A 65-year-old man was admitted to hospital due to severe acute biliary pancreatitis with colangitis. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography was performed with sphincterotomy and extraction of multiple choledocholithiasis.
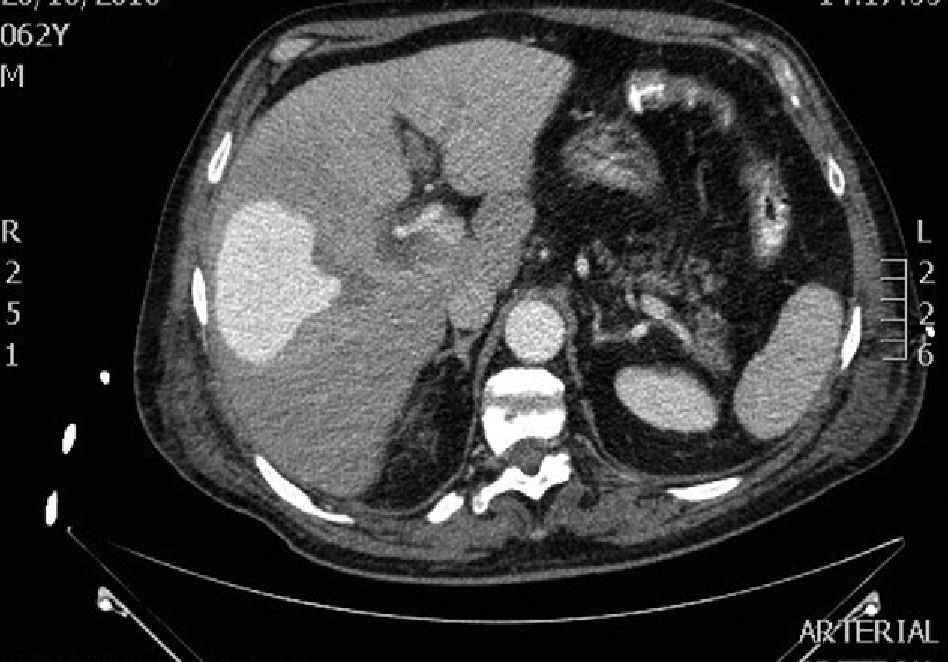
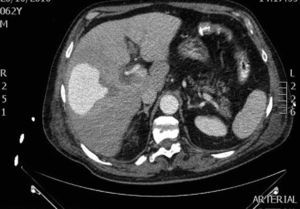
A CT scan performed a week later due to persistent sepsis revealed a round lesion occupying hepatic segments V–VIII, with intense contrast uptake in the arterial phase and clearing in the retarded phase, compatible with an intrahepatic arterial pseudoaneurysm (Fig. 1).
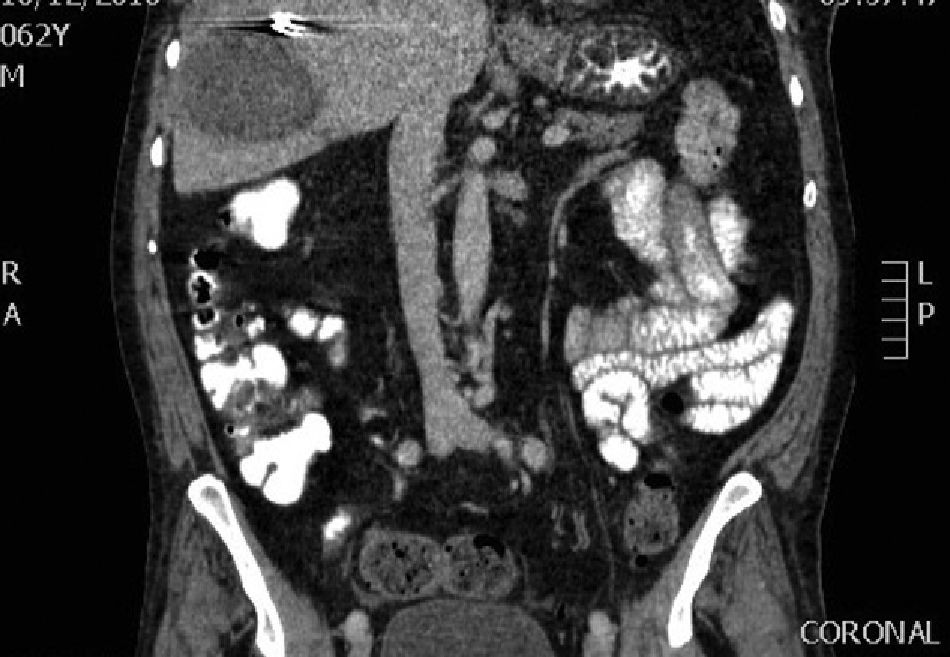
An angiography was performed and two branches of the right hepatic artery feeding the lesion were embolized using spongostan particles (Fig. 2).
Diagnosis: intrahepatic arterial pseudoaneurysm after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
Please cite this article as: Mocanu SN, Palmer Sancho J, González López JA, Villalba Auñón J. Pseudoaneurisma arterial intrahepático. Cir Esp. 2013;91:e23.