Lithium carbonate is an effective medication for the treatment of bipolar disorder. Its long-term administration can stimulate the parathyroid cells and induce hyperparathyroidism secondary to parathyroid hyperplasia or adenoma.1 We present a case of hyperparathyroidism secondary to an adenoma located in the thyroid of a patient treated with long-term lithium carbonate therapy.
The patient is a 49-year-old woman with a medical history of bipolar disorder, for which she had been in treatment with lithium for 20 years. She had been referred to us after the detection of hypercalcaemia during routine lab work. The patient reported no symptoms, and there was no family history of endocrinological disease.
Upon physical examination, no thyroid nodules or cervical lymphadenopathies were palpated. Both the cardiopulmonary auscultation and abdominal examination were normal. Lab work showed: corrected calcium 11.7mg/dL, phosphorus 3mg/dL, creatinine 1.9mg/dL, lithium 0.4mEq/L (therapeutic window 0.4–1.5mEq/L), PTHi 140pg/mL, TSH 1.23μU/mL, free T4 1ng/dL, 25-OH vitamin D 23ng/mL.
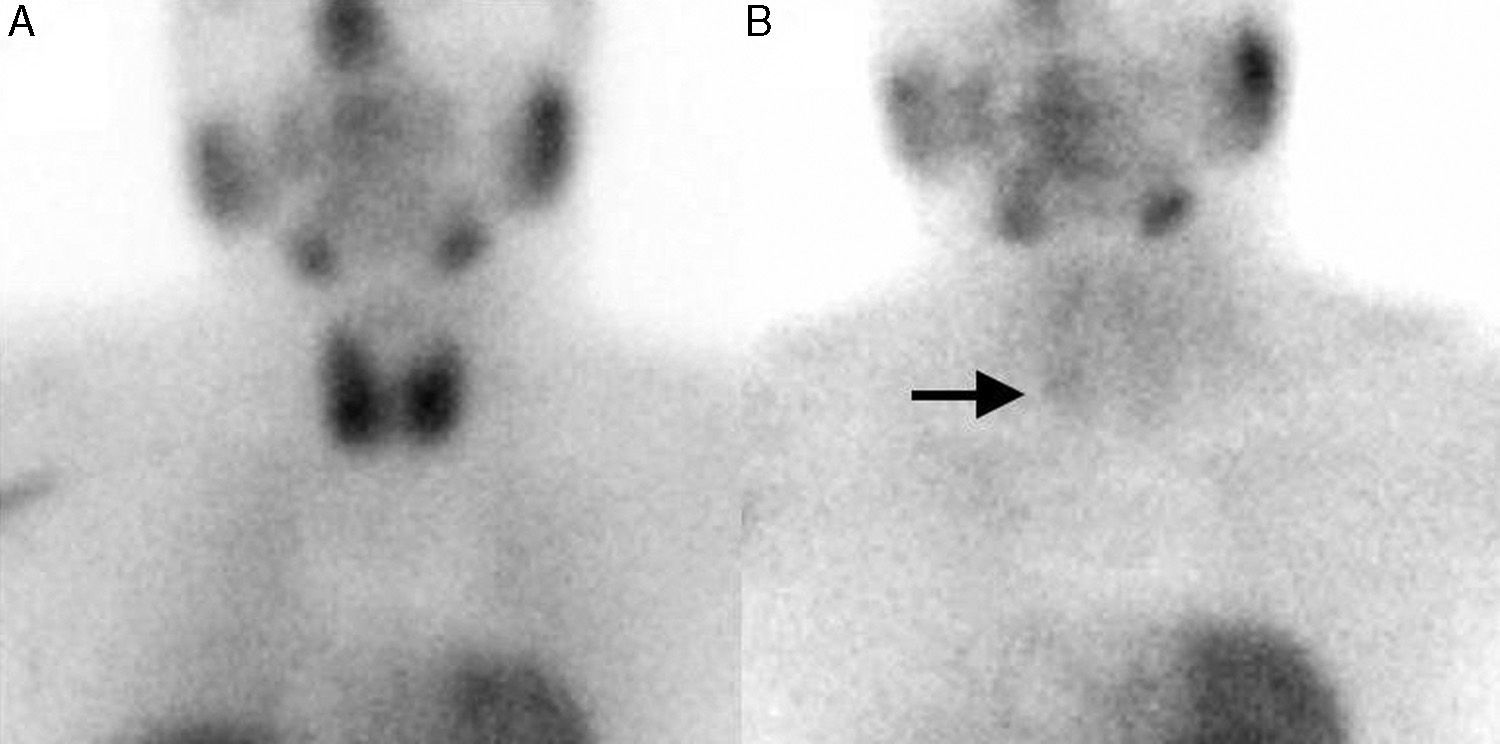
Thyroid ultrasound detected a hypoechoic retrothyroid nodule adjacent to the inferior pole of the right thyroid lobe that measured 1cm in diameter. A solid nodule was also identified in the inferior pole of the left thyroid lobe that was smaller than 1cm in diameter and had benign ultrasound characteristics. In addition, a dual-phase 99mTc-MIBI parathyroid scintigraphy was ordered, which showed an accumulation of radiotracer in the late phase over the inferior pole of the right thyroid lobe, with no observed uptake in the left thyroid lobe (Fig. 1). Given the suspicion of hyperparathyroidism due to a solitary parathyroid adenoma in an asymptomatic patient under the age of 50 with serum calcium levels above 11.5mg/dL, we decided to perform radioguided right inferior parathyroidectomy with associated monitoring of intraoperative PTH, together with total thyroidectomy. This latter procedure was done at the request of the patient, although at the time the nodule was benign.
During surgery, the nodule was observed at the base of the right thyroid lobe, which had an adenomatous consistency and was compatible with an intrathyroid pathological parathyroid gland. The intraoperative scintigraphy initially detected activity at the base of the right thyroid lobe, which ceased after exeresis. Intraoperative PTH monitoring demonstrated a reduction of 88% from baseline levels. Total thyroidectomy was completed and the two superior parathyroid glands were preserved, which presented a normal macroscopic appearance. Nonetheless, the left inferior parathyroid gland could not be located.
In the pathology study, the section of the inferior pole of the right thyroid lobe showed a nodule with cystic appearance measuring 1cm in diameter that was reddish-brown in colour and compatible with a parathyroid gland in a thyroid location. The histology study showed the main cells with variable nuclear size, large hyperchromatic nucleoli and limited mitosis, which confirmed the presence of parathyroid adenoma. In the left thyroid lobe, several thyroid nodules were identified that were whitish and colloid in appearance, corresponding with nodular hyperplasia.
The postoperative period was uneventful, and at the 6-month follow-up visit calcium and PTH levels had normalised.
Long-term lithium use is potentially toxic and can lead to hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Hypercalcaemia is present in patients treated with lithium for prolonged periods at a rate that ranges from 4 to 50%, while hyperparathyroidism occurs in 4%–38% of these patients.2
Lithium alters the calcium balance by a displacement towards the right of the curve that represents the secretion of PTH by the parathyroid glands depending on calcium concentrations, meaning that it modifies the “set point” of the calcium-sensing receptors (CaSR) and therefore greater concentrations of calcium are needed to reduce the secretion of PTH.3,4 Hyperparathyroidism induced by lithium more frequently causes multiglandular involvement,1 especially asymmetrical hyperplasia of the glands. In contrast, in a smaller number of patients, hyperparathyroidism is caused by the presence of adenomas. The mechanism by which these adenomas are formed is debatable. It has been suggested that lithium could accelerate the growth of pre-existing adenomas, or that it could induce its formation ex novo.5 Although surgery of the parathyroid glands has been more inclined towards a selective approach, we should consider that, in cases like the one we present, bilateral cervical examination is the approach of choice. As we have indicated previously, lithium-induced hyperparathyroidism is more frequently related with the presence of hyperplasia, so bilateral cervical examination would reduce the risk of recurrences.6
Furthermore, parathyroid adenomas located in the thyroid parenchyma represent 3%–4% of all parathyroid adenomas. Most are located in the lower third of the thyroid lobes and the right side of the thyroid.7 The preoperative diagnosis is complicated because imaging techniques such as ultrasound and gammagraphy do not always precisely identify the intrathyroid situation of the adenomas. The treatment of choice for parathyroid adenomas located in the thyroid is hemithyroidectomy and not isolated exeresis. Hemithyroidectomy would avoid the “spillage” described by Wheeler (capsule rupture and parathyromatosis), thus reducing the risk of recurrence.7,8 In our case, a bilateral cervical approach was performed with total thyroidectomy.
The finding of an intrathyroidal parathyroid adenoma in a patient under prolonged treatment with lithium carbonate is an exceptional case that is both a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
Conflict of InterestThere are no conflicts of interests.
Please cite this article as: Payá Llorente C, Martínez García R, Sospedra Ferrer JR, Durán Bermejo MI, Armañanzas Villena E. Adenoma paratiroideo de localización tiroidea en paciente bajo tratamiento prolongado con litio. Cir Esp. 2016;94:247–249.