La recuperación intensificada en cirugía abdominal (RICA) constituye un conjunto de estrategias perioperatorias encaminadas a acelerar la recuperación del paciente. La interdisciplinariedad es uno de los puntos claves de los programas RICA.
ObjetivoElaborar un documento de consenso entre los miembros del Área de Nutrición de la Sociedad Española de Endocrinología y Nutrición (SEEN) y del Grupo Español de Rehabilitación Multimodal (GERM), donde se intente homogeneizar el manejo nutricional y metabólico de los pacientes incluidos en un programa RICA.
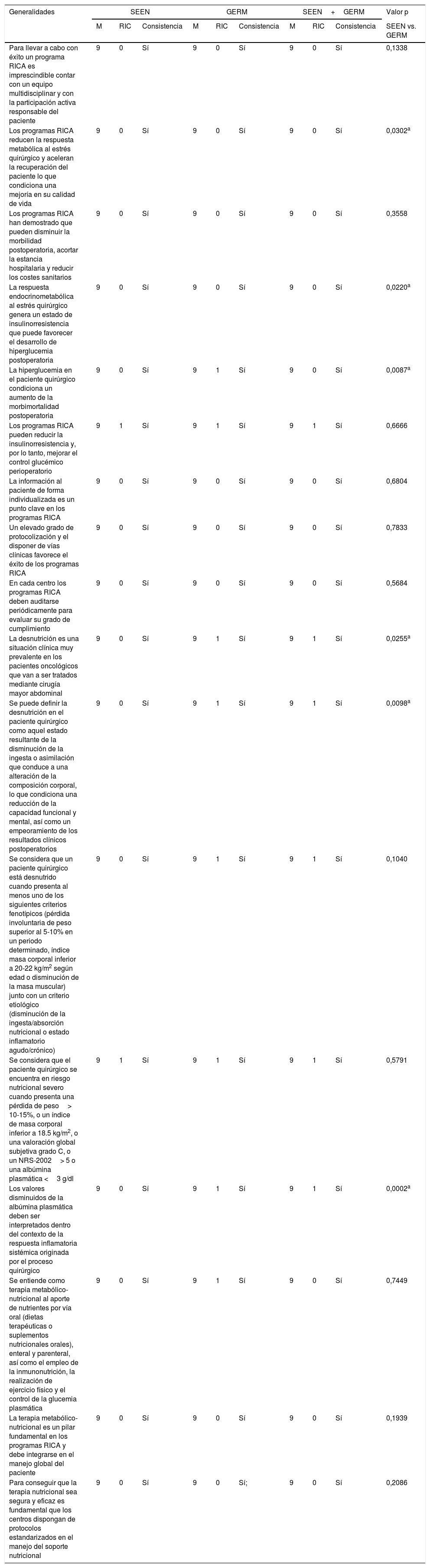
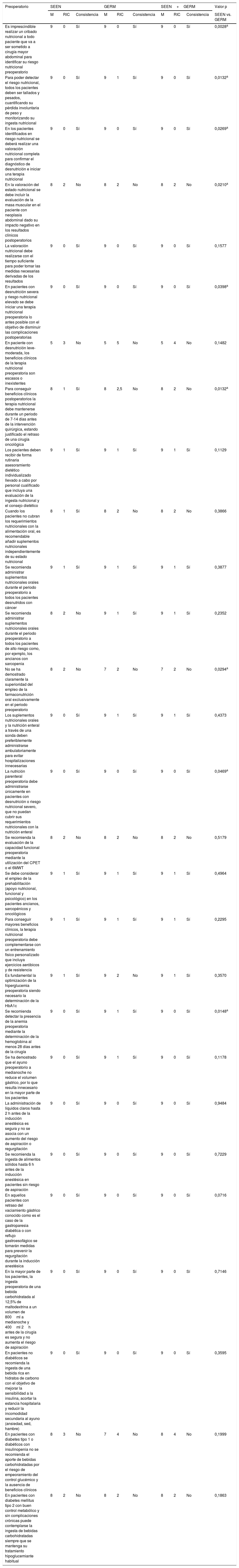
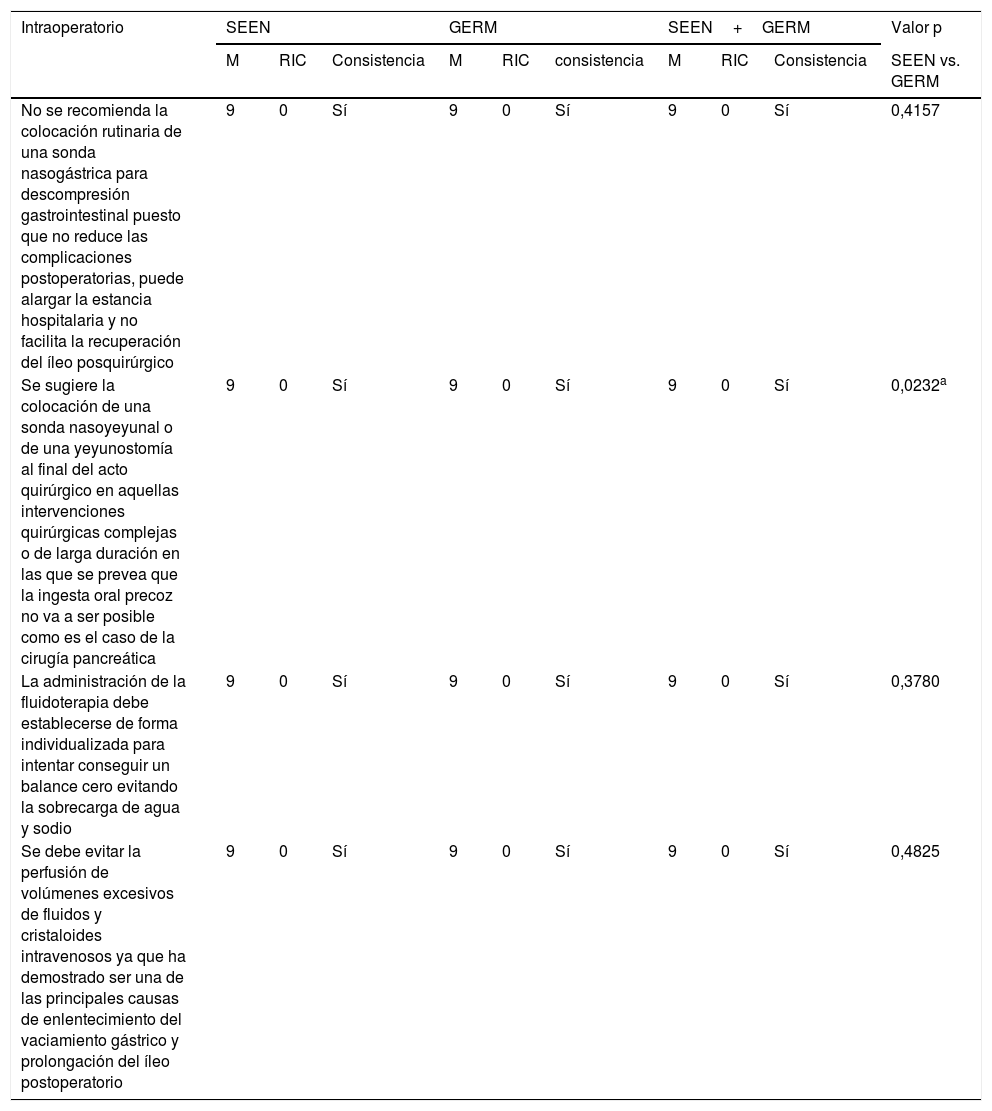
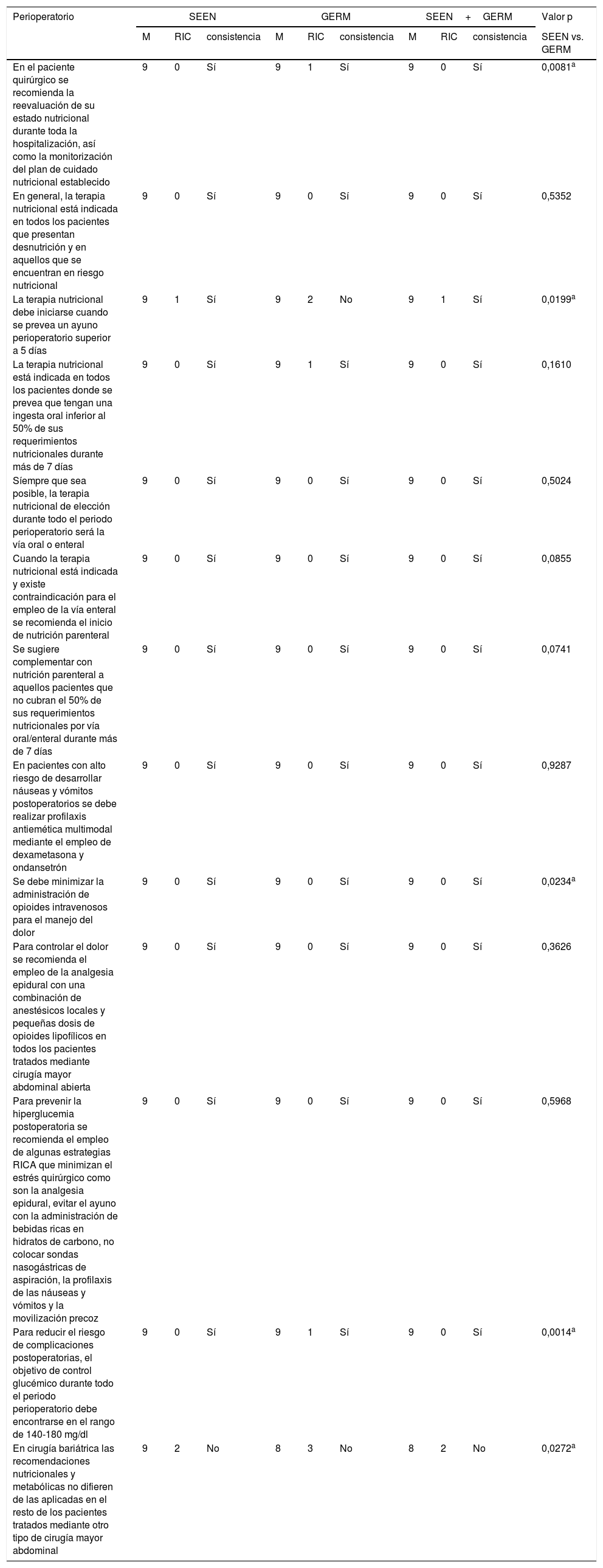
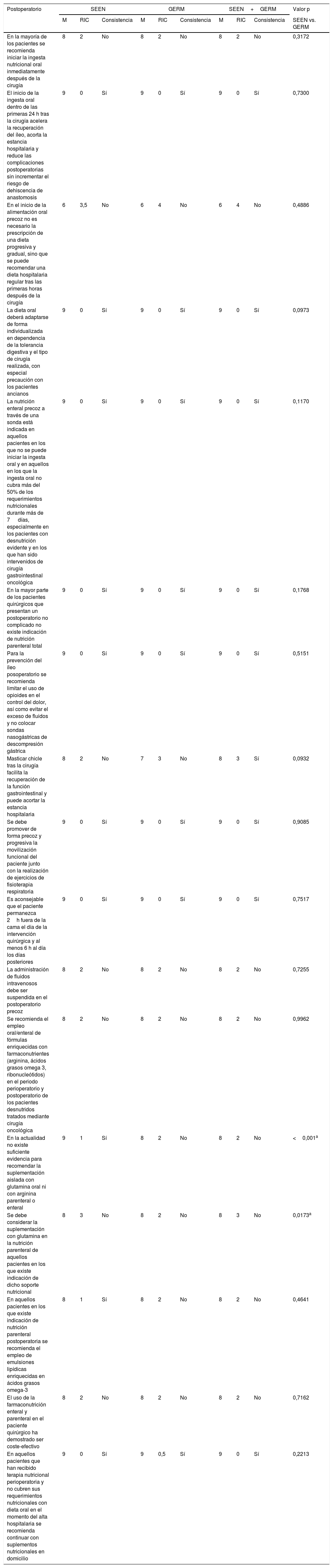
MétodosHan participado 69 especialistas en Endocrinología y Nutrición y 85 miembros del GERM. Tras una revisión bibliográfica fueron propuestas 79 aseveraciones divididas en 5 apartados: 17 de carácter general, 28 referidas al preoperatorio, 4 al intraoperatorio, 13 al perioperatorio y 17 al postoperatorio. Se determinó el grado de acuerdo a través de un proceso Delphi de 2 circulaciones que fue ratificado mediante un análisis de consistencia.
ResultadosDe forma global, en 61 de los 79 enunciados hubo un acuerdo consistente, siendo mayor el grado de consenso entre los miembros de la SEEN (64/79) que en los del GERM (59/79). Dentro de las 18 aseveraciones donde no se alcanzó un acuerdo consistente cabe destacar algunas estrategias nutricionales importantes, como la valoración la masa muscular, el inicio de la alimentación precoz o la farmaconutrición.
ConclusiónQueda consensuada la gran mayoría de las medidas y los cuidados nutricionales incluidos en los programas RICA. Debido a la falta de acuerdo en algunos puntos claves, es necesario seguir colaborando estrechamente entre ambas sociedades para mejorar la recuperación del paciente quirúrgico.
The Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) care pathways include evidence-based items designed to accelerate recovery after surgery. Interdisciplinarity is one of the key points of ERAS programs.
ObjectiveTo prepare a consensus document among the members of the Nutrition Area of the Spanish Society of Endocrinology and Nutrition (SEEN) and the Spanish Group for Multimodal Rehabilitation (GERM), in which the goal is to homogenize the nutritional and metabolic management of patients included in an ERAS program.
Methods69 specialists in Endocrinology and Nutrition and 85 members of the GERM participated in the project. After a literature review, 79 statements were proposed, divided into 5 sections: 17 of general characteristics, 28 referring to the preoperative period, 4 to the intraoperative, 13 to the perioperative and 17 to the postoperative period. The degree of consensus was determined through a Delphi process of 2 circulations that was ratified by a consistency analysis.
ResultsOverall, in 61 of the 79 statements there was a consistent agreement, with the degree of consensus being greater among members of the SEEN (64/79) than members of the GERM (59/79). Within the 18 statements where a consistent agreement was not reached, we should highlight some important nutritional strategies such as muscle mass assessment, the start of early oral feeding or pharmaconutrition.
ConclusionConsensus was reached on the vast majority of the nutritional measures and care included in ERAS programs. Due to the lack of agreement on certain key points, it is necessary to continue working closely with both societies to improve the recovery of the surgical patients.