to 190nm (Fig. S1†). The FEG-SEM for BiOBr-phe sample revealed both size reduction and morphology changes, characterized by the presence of lamellae-like structures having 55nm thickness (Fig. 4g). Fig. 4g and h shows the plate-like morphology originated from the growth of small primary nanoparticles 100nm, indicating an oriented attachment mechanism favoring preferred orientation in [001] direction just as detected from diffractograms. Hence, adjacent nanoparticles were self-assembled sharing a common crystallographic orientation and docking these particles at the planar interface, as found previously by Li and co-workers [35].
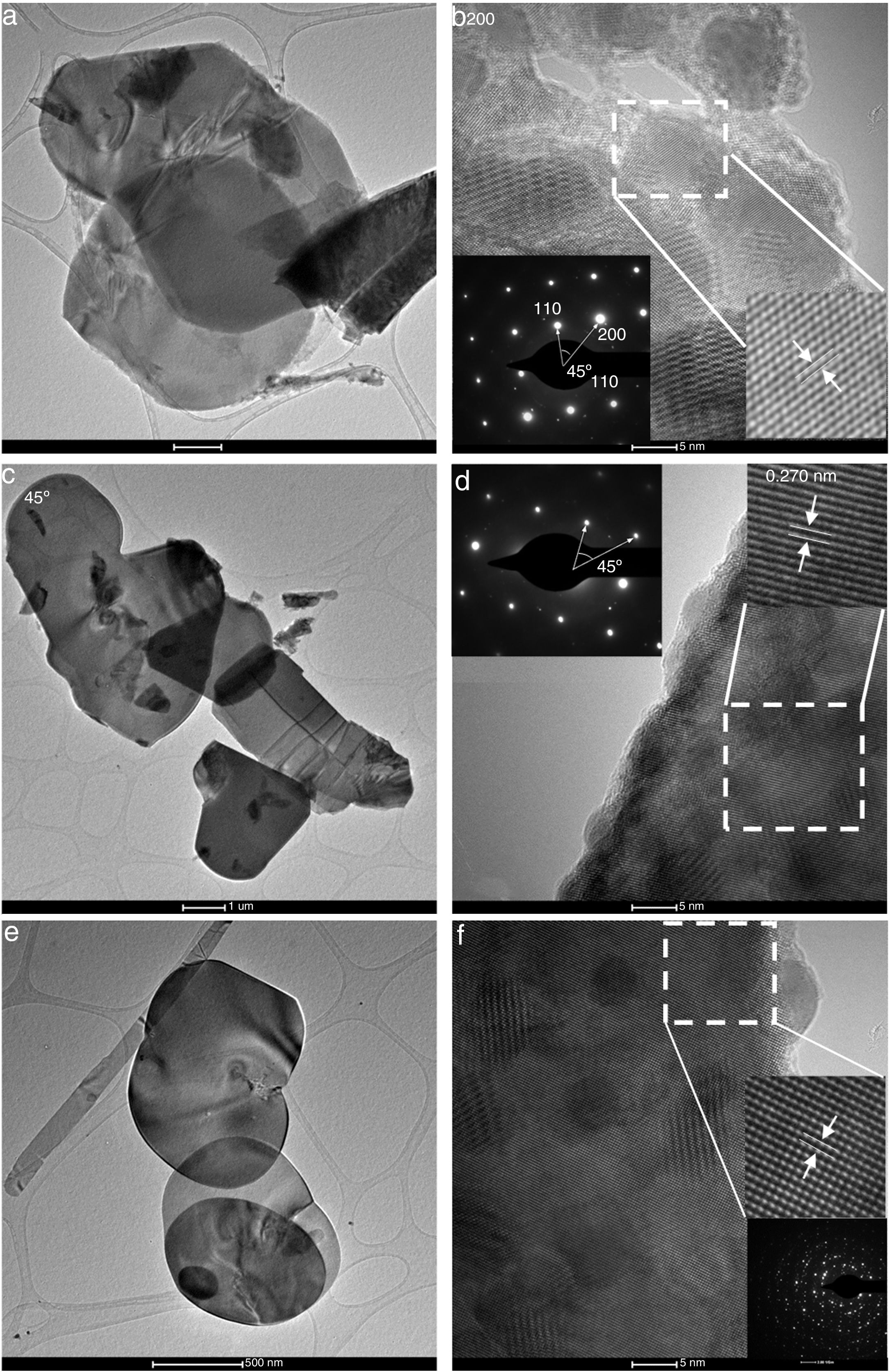
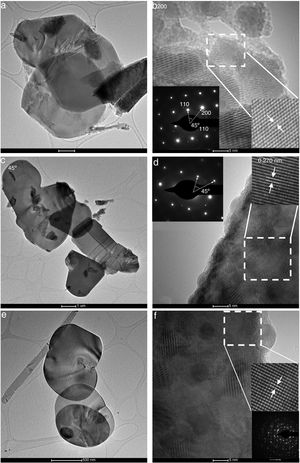
Fig. 5 presents TEM images for BiOBr samples, showing plate-like morphology (BiOBr and BiOBr-gly, Fig. 5(a–d) and lamellae-like morphology (BiOBr-phe, Fig. 5e and f). The microstructures of individual nanoplates were further investigated by High-Resolutin TEM (HRTEM) and Selected Area Electron Diffraction (SAED). The HRTEM images for BiOBr (Fig. 5b) exhibit the usual lattice fringes of nanoplates, with 0.228nm of interplanar distance corresponding to (112) lattice planes, showing the sample was well crystallized and had high crystallinity degree. Differently, the BiOBr-gly and BiOBr-phe samples showed lattice fringes indexed to (003) plane with intervals of 0.270nm. The 45° angle showed in SAED pattern inset (Fig. 5b and d) is assigned to (200) and (110) facets corroborating the theoretical value. These features indicate that BiOBr and BiOBr-gly are single-crystalline, while BiOBr-phe exhibited several diffraction rings indicating polycrystallinity.
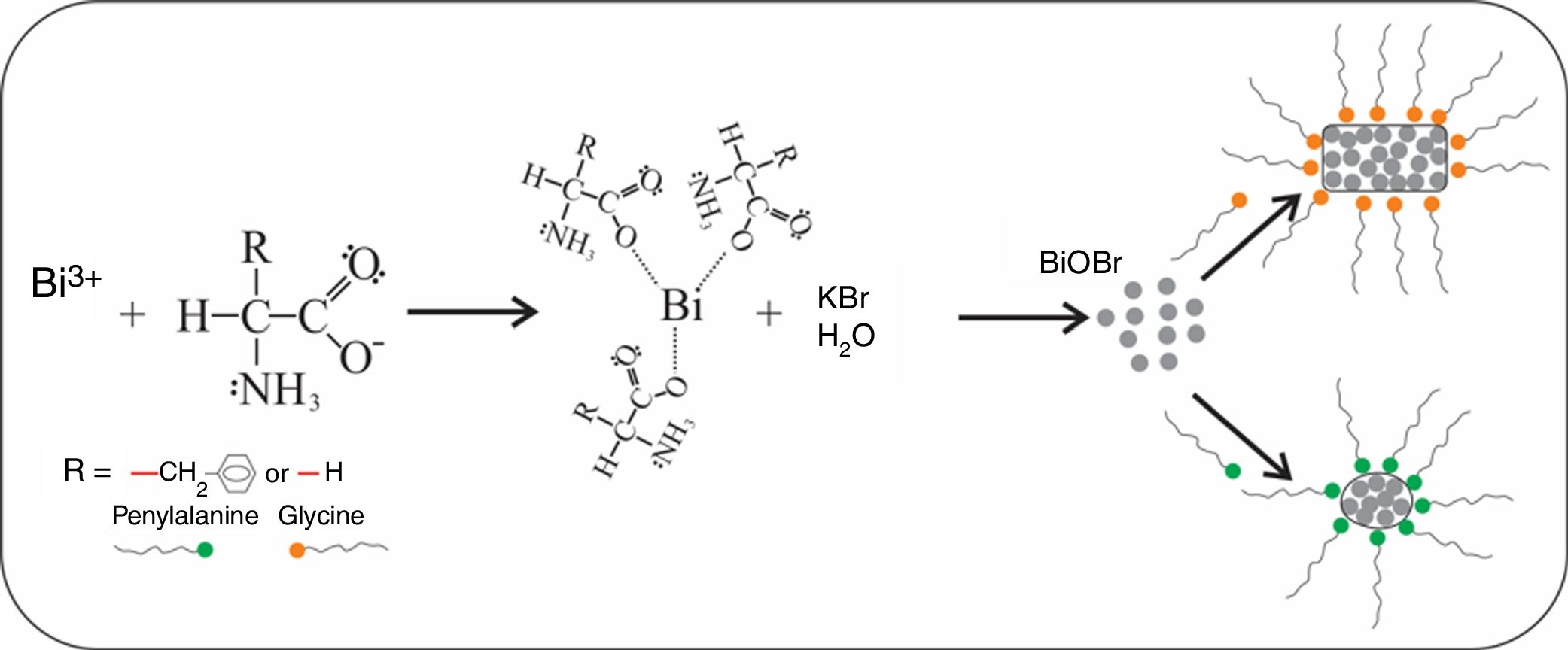
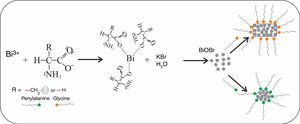
The binding of the amino acid (AA) with Bi3+ leads to the formation of a [Bi(AA)3] complex [36,37] before the Bi3+ cation reacts with the WO42− anion. Thus, we suggest that this binding is not stable and slowly releases Bi3+ cations to form the first BiOBr crystallites. After this formation of BiOBr, a possible interaction of amino acids with high energy surfaces can lead to plate-like and lamellae-like morphologies, as illustrated in Fig. 6. For BiOBr-phe, the branched-chain amino acid (phenylalanine), which has a larger volume (due phenyl group), we propose this can presents more significant interaction with the high energy surfaces, leading to the development of lamellae-like morphology. The use of glycine, which has a smaller volume and interacts weakly with crystals high energy surfaces, results in the formation of plate-like morphology, but with completely different dimensions from those BiOBr control samples. For future work, we intend to perform DFT calculations to investigate the interaction of different amino acids with the surface of nanomaterials to support our assumptions.
The BiOBr band gaps were carried out by UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. The optical energy band gaps (Eg) were calculated from UV–vis reflection spectra using the McLean equation [38,39] in terms of the Kubelka-Munk function, F(R), given by Eq. (1).
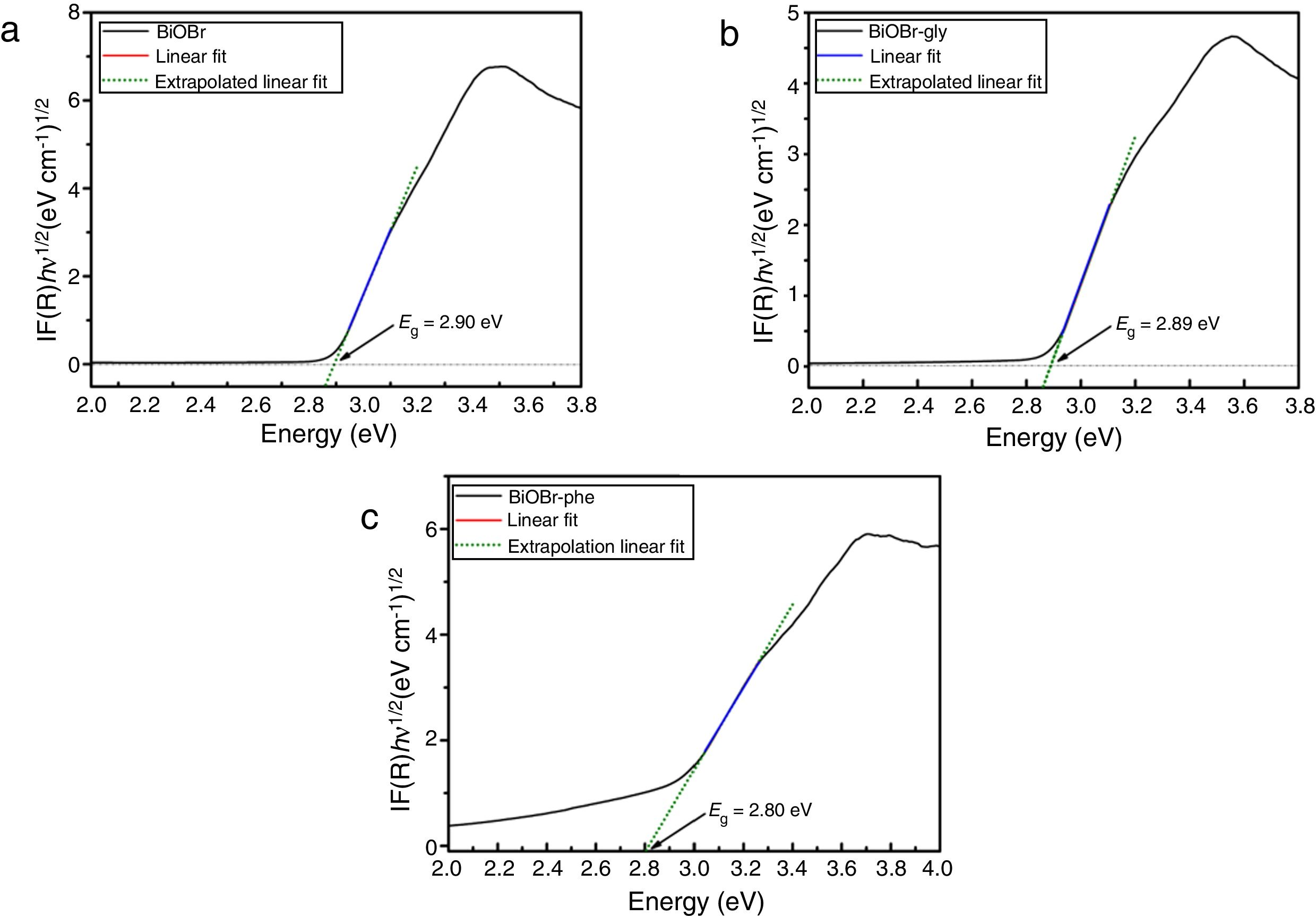
wherein hv is the photon energy, and n is a constant that depends on the optical transition nature. For semiconductors, n can have the following values: 2, 2/3 corresponding to direct allowed, indirect allowed transitions, respectively [33]. According to the literature [40], BiOBr has indirect allowed electronic transition, which implies n=2. Thus, the band gap value was determined by Tauc Plots (F(R)·hv)1/2 vs photon energy. The band gap values for all BiOBr samples are shown in Fig. 7a–c. BiOBr and BiOBr-gly samples presented band gaps around ∼2.90eV, while BiOBr-phe showed 2.80eV band gap.Although the presence of glycine amino acid has changed the morphology for BiOBr-gly, band gap values did not present significant change. Nevertheless, for BiOBr-phe, a little reduction in band gap value was observed. Generally, the narrowing of band gap is related to sub-band states formed in between the valence and conduction bands [41]. However, other factors also can be responsible for reducing of band gap in crystalline materials. In Fig. 7c is possible to see a large Urbach tail. The presence of this tail in the DRS spectrum may reflect the possible existence of disordering/defects which leads to the formation of localized states into forbidden band [41,42]. Thus, reducing of band gap to BiOBr-phe can also be addressed to electronic transition that takes place into localized states. Thus, we suggest that in the synthesis process is created oxygen vacancies, and intrinsic defects are present in BiOBr-phe nanocrystal, which is responsible for reducing band gap value.
BET analysisFig. S2† displays the nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of as-prepared BiOBr compounds. They all show hysteresis loops type H3, indicating the presence of non-rigid aggregates of plate-like particles. The samples were classified as typical type II adsorption-desorption isotherms, according to IUPAC classification [43], which suggests nonporous or macroporous solids. It was observed by BJH analysis a mesoporous structure with pore diameters around 150Å. The BET surface areas measured for BiOBr control, BiOBr-gly, and BiOBr-phe are 2.02, 7.70, and 6.34m2/g, respectively (to see in Table S3).
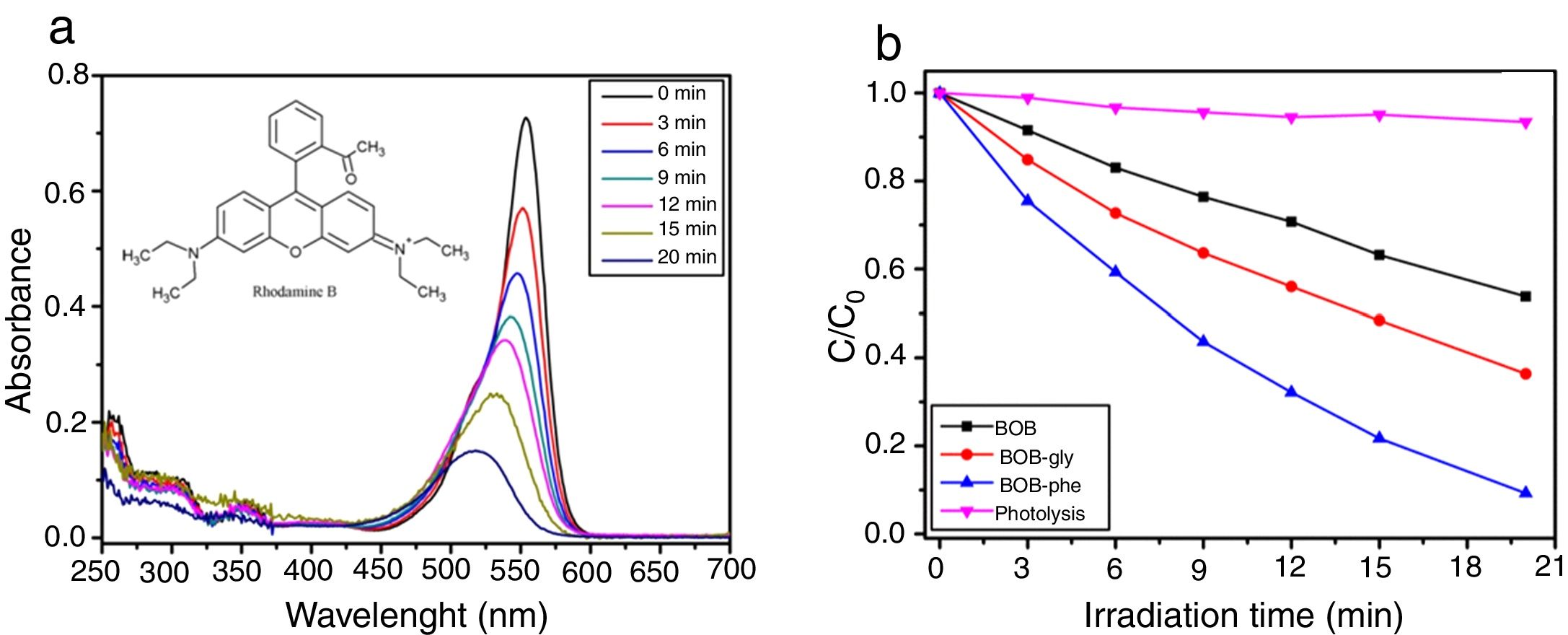
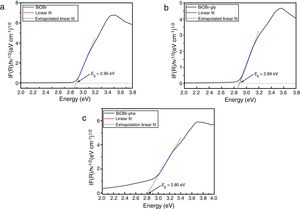
Photocatalytic activityThe degradation of RhB dye was described by a pseudo-first order reaction given by ln(C0/C)=kt, where k is the pseudo-first order rate constant, C0 is the initial concentration of RhB, and C is the concentration of RhB at different reaction times. Fig. 8(a) shows the RhB absorption spectra for BiOBr control, BiOBr-gly and BiOBr-phe samples collected for photodegradation under 350–420nm irradiations. Using BIOBR-phe as the catalyst, 90% of the dye was degraded after 20min, while 40% and 60% of degradation were obtained for BiOBr and BiOBr-gly, respectively. There was no dye photodegradation when the same conditions apply in the catalyst absence. Another important feature, the absorption peak for RhB dye photodegradation (Fig. 8a) blue shifted during the catalytic reaction. The first step in RhB degradation involves amine groups removal, leaving the molecule electronically poorer and resulting in a displacement of the most intense absorption band toward higher energy values, as reported in the literature [44,45].
Fig. 8b illustrates the degradation kinetics for BiOBr samples. BiOBr-phe sample showed a higher kinetic constant (115.3×10−3s−1) compared to BiOBr-gly and BiOBr control values, 30.7×10−3 and 49.2×10−3s−1, respectively. The use of phenylalanine as template result in more significant catalytic activity in RhB dye degradation, compared to other catalysts (BiOBr control and BiOBr-gly). These results are expected, since the samples synthesized using amino acids presented higher surface area than BiOBr control (see in Table S3), resulting in a higher number of active sites on its surface and, consequently, photocatalysis improvement.
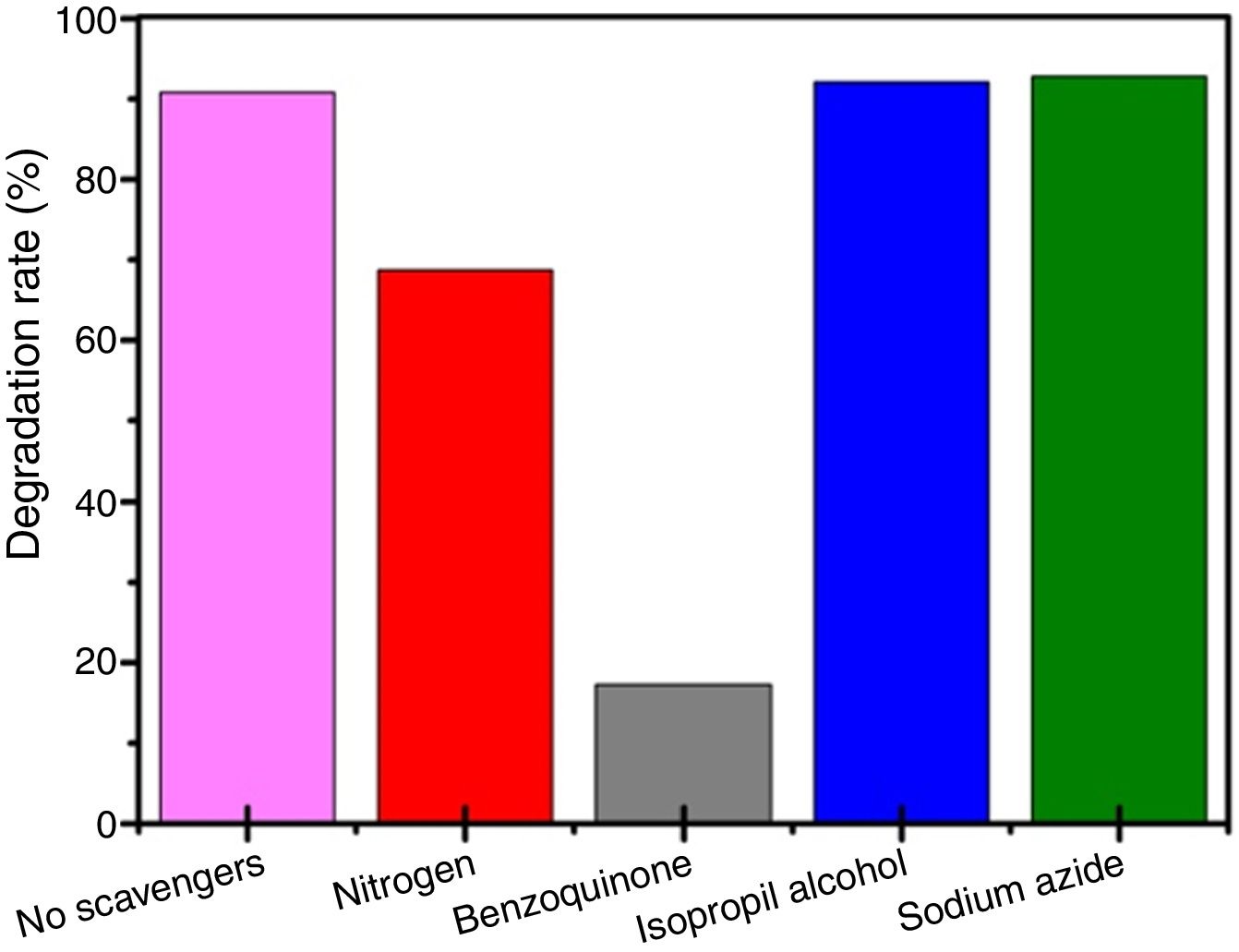
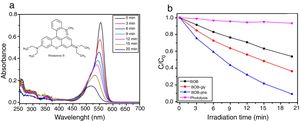
Investigation of the mechanism of photocatalysisFig. 9 shows the results of scavenging experiments performed to understand the photodegradation mechanisms of RhB over BiOBr. We used oxidizable compounds such as isopropyl alcohol, benzoquinone, and sodium azide, which are specific scavengers of OH(, O2(−, and 1O2 species, respectively [46]. Also, N2 gas was bubbled into the reaction system to remove O2 and further inhibit O2(− formation. The results show that isopropyl alcohol addition caused no substantial change in degradation kinetics of the RhB over BiOBr, and the same was observed for the experiment with sodium azide. This shows that neither the hydroxyl radical (OH() nor singlet oxygen (1O2) participates in RhB dye degradation. Differently, the benzoquinone addition to the medium caused a degradation kinetics reduction indicating that superoxide radical directly participated in RhB dye degradation process. Furthermore, when N2 was bubbled through the medium, the efficiency of RhB photodegradation decreased, confirming that oxygen plays a significant role at the beginning of photodegradation and corroborates the results for the experiment with benzoquinone.
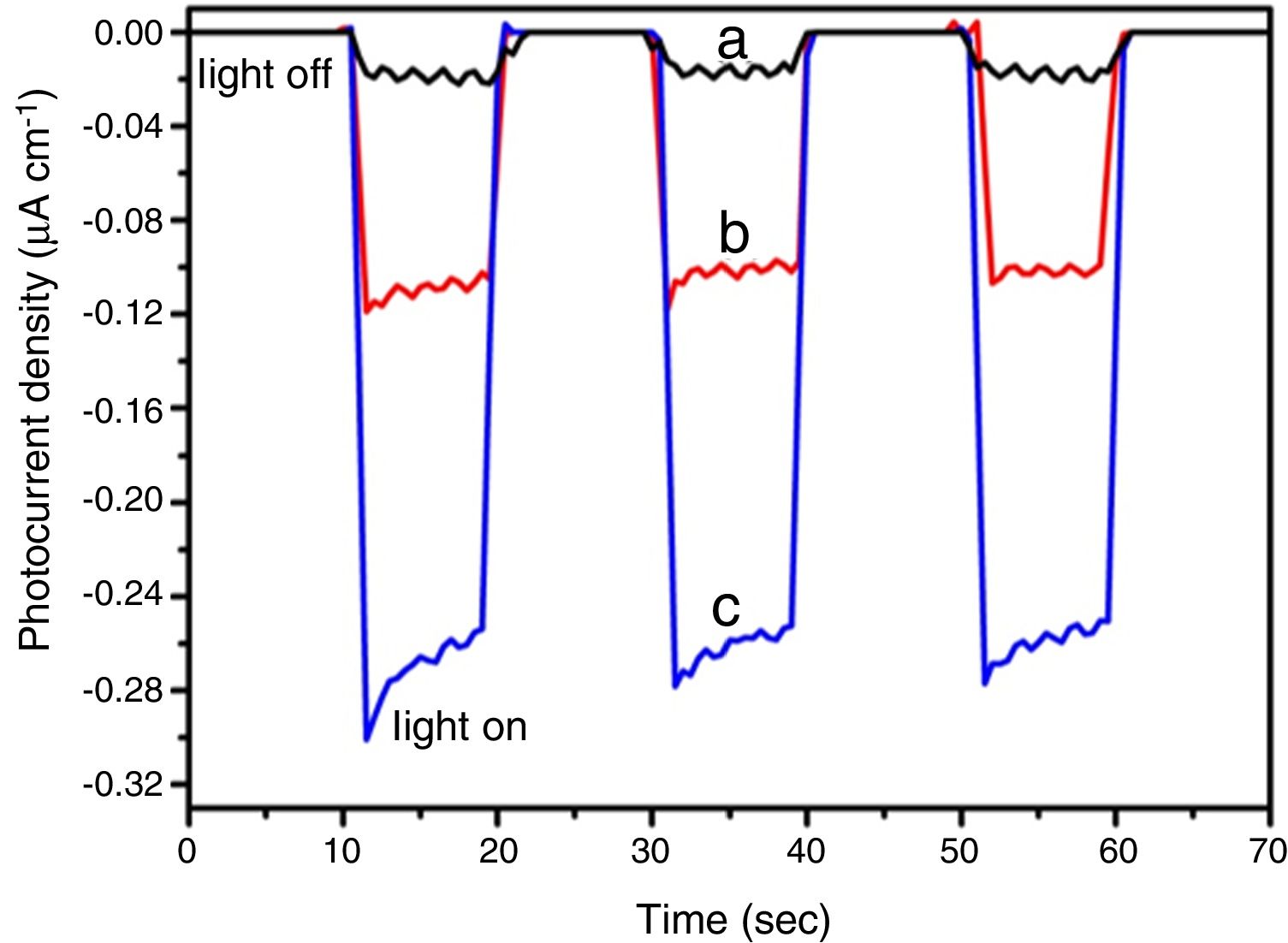
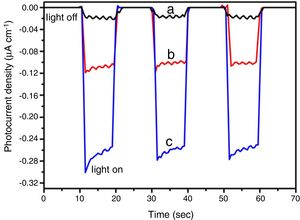
Fig. 10 shows the results for photocurrent measurements performed for all BiOBr photocatalysts synthesized using the different routes. The pristine BiOBr-gly and BiOBr -phe materials exhibited significantly higher photocurrent responses compared to BiOBr (Fig. 10a). The BiOBr-phe photocurrent response was 14.5 and 2.5 times higher compared to BiOBr control and BiOBr-gly values, respectively. The improvement in photocurrent efficiency was consistent with the photocatalytic activity degrees (Fig. 10b and c). Hence, the separation and transfer efficiencies of photoinduced electron-hole pairs are significantly higher for BiOBr-phe and BiOBr-gly than for BiOBr control, explaining the high and low photocatalytic activities for BiOBr-phe and BiOBr control, respectively. These results are consistent with previous reports that shown photocatalytic performance could be correlated with generation and transfer of photoexcited charge carriers during the photocatalytic process [47,48].
Electrons migrate to the dye low unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) while holes are create in high occupied molecular orbital (HOMO). In parallel, LUMO electrons from the dye move to BiOBr conduction band, creating BiO4Br4oxeCB−, since the dye acts as a sensitizer in this process. In the next step, electrons from BiOBr valence band migrate to conduction band forming clusters with high and low electronic density, (BiO4Br4oeCB− and BiO4Br4deCB−, respectively. The clusters can react with H2O or O2 (or surface oxygen) adsorbed on the catalyst surface to form oxidative species (hydroxyl or superoxide radicals) that may be responsible for RhB degradation.
Recent publications reported the relationship between BiOX (X=Cl− or Br−) catalytic activity and increased oxygen vacancies on {001} catalyst surfaces [49–52]. The XRD and Rietveld refinement analysis in this paper showed growth-oriented in (001) plane for BIOBR-phe, thereby the clusters were more distorted, and the bismuth-oxygen binding at the surface was possibly weaker. Hence, the surface oxygen bond (BiO) on the {001} facet (the most exposed face) could be broken forming an oxygen vacancy and releasing oxygen [49,53,54], which could then react with BiO4Br4oeCB−, forming superoxide oxygen (O2), since the process involved UV–vis irradiation. Considering the experiments performed with scavengers only revealed a significant change with benzoquinone addition, we suggest that superoxide radical was responsible for RhB dye degradation, as shown in Eqs. (2)–(6).
ConclusionsIn summary, nano-BiOBr photocatalysts were successfully synthesized using different amino acid solutions in microwave-assisted hydrothermal procedure at 180°C. The XRD patterns of all the samples indicated high crystallinity levels, although their intensities differed. Notably, BiOBr-phe sample presented broader peaks due to size reduction as observed in FEG-SEM images. The BiOBr-phe photocatalyst exhibited higher photocatalytic activity than other samples, reflecting a greater separation of electron-hole pairs. The action of the phenylalanine amino acid, used as a template during synthesis, it was responsible for the creation of a more active surface responsible for RhB dye degradation.
The authors would like to thank the Brazilian funding agency FAPEMA (grants Universal-00795/15, Universal-00798/16 and Universal-01102/18) and FAPESP (grant #2013/07296-2 and grant #2013/23995-8) for financial support. They also wish to thank Rorivaldo Camargo for technical and scientific contributions.