El objetivo del estudio fue describir y analizar las intervenciones enfermeras NIC realizadas en la práctica clínica por las enfermeras de una unidad de cuidados intensivos neonatales.
Material y métodosEstudio descriptivo llevado a cabo en la UCI-Neonatal del Complejo Asistencial Universitario de León. La población de estudio incluyó a todos los niños ingresados en la UCI-Neonatal desde el 1 de marzo hasta el 30 de noviembre del 2011. Se creó una base de datos con el programa informático Epi Info donde se recogieron las intervenciones NIC que previamente habían sido seleccionadas por un panel de expertos.
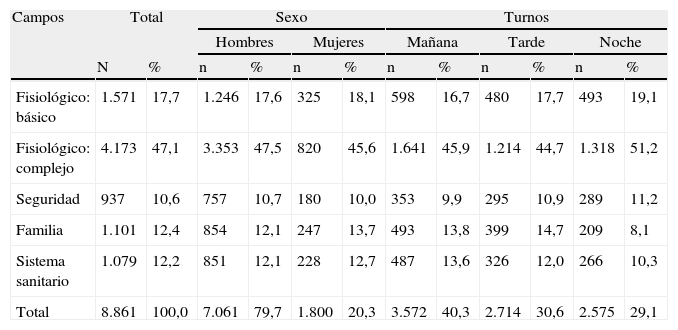
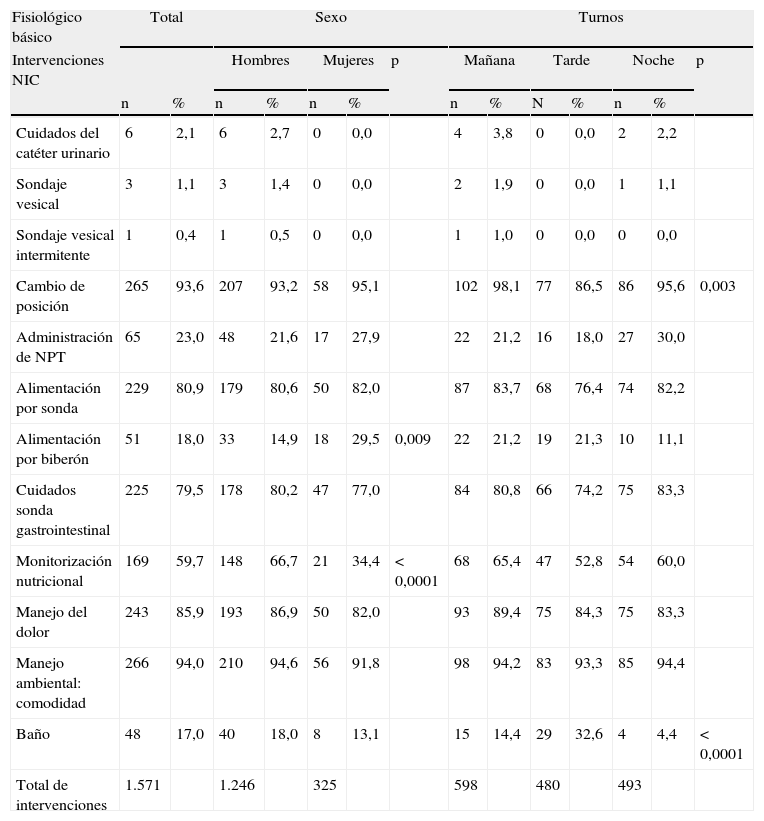
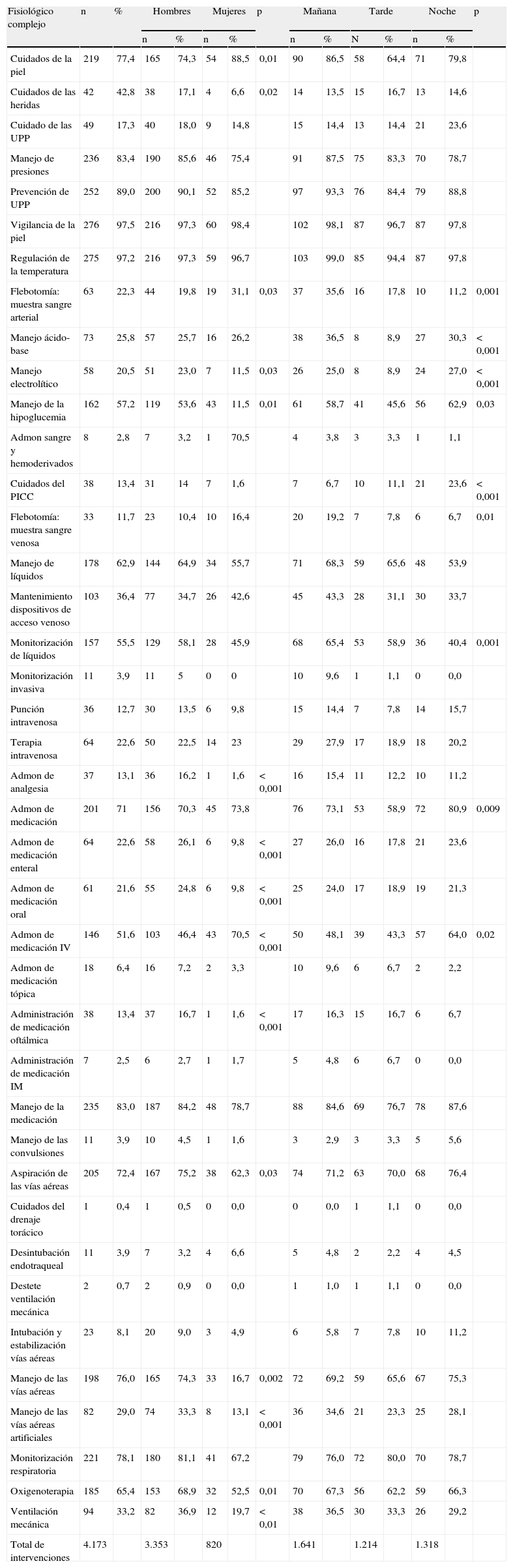
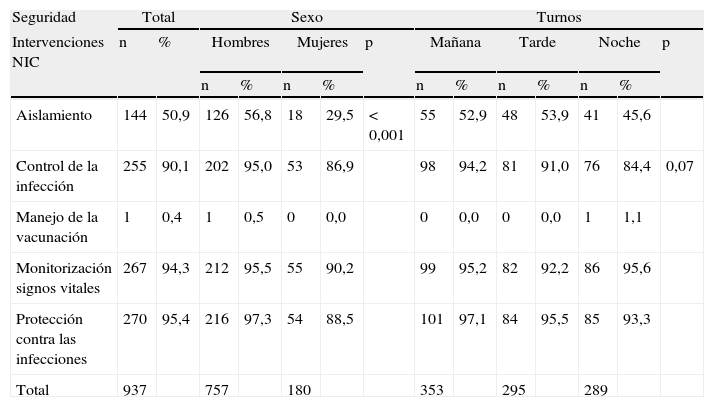
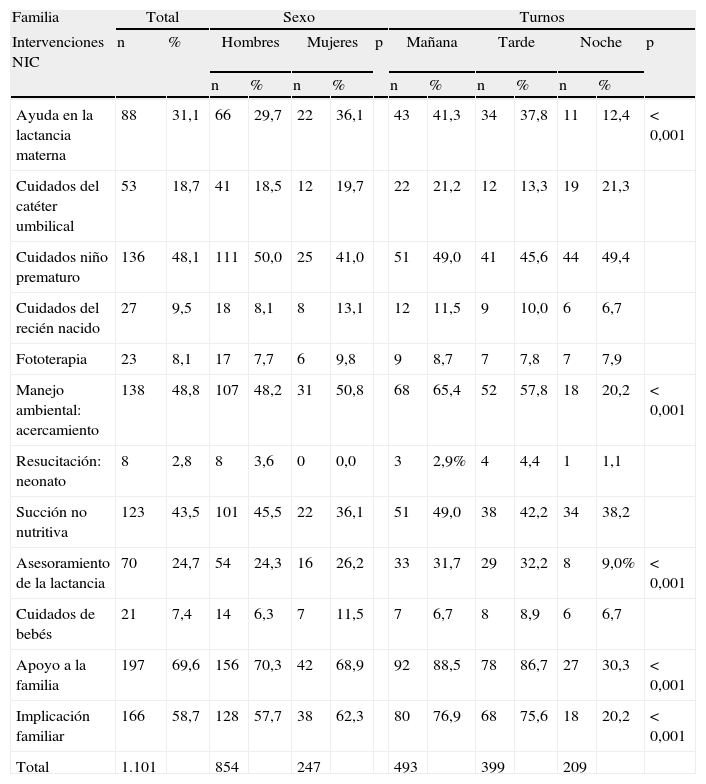
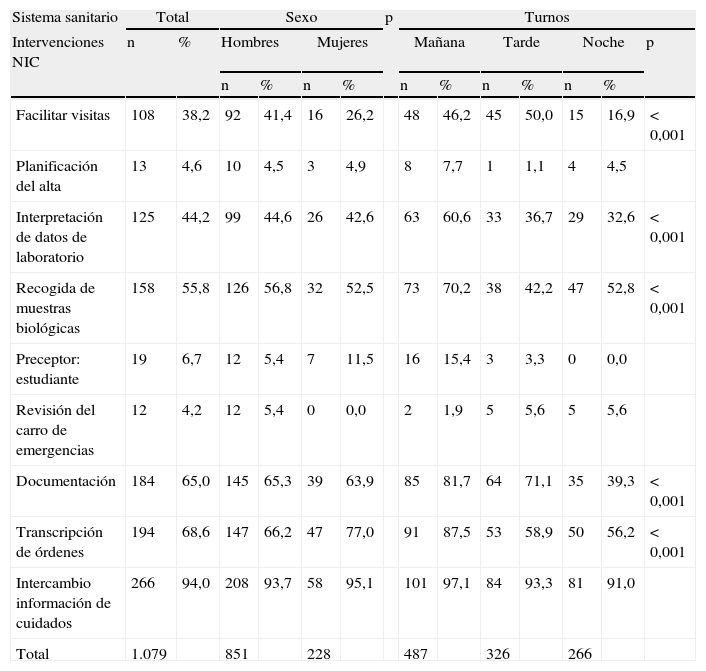
ResultadosSe recogieron un total de 283 registros, correspondientes a 44 neonatos ingresados de peso medio 1.705,5 g y 14,3 días de edad. Se han realizado un total de 8.861 intervenciones NIC. El mayor porcentaje de intervenciones (47,1%) perteneció al campo fisiológico complejo, seguido del fisiológico básico (17,7%). El porcentaje de intervenciones realizadas en turno de mañana, tarde y noche fue del 40,1, el 30,6 y el 29,1%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesEl mayor porcentaje de intervenciones pertenece al campo fisiológico complejo, aunque se puede concluir que en la práctica clínica la solución de problemas no solo depende de intervenciones en esta área, sino en otras áreas como la familia, intervención clave en el cuidado neonatal.
The aim of the study was to describe and analyze the nursing interventions NIC developed in the clinical practice by specialized nurses in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU).
Material and methodsDescriptive study in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of University Complex Hospital of León. The study population included all the neonates admitted in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit from 1 march to 30 november of 2011. Database was created with the statistical program Epi Info where NIC interventions were collected between the selected by the panel of experts.
ResultsWe collected a sum of 283 records of 44 neonates admitted with an average weight of 1705.5 gr and 14.3 days of age. Nurses have performed a total of 8861 NIC interventions. The highest percentage of interventions (47,1%) belong to the complex physiological domain, followed by the basic physiological (17,7%). We found 40,1%; 30,6% and 29,1% interventions in the early, late and night shifts.
ConclusionsThe highest percentage of interventions belong to the complex physiological domain although we can conclude that in the nursing clinical practice the solution of problems not only depend of interventions in that area but other areas such as family key intervention in the neonatal care.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora