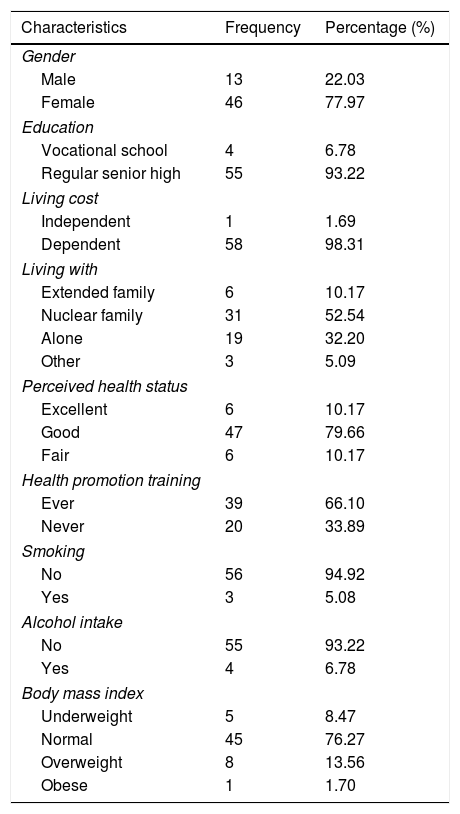
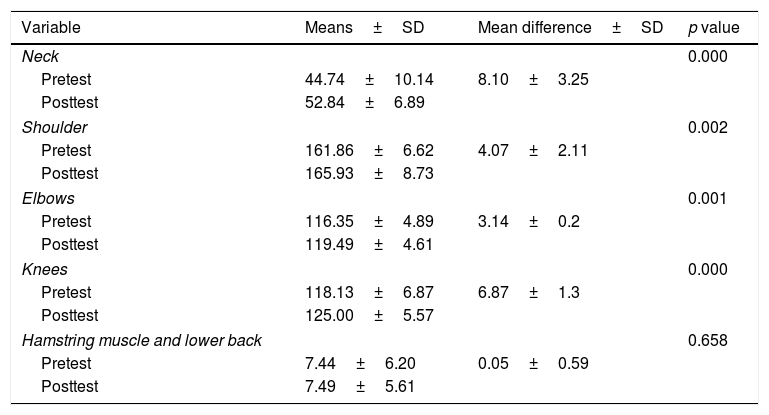
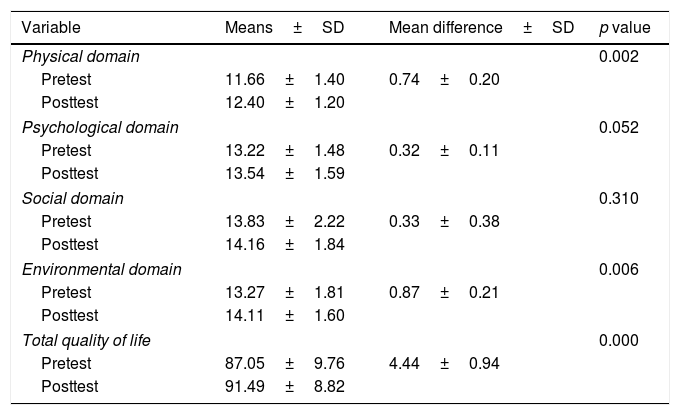
This study aims to evaluate the effect of exercise on the go program on physical fitness and quality of life among nursing students in Bali. The study employed a quasi-experimental design using purposive sampling technique on 59 nursing students in a government university in Bali, Indonesia. Exercise on the go program was a four-week-in-class static stretching exercise given three times a week consisted of eight main movements combined with individual booklet dissemination and an online chat group-based reminder program. Data were collected before and after the exercise on the go program using goniometer and Sit and Reach Test (SRT) box for measuring flexibility (physical fitness) and The World Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF (WHOQOL-BREF) questionnaire to identify the subjects’ quality of life (QoL). There were significant differences at the flexibility level of the neck (8.10°), shoulder (4.07°), elbows (3.14°), and knees (6.87°) before and after the intervention (p<0.05). This study also found that there were significant differences in the mean score in the physical domain (0.74), environment domain (0.87), and the QoL total score (4.44) (p<0.05) before and after the intervention. Exercise on the go program was found to be effective in improving nursing students’ physical fitness and quality of life. This program is suitable for the needs and characteristics of the target participants that focus on the individual's behavioral changes as well as modifies the environmental and social aspects of nursing students.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora