This study aimed to assess the response of supplementation of honey and honey propolis to women who experience mild stress.
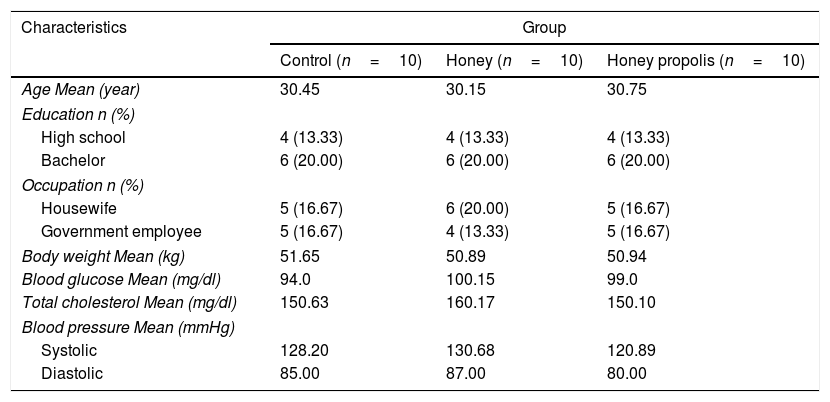
MethodsThe subjects of 30 people were divided into 3 groups; control, honey, and propolis honey every 10 people per group. All groups were given the same dose of 60g/day for 14 days. Measurements of glucocorticoid and cortisol hormones using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and the difference in cortisol hormone levels before and after the intervention were analyzed by a paired T-test.
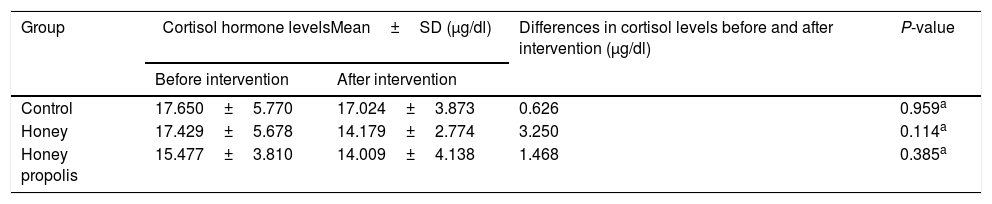
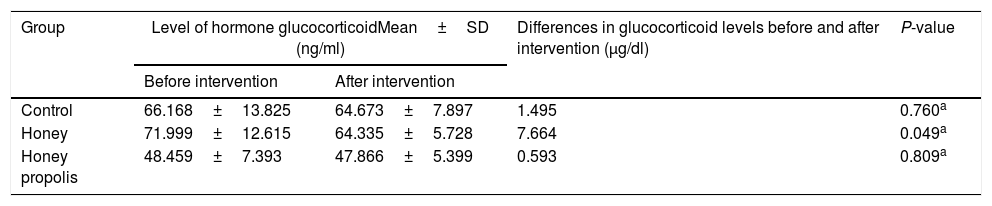
ResultsHoney and propolis honey group decrease cortisol levels but none of the groups have significant changes. This is reciprocal with the changes in the hormone cortisol, the decrease in glucocorticoid hormone levels in the group given honey is the highest following propolis honey and the control group. However, changes in glucocorticoid hormones in the honey group were statistically significant.
ConclusionOur result confirmed that in women who experience mild stress, honey and honey propolis have the potential to reduce stress-related hormones, that is glucocorticoids and cortisol, this reduction does not have the potential to suppress the immune system.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora