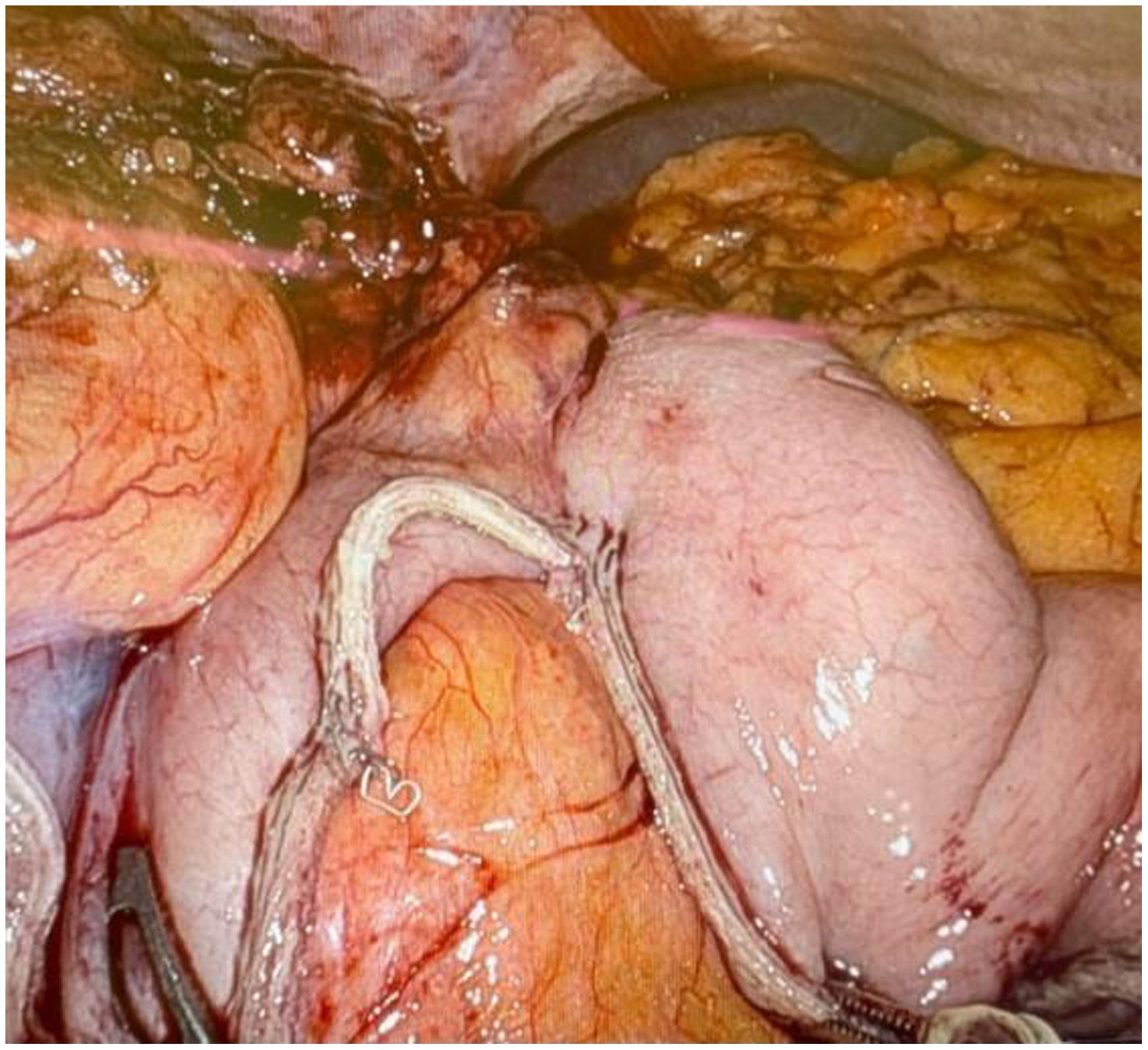
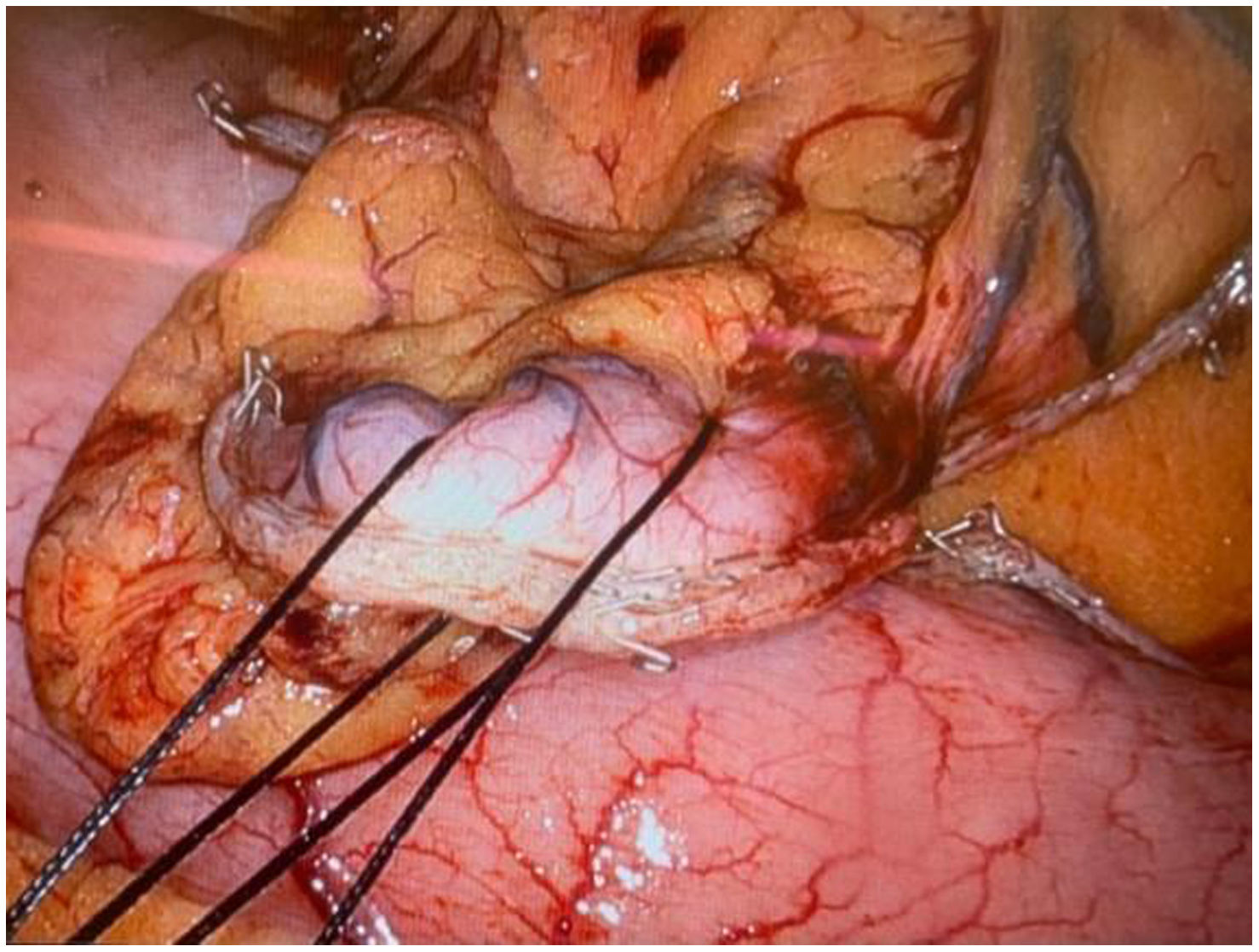
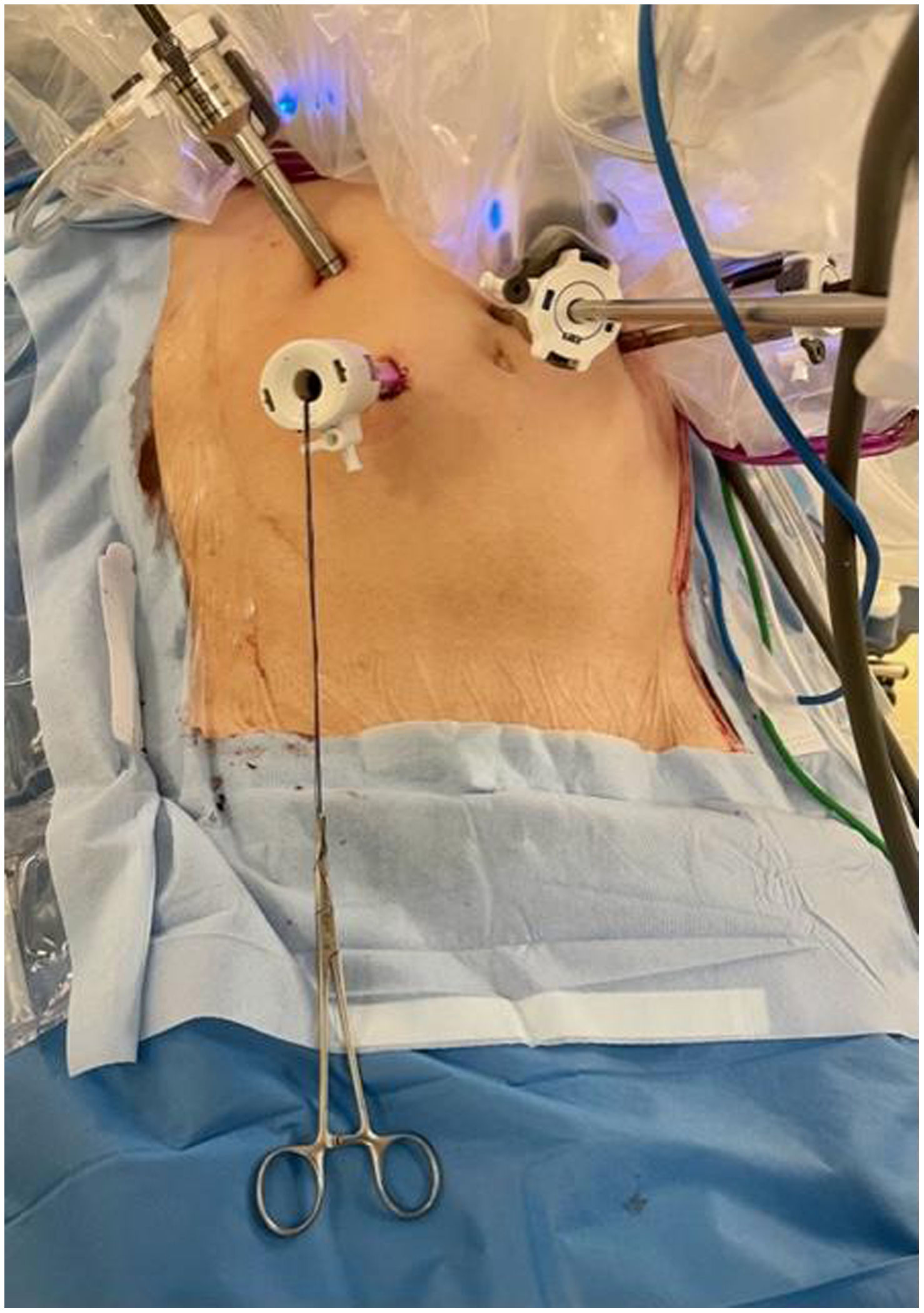
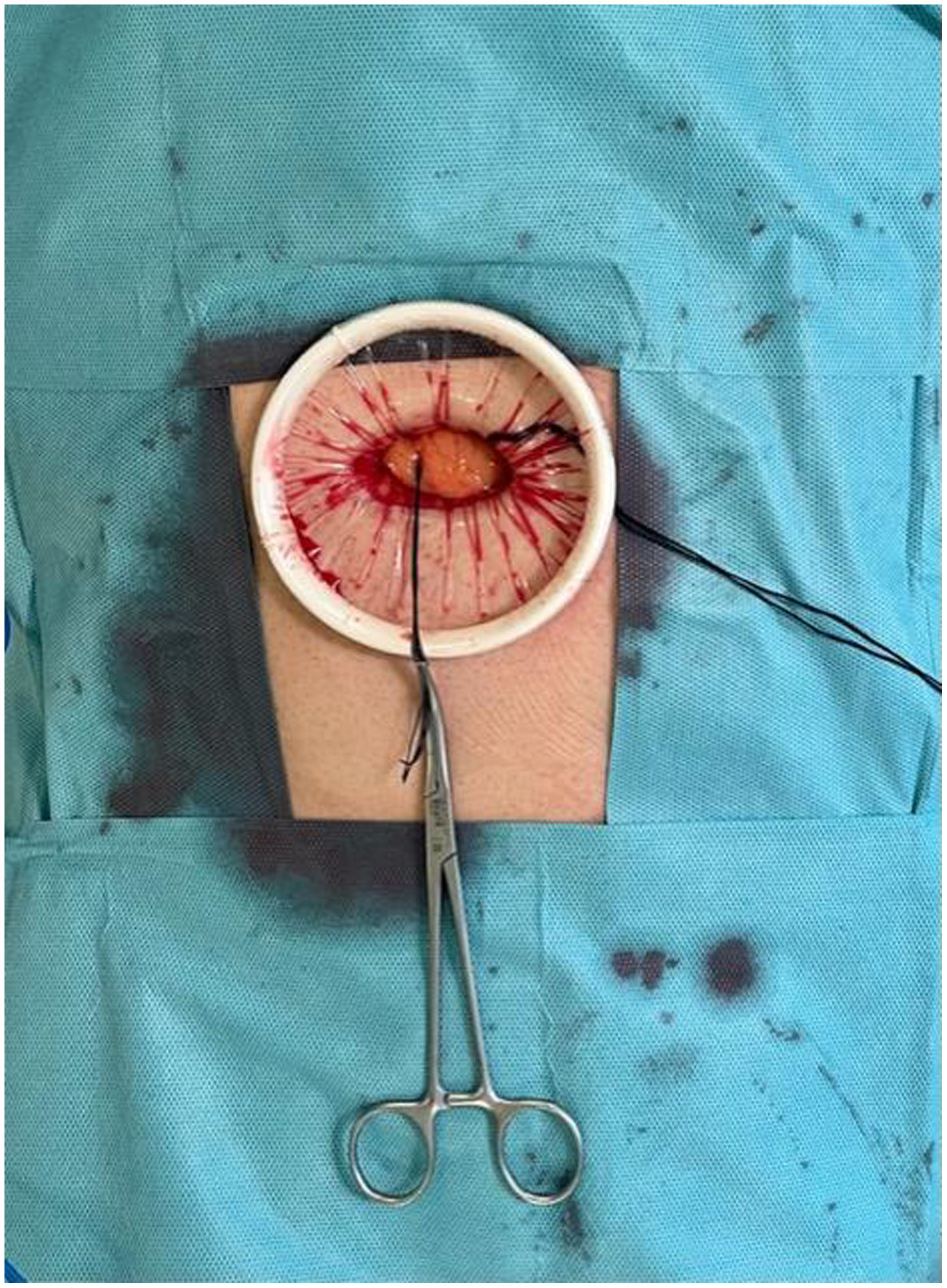
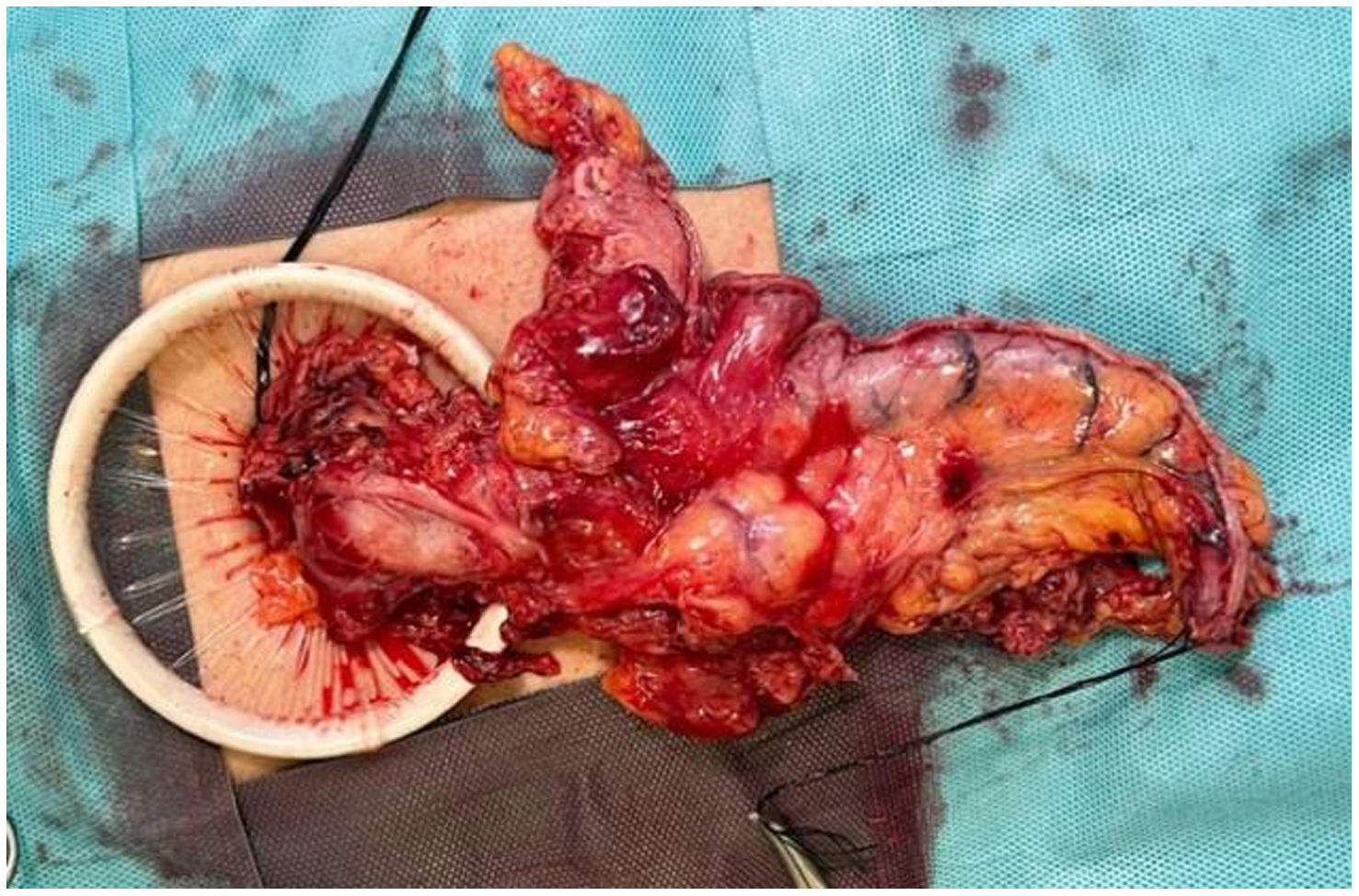
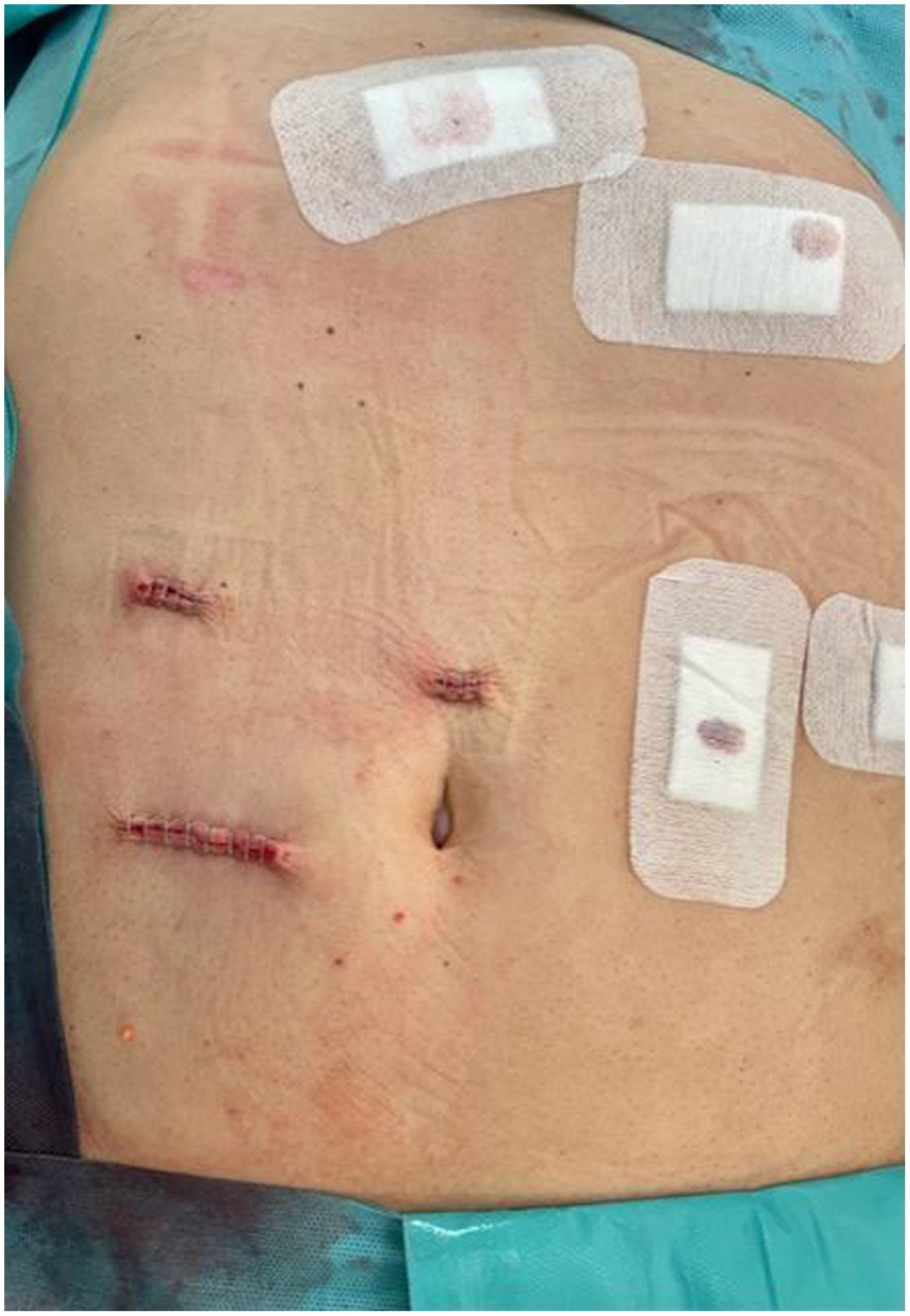
In the surgical treatment of esophageal cancer, robotic surgery allows performing an intrathoracic handsewn anastomosis in a simpler, faster and more comfortable way for the surgeon than open surgery and traditional minimally invasive surgery. With this, we avoid the use of self-suture instruments, some of which require a small thoracotomy for their introduction. However, the retrieval of the specimen requires the practice of this thoracotomy, of variable size, that can be associated with intense chest pain. We describe a technical modification of the classic robotic Ivor Lewis that allows removal of the surgical piece through a minimal abdominal incision, thus avoiding controlled rib fracture, as well as the possible sequelae of making an incision in the chest wall.
En el tratamiento quirúrgico del cáncer de esófago, la cirugía robótica permite realizar una anastomosis manual intratorácica de manera más sencilla, rápida y cómoda para el cirujano que la cirugía abierta y la cirugía mínimamente invasiva tradicional. Con ello, evitamos el uso de instrumentos de autosutura, algunos de los cuales precisan una pequeña toracotomía para su introducción. No obstante, la extracción de la pieza exige la práctica de esa toracotomía, de tamaño variable, y que puede asociar dolor torácico intenso. Describimos una sencilla modificación técnica del Ivor Lewis robótico clásico que permite la extracción de la pieza quirúrgica por una mínima incisión abdominal, evitando la necesidad de fracturar costillas de forma controlada así como las posibles secuelas de practicar una incisión en la pared torácica.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora