This study aimed to analyze the factors related to stunting in children aged 0–59 months.
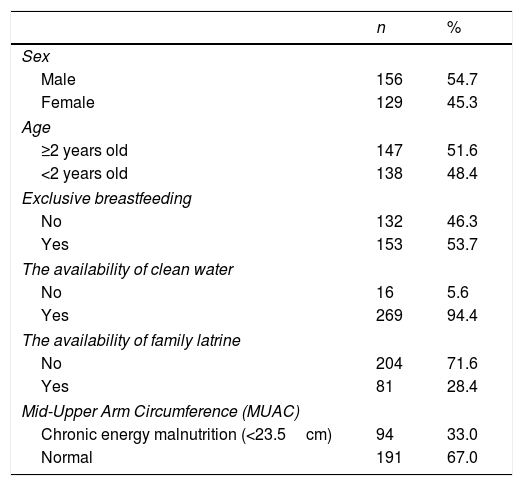
MethodsThis cross-sectional study involved a total sampling of 285 children <5 years. Data collected were age, sex, exclusive breastfeeding, Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC), water source and family latrine. Chi-square and multivariate logistic regression were performed.
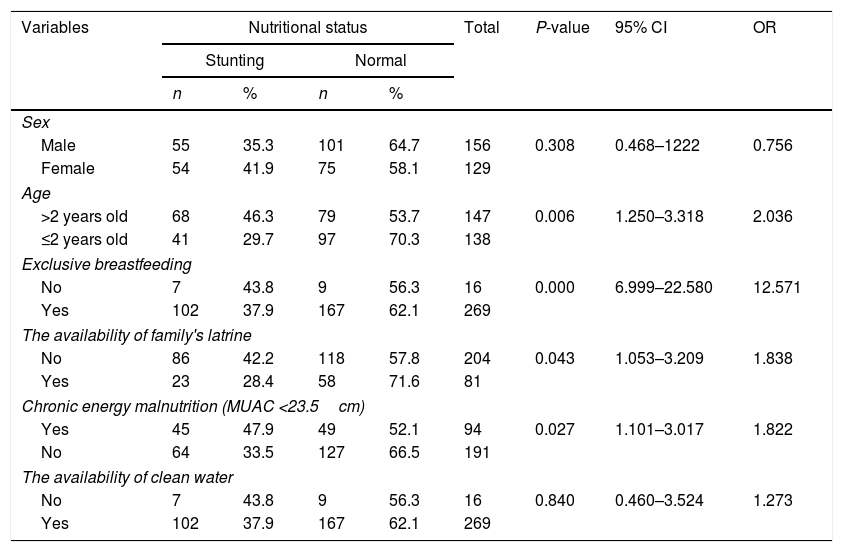
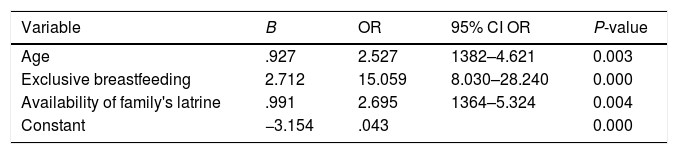
ResultsThe results showed that age, exclusive breastfeeding, MUAC, the availability of family latrine were significantly related with the incidence of stunting (P<0.05). Furthermore, the results of multivariate analysis showed that the risk factors that most affected stunting were non-exclusive breastfeeding (OR=15.059; 95% CI 8.030–28.240), poor family latrine (OR=2.695; 95% CI 1.364–5.324) and age (OR=2.527; 95% CI 1.382–4.62).
ConclusionsThe strongest risk factors for stunting are non-exclusive breastfeeding, poor family's latrines, and the sex of the children. It is recommended that to strengthen multisectoral interventions to reduce stunting.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora