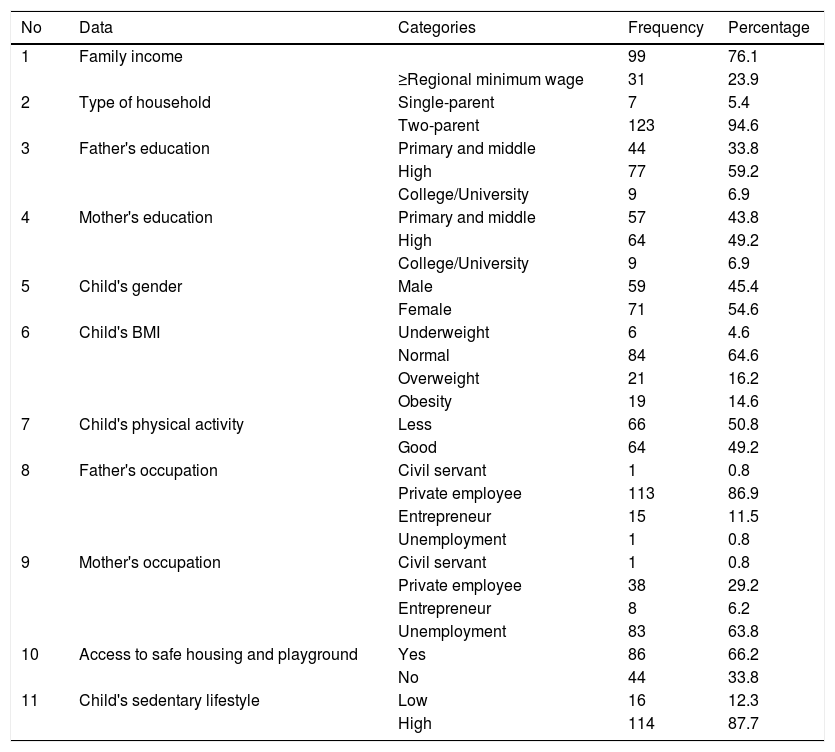
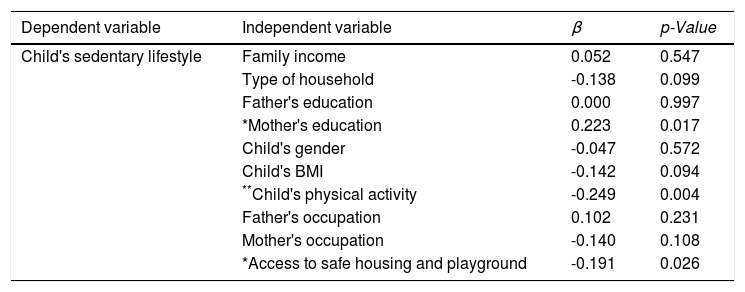
Sedentary lifestyle among school-aged children may cause many health problems in the future. This study was aimed to analyze the determinants of a sedentary lifestyle among school-age children. This was a descriptive-analytical study a with cross-sectional approach. The sample was 130 pairs of school aged-children and their mother/father, involved by using stratified random sampling. The independent variables were family income, household's type, parents’ education, child's gender, Body Mass Index (BMI), activity level, parent's occupation, and access to safe housing and playgrounds. The dependent variable was the level of children's sedentary lifestyle. The data was collected by using a questionnaire and analysed by using chi-square dan linear regression. The result showed that there was a significant correlation between mother's education, children's activity level, and access to safe housing and a playground with a sedentary lifestyle (p<0.05). School-aged children must be facilitated to be more physically active, and the mother can be involved in this case.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora