4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
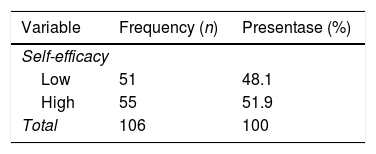
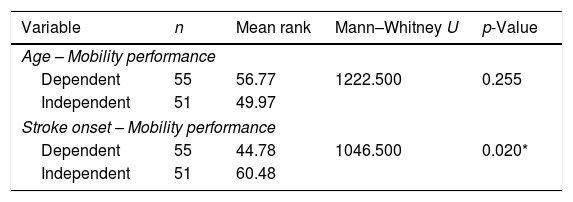
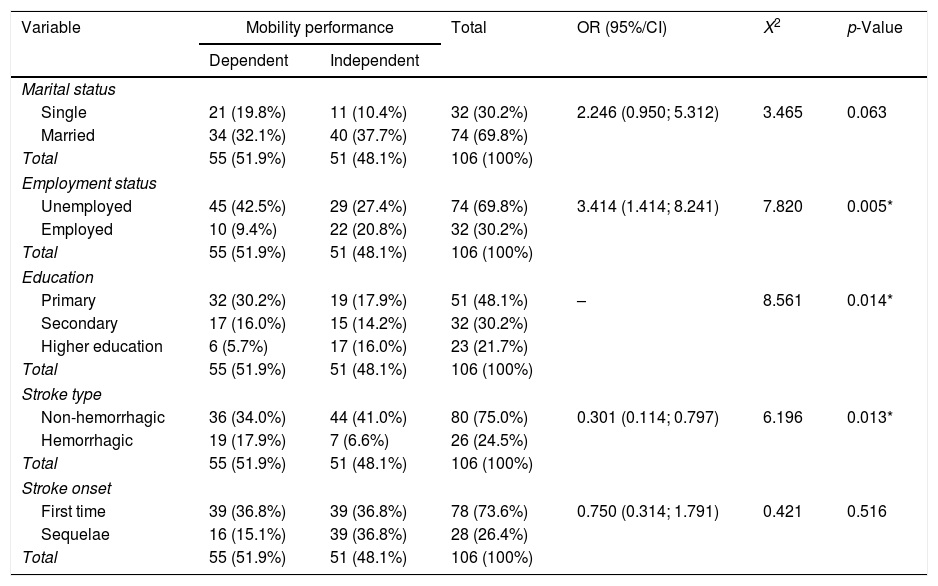
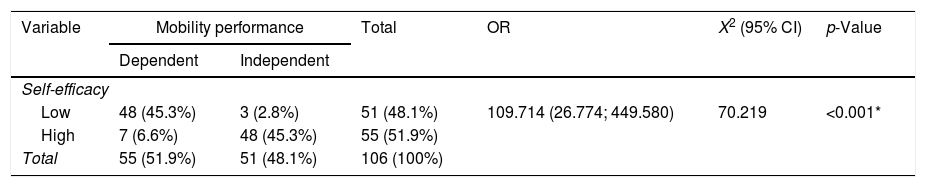
Más datosStroke may cause extensive brain damage that can hamper a patient's mobility performance to carry out their daily activities. This study aimed to examine the links between mobility performance and the self-efficacy and characteristics of stroke patients. A cross-sectional survey was undertaken at a hospital in Bandung, Indonesia. A total of 106 respondents, recruited by using consecutive sampling, filled out the Stroke Self-Efficacy and Barthel Index, together with socio-demographic questionnaires. Stroke onset, stroke type, employment status, and education level were found to have significant relationships with mobility performance (p<0.05). A significant relationship was also identified between the level of self-efficacy and mobility performance (p<0.001). Self-efficacy is linked to the mobility performance of stroke patients. Nurses should pay more attention to the self-efficacy of these patients during their rehabilitation period.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora