Conocer el efecto de la punción seca (PS) en puntos gatillo miofasciales (PGM) del músculo gastrocnemio sobre la tensión neural adversa (TNA) y el dolor percibido.
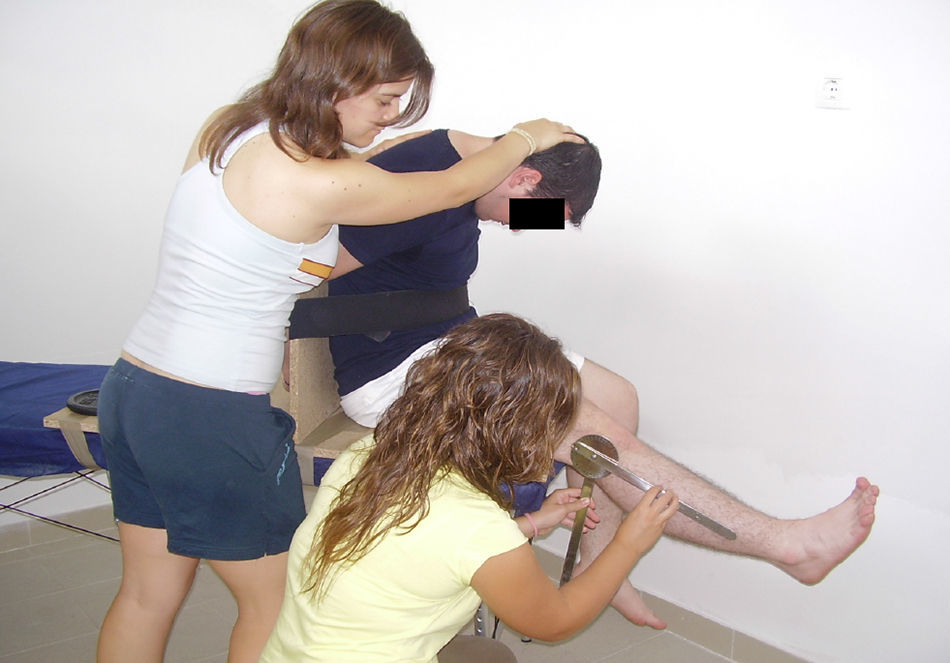
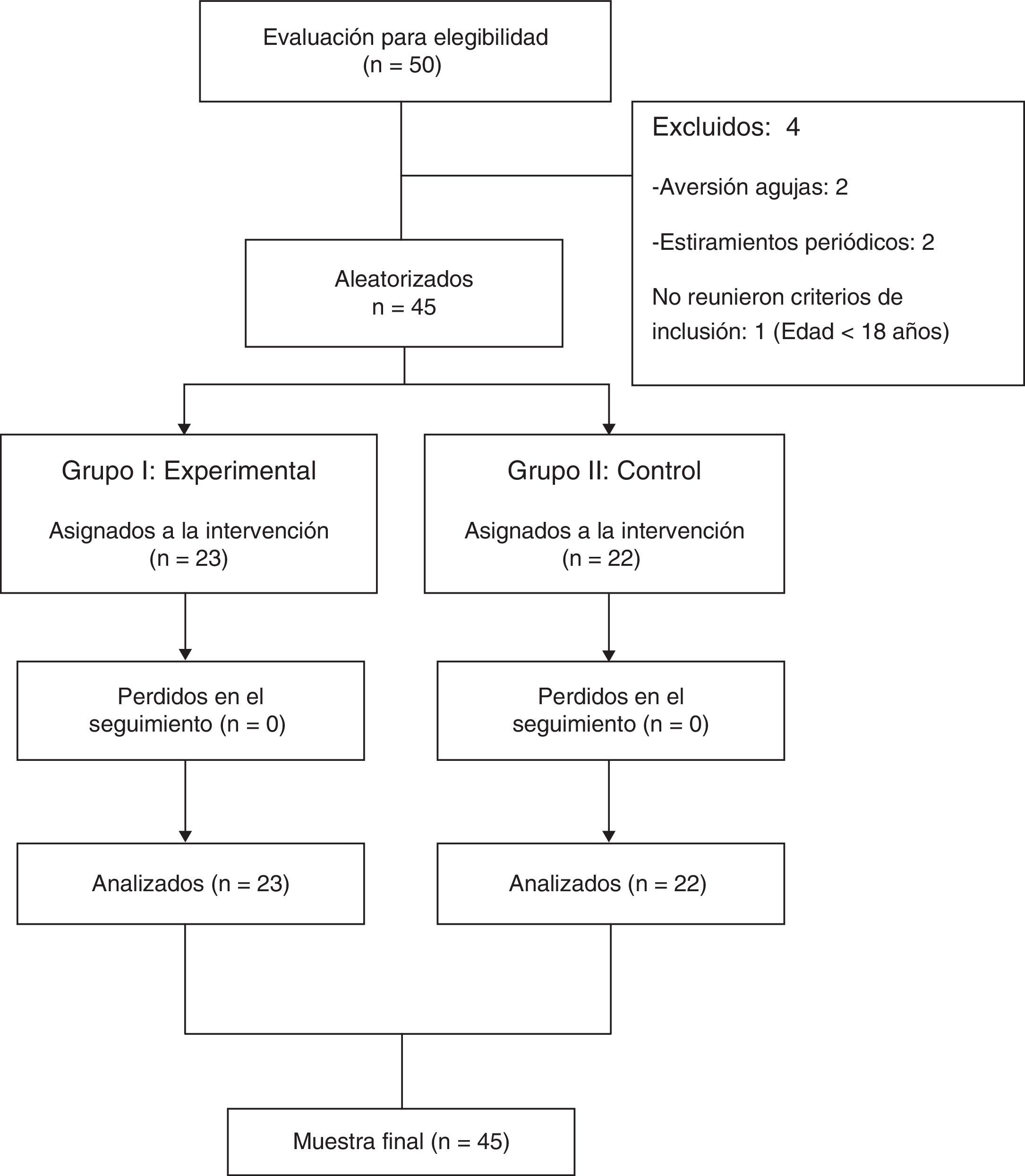
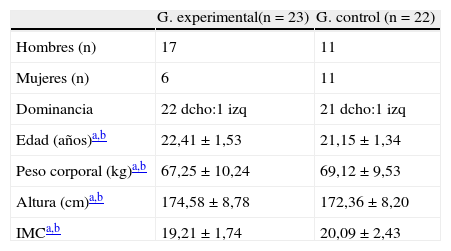
Material y métodosCincuenta adultos se prestaron al estudio. Tras aplicar criterios de inclusión y exclusión, obtuvimos una muestra final de 45. Fueron asignados aleatoriamente al grupo 1 o experimental (n=23, edad media: 22,41±1,53) y al grupo 2 o control (n=22, edad media: 21,15±1,34). Una vez localizado y confirmado el PGM por el evaluador ciego, se aplicó la técnica de PS profunda. Para el grupo 2 se utilizó la misma aguja, diferenciándose en la capacidad de retracción de la misma, sin llegar a perforar la piel. La TNA fue valorada mediante el test neurodinámico de Slump y el dolor percibido mediante escala visual analógica (EVA) justo antes (pretest) y en 2 momentos posteriores (inmediato y a 48 h). Los datos fueron tratados con el paquete estadístico SPSS versión 19.0.
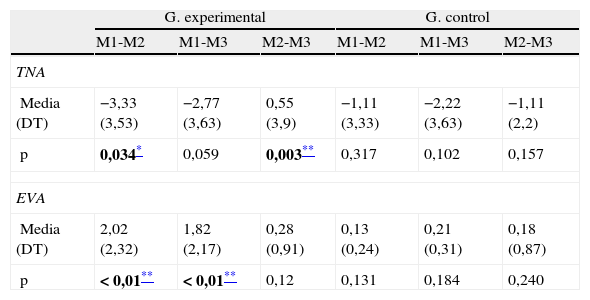
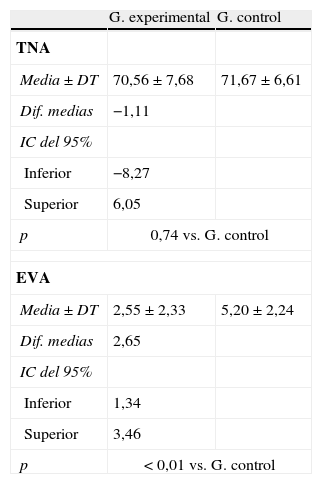
ResultadosSe observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas (p<0,05) en el grupo 1 entre pretest y postest inmediato y entre postest inmediato y tardío (48 h) para la variable TNA. El dolor percibido mostró diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre el pretest y los 2 momentos de valoración posterior (p<0,001), mientras el grupo 2 no evidenció mejoras. Se observaron diferencias entre grupos en el postest inmediato del dolor percibido.
ConclusionesLa PS sobre PGM latentes del músculo gastrocnemio disminuye el dolor percibido al menos 48 h, no obteniendo cambios significativos sobre la TNA medida mediante test de Slump.
To determine the effect of dry needling (DN) in the myofascial trigger points (MTrP) of the gastrocnemius muscle on adverse neural tension (ANT) and perceived pain.
Material and methods50 adults were selected for the study. After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, we obtained a final sample of 45. They were randomly assigned to group 1 or experimental (n=23, mean age: 22.41±1.53) and group 2 or control (n=22, mean age: 21.15±1.34). Once allocated and confirmed by the blind assessor, deep dry needling technique on the MTrP was applied. For group 2 the same needle was used, differing in shrinkage capacity therefore without perforating the skin. The ANT was assessed using the Slump neurodynamic test and perceived pain by visual analogue scale (VAS) just before (pre-test) and in two subsequent times (immediately and 48hours). The data were processed with SPSS version 19.0.
ResultsWe observed statistically significant differences (P<.05) in group 1 between pretest and immediate posttest and between immediate and delayed post-test (48hours) for the variable ANT. The perceived pain showed statistically significant differences between the pretest and the two later time points (P<.001), while group 2 showed no improvement. Differences between groups were observed in the immediate posttest perceived pain.
ConclusionsThe dry needling in the MTrP latent on gastrocnemius muscle decreases perceived pain at least 48hours, not getting on the ANT significant changes measured by Slump test.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora