Anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS) are synthetic compounds that are structurally related with testosterone. They promote the development of male secondary sex characteristics and accelerate muscle growth.1,2
In the United States, approximately 2.9% of young people have used AAS, and among people who work out in gyms this percentage ranges from 15% to 30%. Similar data have been reported in several European countries.3 The improper, surreptitious abuse of these substances can have important health consequences.
Athletes and body-builders use these compositions in high doses in order to increase their muscle mass and strength to improve performance.2,3 AAS cause changes in the organism, causing gynecomastia, ischemic heart disease and testicular atrophy.3 They also affect the liver, resulting in peliosis, cholestasis, hepatocellular adenoma and liver tumors.4,5
We present the case of a 30-year-old male body-builder who came to our Emergency Department due to asthenia, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. He had a long-term history of synthetic steroid and hormone use. On the initial assessment, the patient presented tachycardia and hypotension and was pale, perspiring and tachypneic. On physical examination, the abdomen was painful to palpation in the right hypochondrium and hepatomegaly was detected. The lab work-up showed leukocytosis 20310/μl, Hb 8.2g/dl, platelets 235000/μl, creatinine 3.21mg/dl, ALT 390U/l, AST 602U/l. Abdominal ultrasound revealed hepatomegaly and liver parenchymal destruction. The patient was admitted to the Intensive Care Unit for monitoring, transfusion and treatment with vasoactive drugs.
Computed tomography (CT) revealed hepatomegaly and destruction of the right liver lobe. The repeated work-up showed Hb 5.9g/dl, platelets 97000/μl, ALT 1693U/l, AST 3223U/l and act. prothrombin 37%. The patient was therefore transferred to our hospital due to liver failure and the possible need for liver transplantation.
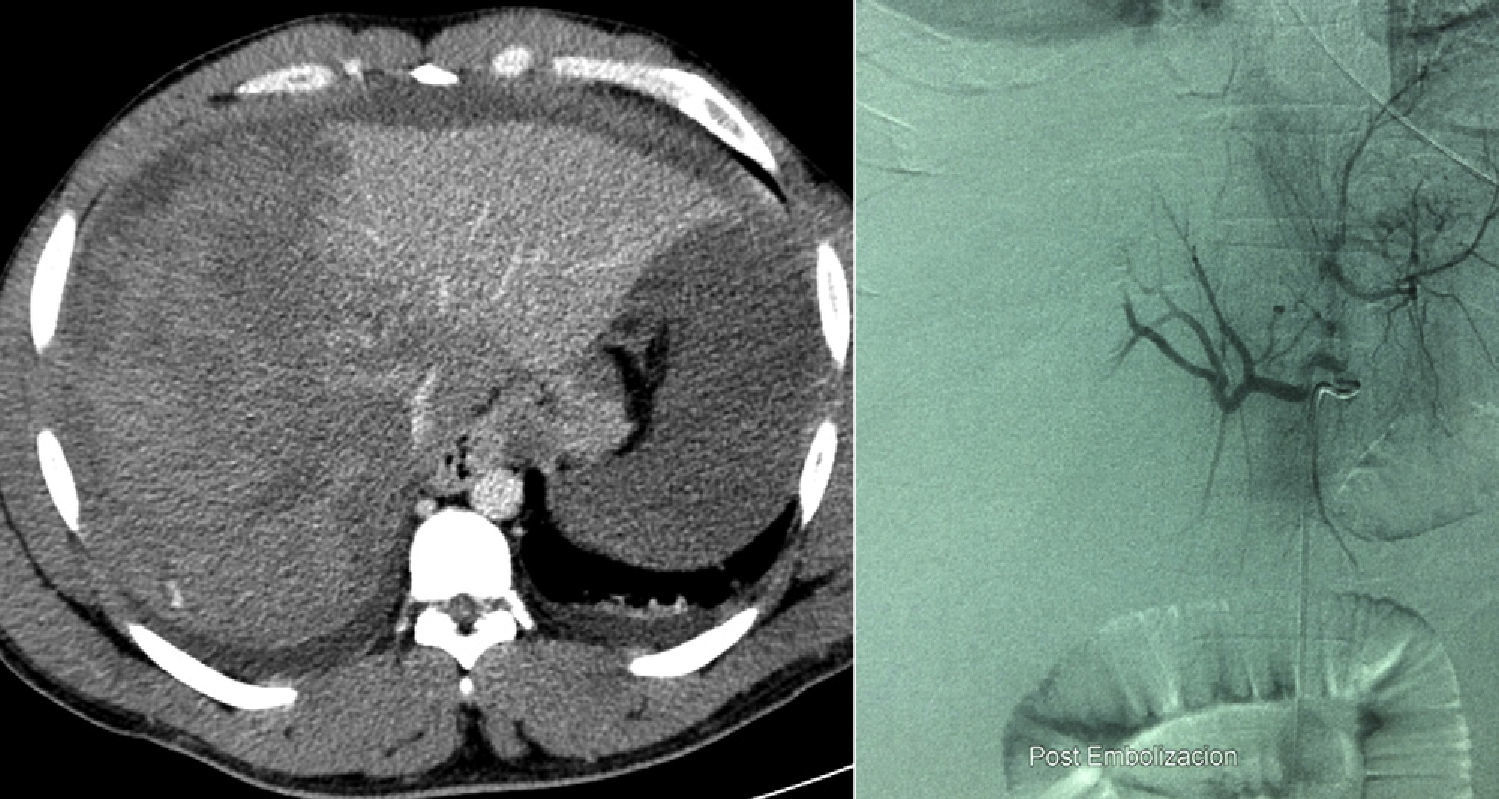
A second CT confirmed hematoma of the liver with active bleeding and hemoperitoneum. Given these findings, an arteriography of the right hepatic artery was done, which showed no signs of active bleeding; even so, diffuse embolization was performed on the right hepatic artery (RHA) (Fig. 1). The patient evolved with progressive increase of the intraabdominal pressure and anuria. Due to this, we decided to perform urgent surgery.
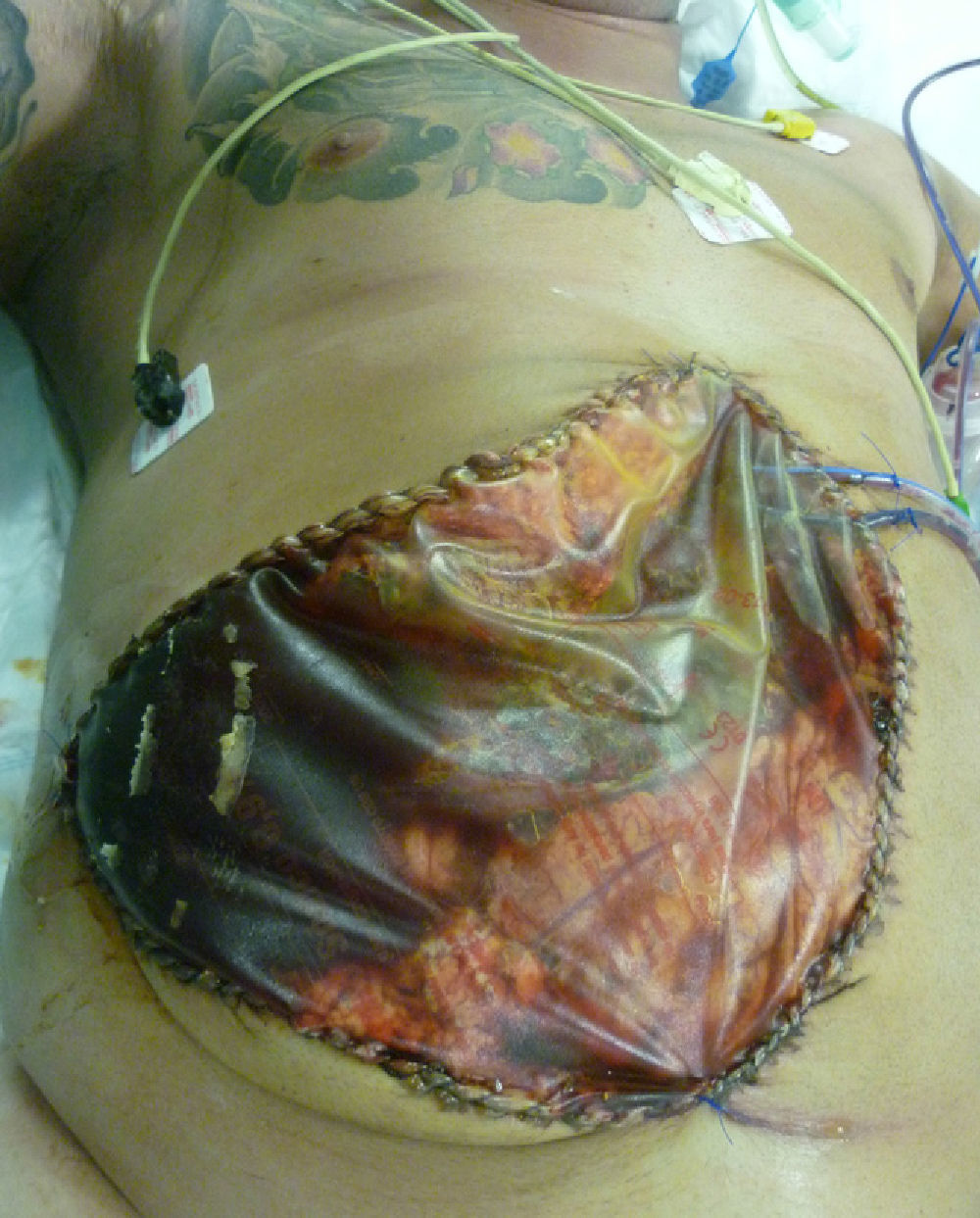
The approach was midline supraumbilical and transverse laparotomy on the right side. Evidence was observed of hemoperitoneum and subcapsular hematoma of the right liver lobe with active bleeding. The RHA was ligated and perihepatic packing used, and the abdomen was left open with a Bogota bag (Fig. 2). The packing was removed 48h later and necrotic liver segment vii was resected. After 72h, the area was reviewed; necrosis was identified in segment VIII, which was resected, and the laparotomy was closed.
The patient evolution was satisfactory, and we observed a correction of the hepatic and renal functions. A postoperative abdominal CT ruled out any liver lesions that could have caused the clinical symptoms. The pathological analysis of the devitalized liver surface showed ischemic necrosis, congestion and areas of hemorrhage.
Spontaneous hepatic rupture is a rare condition that presents as an acute complication of several liver diseases. The identifiable causes are liver tumors, traumas, coagulopathies and microaneurysms.5,6
The association between primary liver tumors and the use of AAS is well known. In general, the course is benign, with spontaneous regression of the tumor after steroid use stops.1,5
Symptoms vary from an incidental finding of a liver tumor, abdominal pain and sometimes secondary bleeding or even hepatic rupture, which can trigger hemodynamic collapse and liver failure.6 Without early intervention, bleeding due to hepatic rupture can lead to catastrophic results. When this condition is suspected, urgent abdominal CT is necessary.7 Treatment should be individualized based on the symptoms, etiology, characteristics of the lesion, skill of the surgeon and the possibilities for treatment at the hospital. Options include conservative treatment, arterial embolization and surgery.6
If active bleeding is confirmed, selective embolization should be attempted as an initial option7,8; if this is not effective, surgical treatment should be considered, including packing, hepatectomy or liver transplantation.6 On most occasions, midline laparotomy is done due to its rapid execution, possibility to be extended and the ability to inspect the entire abdominal cavity. If, however, there is a definitive diagnosis of only a liver lesion, the bilateral subcostal incision is the approach of choice.
Once the hemorrhage is controlled, it is important to assess the extension of the lesions and resect the devitalized liver fragments. Standard hepatectomies are not recommended due to the high morbidity and mortality. In serious hepatic lesions, transplantation has been used, although these are exceptional situations.6
Prognosis depends on the etiology, severity of the hemorrhage and the speed and efficacy of treatment. The case that we present is a spontaneous hepatic rupture due to AAS use. The radiological and pathological studies ruled out other etiologies that would have explained the rupture.
Given that the use of anabolic steroids is currently on the rise, patients and physicians should remember that the use and abuse of AAS can lead to potentially fatal consequences.
Please cite this article as: Marcacuzco Quinto AA, Manrique Municio A, Loinaz Segurola C, Jiménez Romero LC. Rotura hepática espontánea secundaria al uso de esteroides anabolizantes. Cir Esp. 2014;92:570–572.