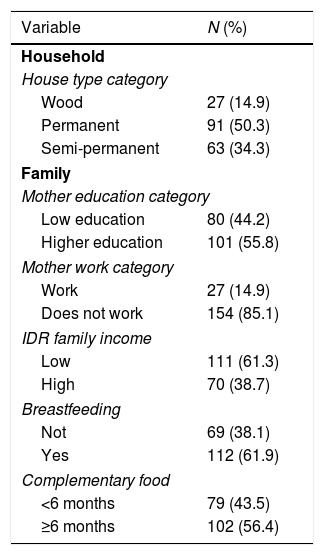
Nutrition plays an important role in the human life cycle, more specifically for children aged 2 years because this is a period of golden children that determines the health status of their future children. The aim of this study was to analyze the nutritional status of children aged 0–23 months toward breastfeeding and complementary food status.
MethodsThis study was an observational analytic study with a cross sectional study design carried out in Malili sub-district, East Luwu district, Indonesia. This research was conducted from April to June 2019, involving 4 Villages. The number of samples is 181 infants aged 0–23 months.
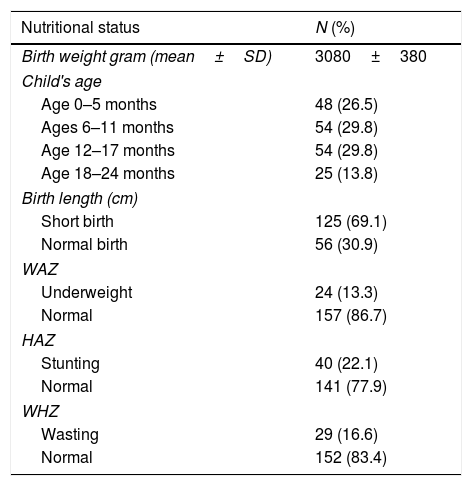
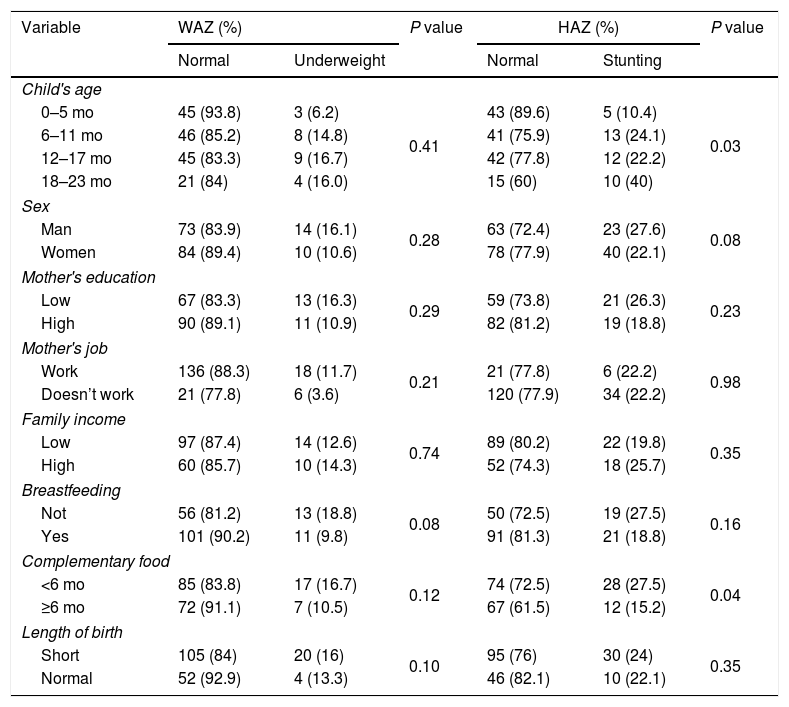
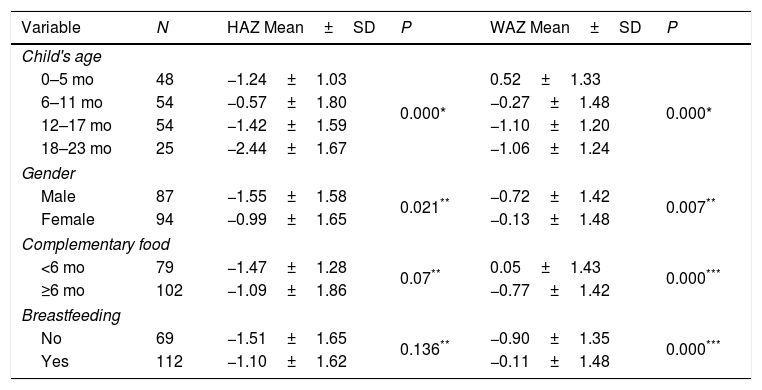
ResultsThis study obtained the status of thin children 13.3%, stunting 22.1%, and waste 16.6%. The frequency of non-breastfeeding mothers was 38.1% and those who received complementary food earlier were 43.5%. This study also showed an association between the stunting category with breastfeeding (p<0.05) and there was a relationship between underweight categories with breastfeeding at the boundary value (p value=0.08).
ConclusionThe nutritional status of stunting and underweight related to breastfeeding and the provision of Complementary food.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora