This study was conducted to analyze the effect of patient perceptions regarding TB on medication adherence.
MethodsThis study used a quantitative approach with a cross-sectional survey method. The sample was determined by census technique in a total of 128 patients which from Makassar City that covered up Panakkukang, Makassar, Rapoocini, and Tallo sub-Districts from February to May 2018. The data were analyzed in quantitative statistics (descriptive and statistical statistics).
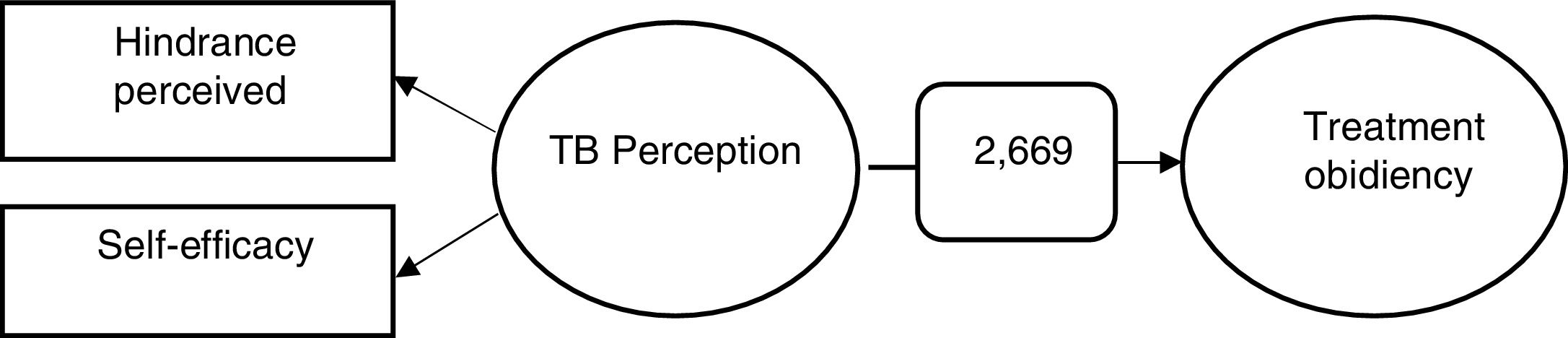
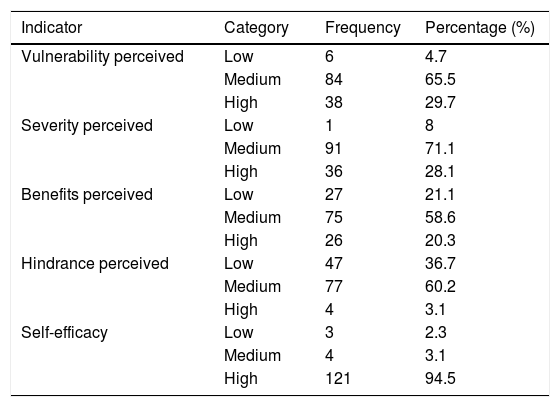
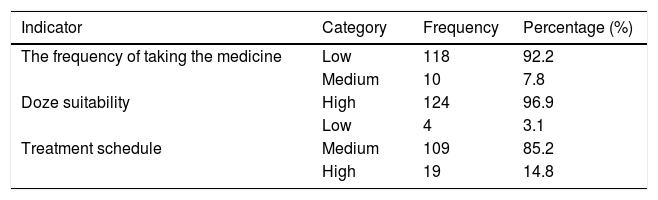
ResultThe outcome revealed that the patient's medication adherence was classified as high, which meant that TB patients were obedient during the treatment process. Patients’ perceptions about TB reflected by hindrance indicator and self-efficacy perceived by the patients impacted significantly to TB patients’ treatment, and they were TB patients’ perceptions.
ConclusionTreatment compliance for TB patients in Aisyiyah's TB care community program in Makassar City is relatively high. This means that TB sufferers adhere to the treatment process. Patients’ perceptions about TB are reflected indicators of perceived resistance and self-efficacy significantly affect treatment compliance.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora