The correct identification of the species within the Candida parapsilosis complex has become relevant due to the resistance of Candida metapsilosis to antifungals. We describe the characteristics of the Candida parapsilosis complex isolates, with respect to antifungal resistance and biofilm formation.
MethodsWe perform a descriptive cross-sectional study in 30 strains, collected in a tertiary hospital. All strains, were identified by Vitek2, Vitek-MS™ systems and by ITS sequencing. The antifungal susceptibility profile was obtained with Sensititre™ panels, while biomass production and metabolic activity were quantified by means of crystal violet and XTT reduction assay, respectively.
ResultsThere was a 100% correlation between Vitek-MS™ and ITS sequencing. All isolates were susceptible to the nine antifungals tested. The metabolic activity and biomass production tests did not show any difference among the subtypes.
ConclusionsThe Vitek-MS™ system provides acceptable identification. We did not find significant differences neither in azole resistance nor in biofilm formation.
La correcta identificación del complejo Candida parasilopsis es relevante debido a la resistencia antifúngica de Candida metasilopsis. Describimos las características de aislados del complejo Candida parapsilosis respecto a la resistencia antifúngica y formación de biopelícula.
MétodosSe realiza un estudio descriptivo transversal de 30 cepas recolectadas en un hospital terciario. Todas se identificaron por los sistemas Vitek2, MALDI-TOF MS Vitek-MSTM y por secuenciación de las regiones ITS. La sensibilidad antifúngica se realizó con paneles SensititreTM. Para la producción de biomasa y la actividad metabólica se emplearon la medición de cristal violeta y el ensayo de reducción de XTT, respectivamente.
ResultadosHubo una correlación del 100% entre Vitek-MSTM y la secuencia de ITS. Todos los aislados fueron sensibles a los 9 antifúngicos evaluados. Los ensayos de actividad metabólica y producción de biomasa no arrojaron diferencias entre los subtipos.
ConclusionesEl sistema Vitek-MSTM proporciona una identificación aceptable. No encontramos diferencias significativas ni en la resistencia a azoles ni en la formación de biopelículas.
Candida parapsilosis complex is becoming one of the emerging causes of candidaemia in the world, being the second or third cause of candidaemia, after Candida albicans.1C. parapsilosis complex is well known as a cause of nosocomial infection, particularly in neonates and especially associated with intravascular devices and parenteral nutrition.2
Roy and Meyer in 1998 confirmed, with DNA relatedness and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analyses, different genotypes within the C. parapsilosis group, separating them into three subtypes I–III.3 It was Tavanti et al., in 2005, who called the three groups C. parapsilosis sensu stricto (I), Candida orthopsilosis (II), and Candida metapsilosis (III).4 Until recently, the commercial systems did not differentiate these groups, making it necessary to carry out a restriction analysis of polymorphisms in the alcohol dehydrogenase (SADH) gene to differentiate them, common in the three species, also proposed by Tavanti in 2007.5 In 2008, Lockhart et al. added a new subtype to this complex, Lodderomyces elongisporus.6 The matrix-assisted laser desorption/isolation-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) technique can identify the four subtypes.
The percentage of Candida orthopsilosis (5.1–6.5%) and Candida metapsilosis (1.5–1.8%) subtypes compared to C. parapsilosis sensu stricto is low in the larger series.6,7 In Spain, although this percentage was 8.2% and 1.1% respectively in 2011,8 in our hospital these percentages are 4.21% for C. metapsilosis and 1.05% for C. orthopsilosis.9
Antifungal susceptibility profiles of the C. parapsilosis species complex reveals only slight differences between the three Candida subspecies, which has suggested that their routine discrimination is not necessary for the clinical laboratory.10 But very few isolates have been compared in those studies.
Taking into account the above, in this study we carried out a characterization of our C.parapsilosis species complex isolates in order to: (i) look for phenotypical differences; (ii) check the suitability of MALDI-TOF for identification, (iii) test the antifungal susceptibility, and (iv) assay the biofilm formation.
MethodsCandidaspp. strains. Twelve C. metapsilosis and eight C. orthopsilosis clinical strains, collected between 2005 and 2019 in the Microbiology Department of the University Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain, were chosen. For the global study, a collection of 10 Candida parapsilosis sensu stricto strains, obtained from blood cultures during the same period, were also added to the analysis.
The eight C. orthopsilosis strains were collected from: blood cultures (3), urine, external ear exudate (1) and biopsy (1). The 12C. metapsilosis strains were collected from: blood cultures (8), external ear exudate (1), vaginal exudate (1), induced sputum (1) and tracheal aspirate (1).
Phenotypic automated system. The Vitek®2 with AST-YS8 identification cards (bioMérieux, Marcy-I’Etoile, France) were used for the analysis according to the manufacturer's instructions.
MALDI-TOF MS Vitek-MS™ system (bioMérieux, Marcy-I’Etoile, France). Identification of strains was performed following manufacturer's recommendations. Measurement was performed with a Vitek-MS™ instrument supported by SARAMIS MS-IVD v3.0, and v3.2 databases (Anagnos Tee GMBH, BioMérieux).
Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS). The ITS region was amplified with primers described previously by White el al.11 The sequences of the isolates were compared with those deposited in the GenBank database using BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
Antifungal susceptibility test. The antifungigrams were performed with Sensititre™ YeastOne YO10 (TREK Diagnostic Systems, East Grinstead, United Kingdom), following the manufacturer's recommendations. Antimicrobial susceptibility was analyzed according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI-M59).
Static biofilm formation assays. Assays were performed in 96-well polystyrene plates, as previously reported.12 Finally, we filled two plates with samples in triplicate for the two assays and incubated them at 37°C for 24h.
Crystal violet biofilm inhibition assay. Biomass formation was quantified after staining with crystal violet (125μL 0.1%) and extracting the crystal violet with acetic acid (125μL 30%). Absorbance was measured at 550nm using a microplate reader (Tecan Microplate Reader, Infinite 200 PRO, Männedorf, Switzerland). Strains were tested in triplicate and classified according to Marcos-Zambrano et al.13 score as low biofilm forming (LBF; <0.44), moderate biofilm forming (MBF; 0.44–1.17), and high biofilm forming (HBF; >1.17).
XTT reduction assay. To quantify biofilm metabolic activity, the reduction of 2.3-Bis-(2-methoxy-4-nitro5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide (XTT) was measured in the other plate.14 The optical density (OD) value at 490nm was measured using a microplate reader (Tecan Microplate Reader, Infinite 200 PRO, Männedorf, Switzerland). Strains were tested in triplicate and classified based on their metabolic activity using the XTT reduction assay as low metabolic activity (LMA; <0.097), moderate metabolic activity (MMA; 0.097–0.2), and high metabolic activity (HMA; >0.2).13
Data analysis. The statistical analysis was carried out using the SPSS computer software (IBM SPSS Version 20.0). The analysis of differences, in antifungal susceptibility and biofilm formation patterns among subspecies, were evaluated using non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test.
ResultsMALDI-TOF Vitek-MS™, with v3.2 library version, identified correctly all the isolates with a crude agreement of 100% (20/20) compared to the sequencing. Only some of these strains were analyzed by v3.0 library version, where C. metapsilosis was not included, so it misidentified 44.4% (4/9) of the isolations as C. orthopsilosis and 55.5% (5/9) as C. parapsilosis, while C. orthopsilosis were all correctly identified, 100% (7/7).
Vitek2 didn’t include these species in the database, so the strains were identified only at the species complex level. In an in-depth analysis of AST-YS8 cards in the C. orthopsilosis group 75% (6/8), 87.5% (7/8) and 87.5% (7/8) of the strains turned positive in L-lisine aramidase, D-melobiose assimilation and D-sorbose assimilation, respectively, while only 1% turned positive in C. parapsilosis sensu stricto group and none in C. metapsilosis group. Also, in C. parapsilosis sensu stricto group, tirosin arilamidase became positive in 70% (7/10) of the strains while only in 16.6% (2/12) and 12.5% (1/8) became positive in C. metapsilosis and C. orthopsilosis groups, respectively.
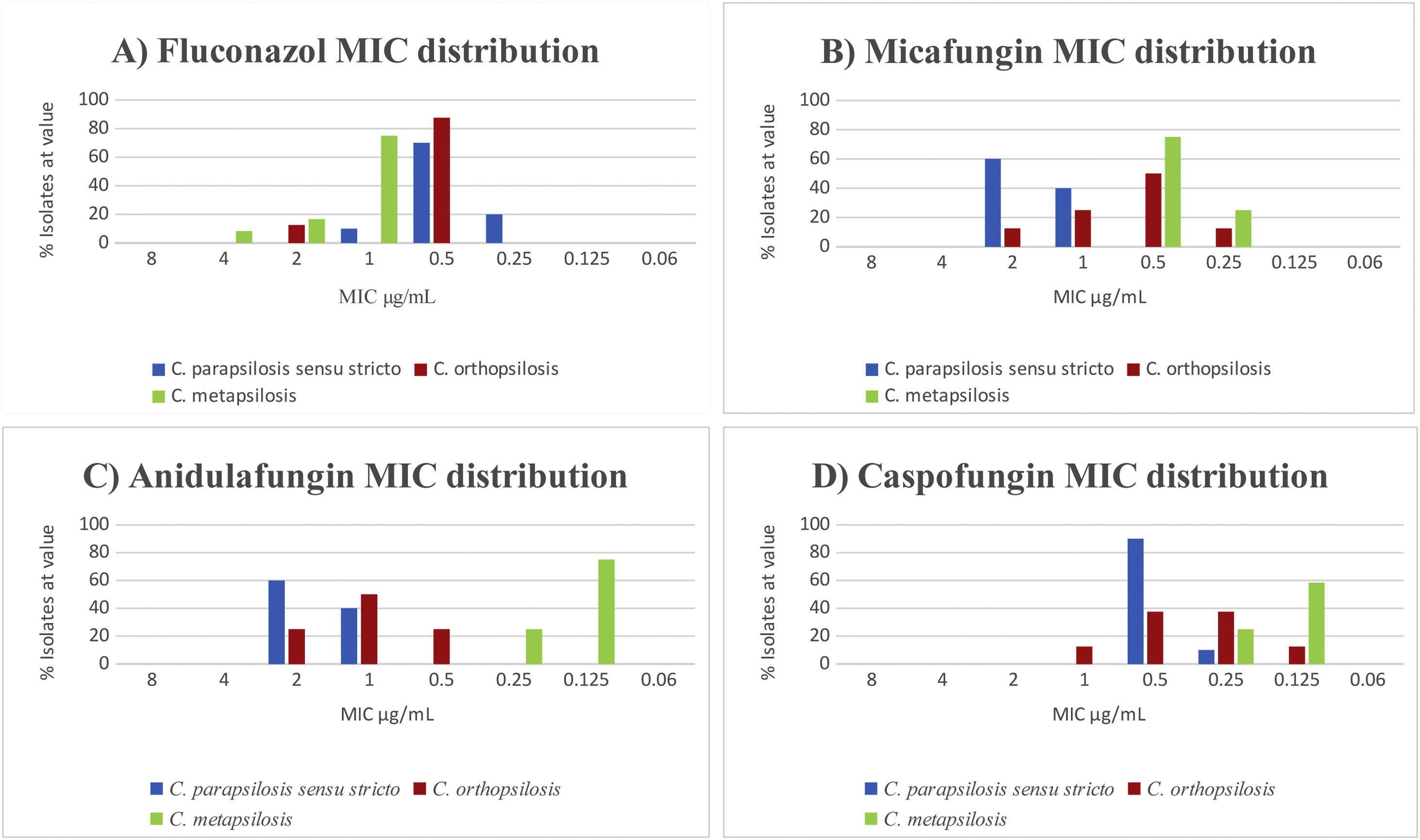
The results of antifungal susceptibility tests confirmed that all isolates were susceptible to the nine antifungals tested. We found significant differences in the susceptibility to fluconazole of C. metapsilosis with respect to C. parapsilopsis (p<0.01). In contrast, we did not find significant differences in susceptibility between C. metapsilosis and C. orthopsilosis (p=0.14) (Fig. 1A). The strains were equally susceptible to amphotericin B showing a slightly higher MICs for micafungin and anidulafungin.
We observed statistically significant differences for micafungin in C. parapsilosis sensu stricto in relation with C. metapsilosis (p<0.01) but not in C. parapsilosis sensu stricto regarding C. orthopsilosis (p=0.06). On the other hand, the difference in susceptibility to anidulafungin was statistically significant in C. parapsilosis sensu stricto with regard to C. metapsilosis (p<0.01). Conversely, differences between C. parapsilosis sensu stricto and C. orthopsilosis were not statistically significant (p=0.078). In fact, C. metapsilosis showed lower MICs (Fig. 1B–D).
We found statistically significant differences between C. parapsilosis sensu stricto and C. metapsilosis (p<0.01). Conversely, the metabolic activity of the strains was not useful to distinguish the species from each other (Table 1).
Strains of Candida parapsilosis complex classified according to the degree of biomass production and metabolic activity.
| Biomass production | Metabolic activity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBF (<0.44 OD) | MBF (0.44–1.17 OD) | HBF (>1.17 OD) | LMA (<0.09 OD) | MMA (0.09–0.2 OD) | HMA (>0.2 OD) | |
| C. orthopsilosis (8) | 2 (25%) | 4 (50%) | 2 (25%) | 0 | 7 (87.5%) | 1 (12.5%) |
| C. methapsilosis (12) | 2 (16.7%) | 8 (66.6%) | 2 (16.7%) | 1 (8.4%) | 9 (75%) | 2 (16.6%) |
| C. parapsilosis sensu stricto (10) | 4 (40%) | 2 (20%) | 4 (40%) | 0 | 4 (40%) | 6 (60%) |
| n=30 | 8 (26.7%) | 14 (46.6%) | 8 (26.7%) | 1 (3.4%) | 20 (66.6%) | 9 (30%) |
*LBF: low biofilm former, MBF: medium biofilm former, HBF: high biofilm former, LMA: low metabolic activity, MMA: medium metabolic activity, HMA: high metabolic activity, OD: optical density.
Although identification of clinical isolates of C. parapsilosis complex belonging to the subtypes C. metapsilosis and C. orthopsilosis cannot be accomplished following phenotypic systems,15 the results of this study, allow to update the databases of these systems, since not all microbiological laboratories have access to MALDI-TOF systems.
On the other hand, although currently there are very few reported clinical isolates of the two subtypes considered here, this is expected to change with the implementation of new identification systems, such as with the latest version of MALDI-TOF database. This will influence the determination of the real prevalence and incidence, probably increasing the magnitude of the latter with respect to the prevalence.
We can confirm the moderate or high production capacity of biofilm production of the complex in our strains, as previously reported,13 as well as a slightly higher metabolic activity in the C. parapsilosis sensu stricto group (Table 1).
Finally, we consider desirable the identification of the three subtypes, both for epidemiological surveillance and for the different susceptibility patterns to fluconazole, anidulafungin and micafungin. In our strains, we found C. metapsilosis more resistant than C. parapsilopsis sensu estricto as previously reported,5 but not in C. orthopsilosis, in contrast to de Toro et al.10 Currently there is no scientific evidence that does not justify the use of fluconazole in C. metapsilosis, but it is worth highlighting the little information available on the epidemiological distribution and resistance of the C. parapsilosis complex. Otherwise, all the strains were equally susceptible to flucytosine in contrast to other authors.5 Finally, the MICs of amphotericin B and echinocandins were lower against C. orthopsilosis and C. metapsilosis than those against C. parapsilosis sensu stricto as in previous studies.6,10
Transparency declarationsAll authors have nothing to declare. This study has not been financially supported by any Diagnostic/Pharmaceutical company.
Ethical approvalNot applicable
FundingThis study was supported by Plan Nacional de I+D+i 2013–2016, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Subdirección General de Redes y Centros de Investigación Cooperativa, Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Spanish Network for Research in Infectious Diseases (REIPI RD16/0016/0007).
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
We thank Dr. Alain Ocampo Sosa and Dr. Israel Nieto Gañan for reviewing and correcting the manuscript.