Estimar la concordancia en las mediciones obtenidas de tres queratómetros en pacientes fáquicos sin cirugía de cristalino previa y en un grupo de controles sanos, estimando su relación con las variables edad, sexo y patología de catarata.
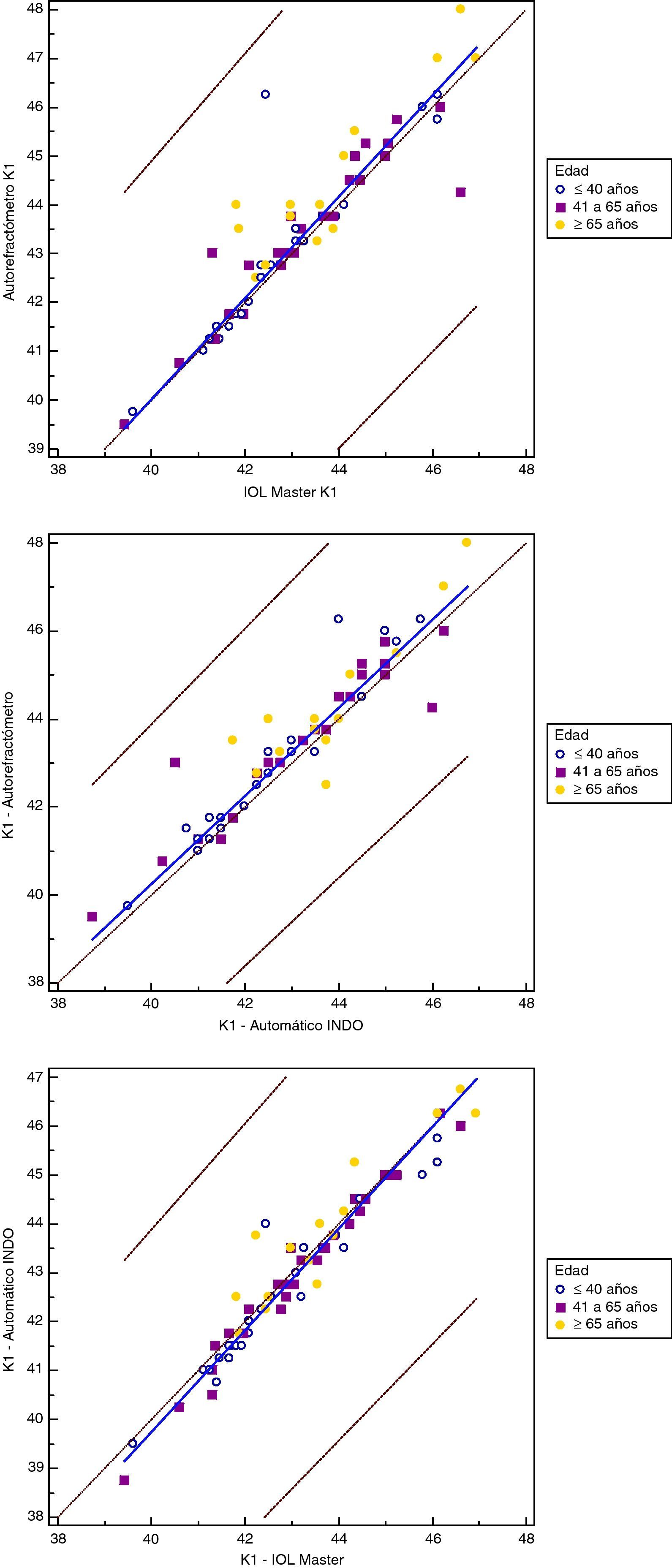
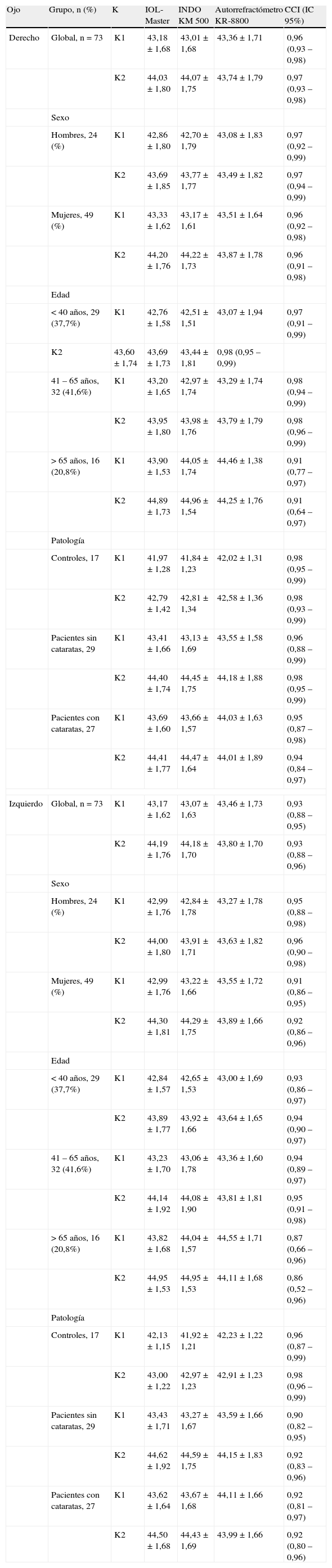
MétodoEstudio descriptivo de concordancia de resultados entre tres técnicas de queratometría corneal en una muestra de 56 pacientes reclutados de forma consecutiva en una consulta de Oftalmología. Se añadió un grupo control de 17 profesionales del Servicio de Oftalmología. Se utilizaron tres queratómetros: automático INDO KM-500, el incorporado al biómetro de láser de barrido IOL-Master y el incorporado al autorrefractómetro KR-8800. La concordancia se estimó según el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI) y la presencia de errores sistemáticos mediante gráficos de Bland-Altman y con la regresión no paramétrica de Passing y Bablok.
ResultadosSe seleccionaron 24 hombres y 49 mujeres con una edad media de 48,2 años (DE 18,5; rango de 13 a 86 años). Las concordancia fueron muy altas en todas las mediciones realizadas, con CCI que variaron desde un mínimo de 0,86 (IC95% 0,70 a 0,95) en mayores de 65 años hasta un máximo de 0,98 (0,96 a 0,99), en los más jóvenes (menores de 40 años). No se detectaron errores sistemáticos, constantes ni proporcionales entre los tres queratómetros.
ConclusionesLas queratometrías son coincidentes entre los tres métodos aunque en pacientes mayores de 65 años la concordancia es menor, lo cual puede comprometer los estudios biométricos en pacientes que vayan a ser intervenidos de cataratas.
To estimate the agreement between the results obtained from three keratometers in phakic patients without previous crystalline surgery and a healthy control group, taking into account its relationship with variables such as, age, gender and pathology of cataracts.
MethodDescriptive study of the agreement of results between three corneal keratometry techniques in a sample of 56 patients enrolled consecutively in a Department of Ophthalmology. A group of 29 professionals of the Department was included as controls. Three keratometers were used: An Auto INDO KM-500, one incorporated into the laser scanning biometer IOL-Master and another in the autorefractor KR-8800. Agreement was estimated by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and the presence of systematic errors was tested by Bland-Altman method and non-parametric regression (Passing and Bablok).
ResultsWe selected 24 men, 49 women with a mean age of 48.2 years (SD 18.5, range 13 to 86 years). The agreement was very high in all measurements, with ICC ranging from a low of 0.86 (95% CI: 0.70 - 0.95) over 65 years to a maximum of 0.98 (95% CI: 0.96 - 0.99) in the youngest (under 40 years). No systematic, constant and proportional errors were detected among the three keratometers.
ConclusionsThe keratometry was consistent between the three methods, although the correlation is lower in patients over 65 years, which may compromise the biometric studies in patients who undergo surgery for cataracts.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora