Según la literatura consultada, el enfoque biomédico continua dominando el modo en que las enfermeras piensan, trabajan y se comunican. Para estudiar si esta situación se produce en nuestro contexto, se propone: 1) describir el valor que las enfermeras otorgan a diferentes acciones instrumentales, estratégicas y comunicativas, según la teoría de la acción comunicativa; y 2) analizar su posible relación con el tipo de unidad de hospitalización.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo con 89 enfermeras de unidades de hospitalización médica, quirúrgica y oncohematológica del Hospital Reina Sofía de Córdoba. Para la recogida de datos se creó un cuestionario con 4 acciones instrumentales, 4 estratégicas y 4 comunicativas que tenían que ser referidas a 3 ámbitos (pensamiento, práctica, y registro) y puntuadas del 1 al 5 según su valor o importancia. El cuestionario era autocumplimentado y recogido tras una semana.
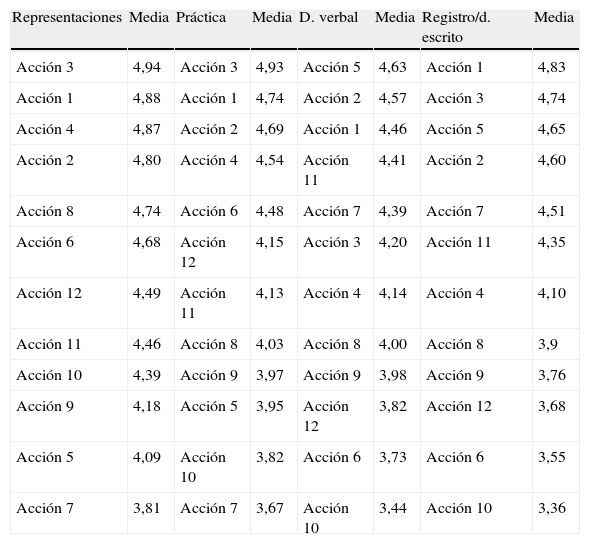
ResultadosEn el ámbito del pensamiento y la práctica las puntuaciones medias mayores corresponden a acciones instrumentales (19,49 y 18,9, respectivamente), seguidas de acciones comunicativas y estratégicas, por este orden. No obstante, en el ámbito del registro las acciones estratégicas superan a las acciones comunicativas (17,27 vs 14,49), que descienden al último lugar. Sólo en unidades de oncohematología el registro de estas acciones se mantiene en cifras elevadas (17,26).
ConclusionesLos resultados ponen de relieve la hegemonía del modelo biomédico, representado por las acciones instrumentales y estratégicas, y dibuja una situación difícil para la acción comunicativa, que tiene, ante todo, que buscar su hueco en el discurso profesional.
According to the literature consulted, the biomedical approach continues dominating the ways in which nurses think, work and inform. In order to study whether this situation also occurs in our context, this research proposes to 1) describe the value or weight nurses give to the different instrumental, strategic and communicative actions, according to Habermas’ Theory of the Communicative Action; as well as 2) analyse its possible relationship with the type of unit in which nurses work.
MethodsIt is a descriptive study including 89 nurses, conducted in medical, surgical and onco-haematological hospital wards in the Hospital Reina Sofia of Cordoba. For the data collection, a questionnaire was created specifically for the study, made up of 4 instrumental actions, 4 strategic actions and 4 communicative actions that were scored 1-5 according to their value or importance. The questionnaire was self-administered and collected after one week.
ResultsThe instrumental actions obtain the highest scores in the area of thoughts (19.49) and practice (18.9), followed by the communicative actions. Nevertheless, the strategic actions exceeded the communicative actions in the record (17.27 vs 14.49). Only in the onco-haematology units, communicative actions maintained high scores (17.26).
ConclusionsThe results from the present study emphasise the hegemony of the biomedical model, represented by instrumental and strategic actions, and draw a difficult situation for the communicative action, which has to find its place in the professional speech.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora