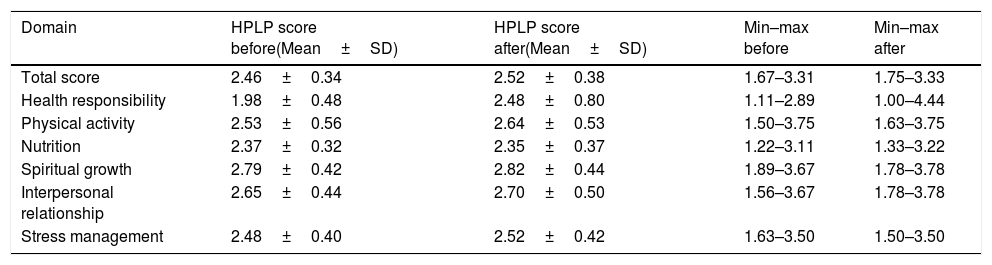
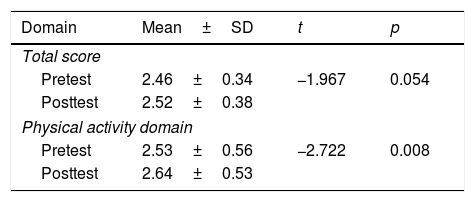
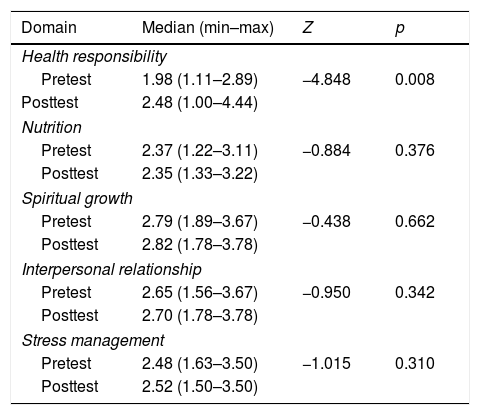
School-based health promotion is an effort to combine health education with other relevant factors that contribute to fostering students’ health behaviors as the main prerequisite to create a health-promoting school. An alternative to a conventional health education method is peer-led education. This study aimed to determine the effect of a school-based peer-led education program on health behaviors among high school students in a boarding school located in a rural area in Bali, Indonesia. This study used a one-group pretest-posttest design with a purposive sampling technique, and sampling was conducted among all students of the target boarding school grades 10–12. Respondents were requested to complete a self-administered questionnaire before and after the intervention. The questionnaire was adapted from an existing instrument (Health-Promoting Lifestyle Profile II/HPLP-II) consisting of 52 items. A 4-week intervention was delivered by peer educators who had completed a 10-day training program given by the research team in collaboration with practitioners from the local health office. The intervention was based on Pender's health promotion model. A paired t-test on the total HPLP-II scores yielded a non-significant result of t=−1.967 and p=.054 (p>.05). Physical activity (t=−2.722, p=.008) and health responsibility (z=−4.848, p=.008) domains showed significant results (p<.05). These findings show that there is no effect of the implementation of the school-based peer-led education program on the health behaviors among high school students. Nevertheless, the program has the potential to increase the students’ physical activity level and their responsibility toward their health. The effectiveness of peer-led education programs can be fostered by putting more attention on the target population's characteristics, intervention methods, resource mobilization including facilitating greater involvement of relevant stakeholders, and ensuring the availability of a more conducive environment that supports the adoption of health behaviors.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora