El objetivo del presente estudio es describir los cambios en la puntuación del cuestionario WOMAC, Berg Balance y prueba de marcha de 6 min, después de observar un entrenamiento fisioterapéutico que incluye realidad virtual en este tipo de pacientes.
Material y métodoEl presente estudio prospectivo, de diseño descriptivo de serie de casos, fue realizado en el Hospital Clínico San Borja Arriarán (Chile). Mediante un muestreo por conveniencia, se seleccionó a 12 pacientes con diagnóstico de artroplastia total de cadera: se observaron 10 sesiones de fisioterapia, que incluían la realidad virtual como parte del tratamiento. Las medidas de resultado fueron: funcionalidad, con el cuestionario WOMAC; riesgo de caída, a través de la escala Berg Balance; diferencia de la carga de peso en las extremidades inferiores, a través del juego Wii Fit™ Plus, y distancia recorrida a través de la prueba de marcha de 6 min. No se registraron pérdidas de participantes.
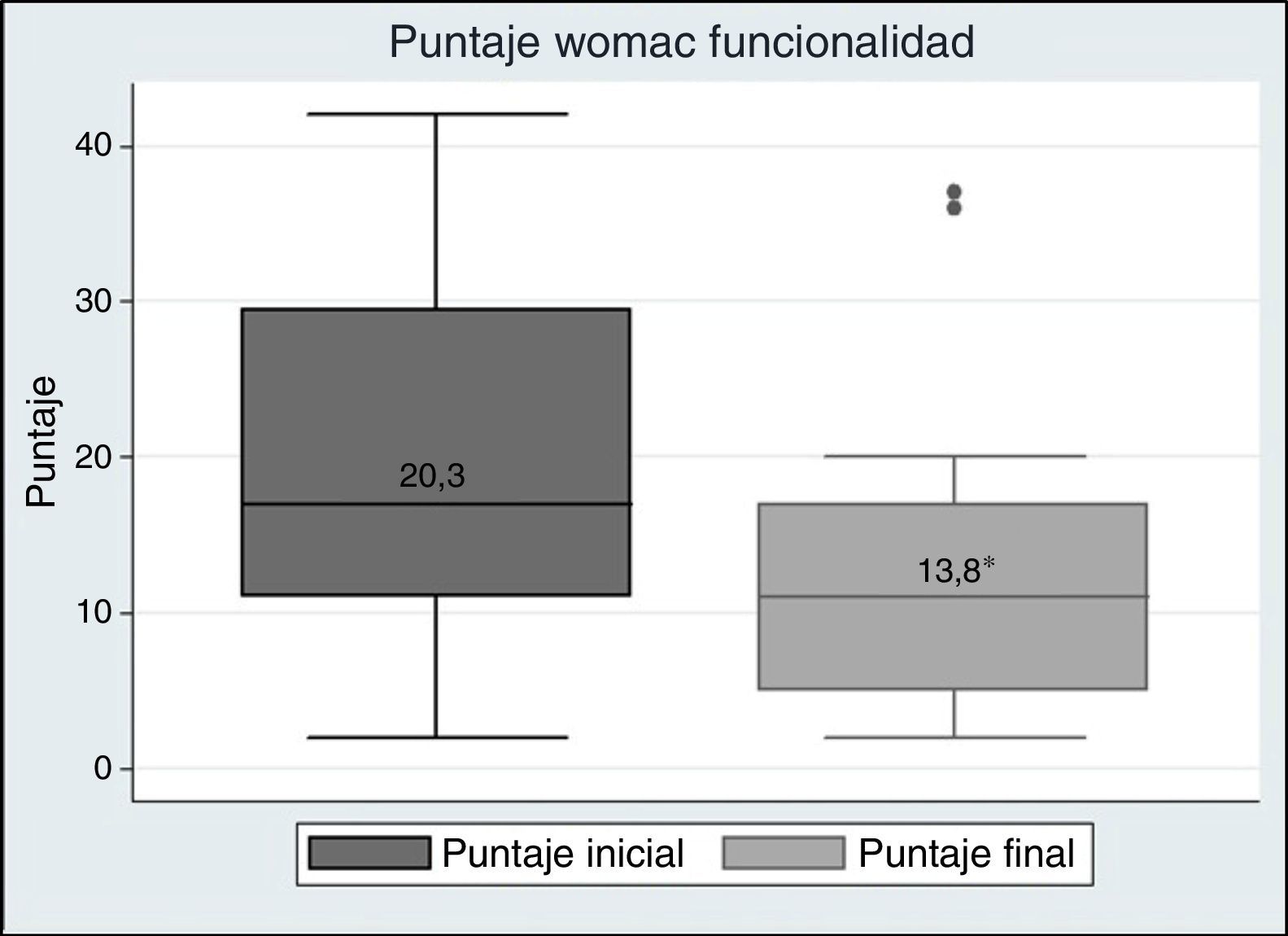
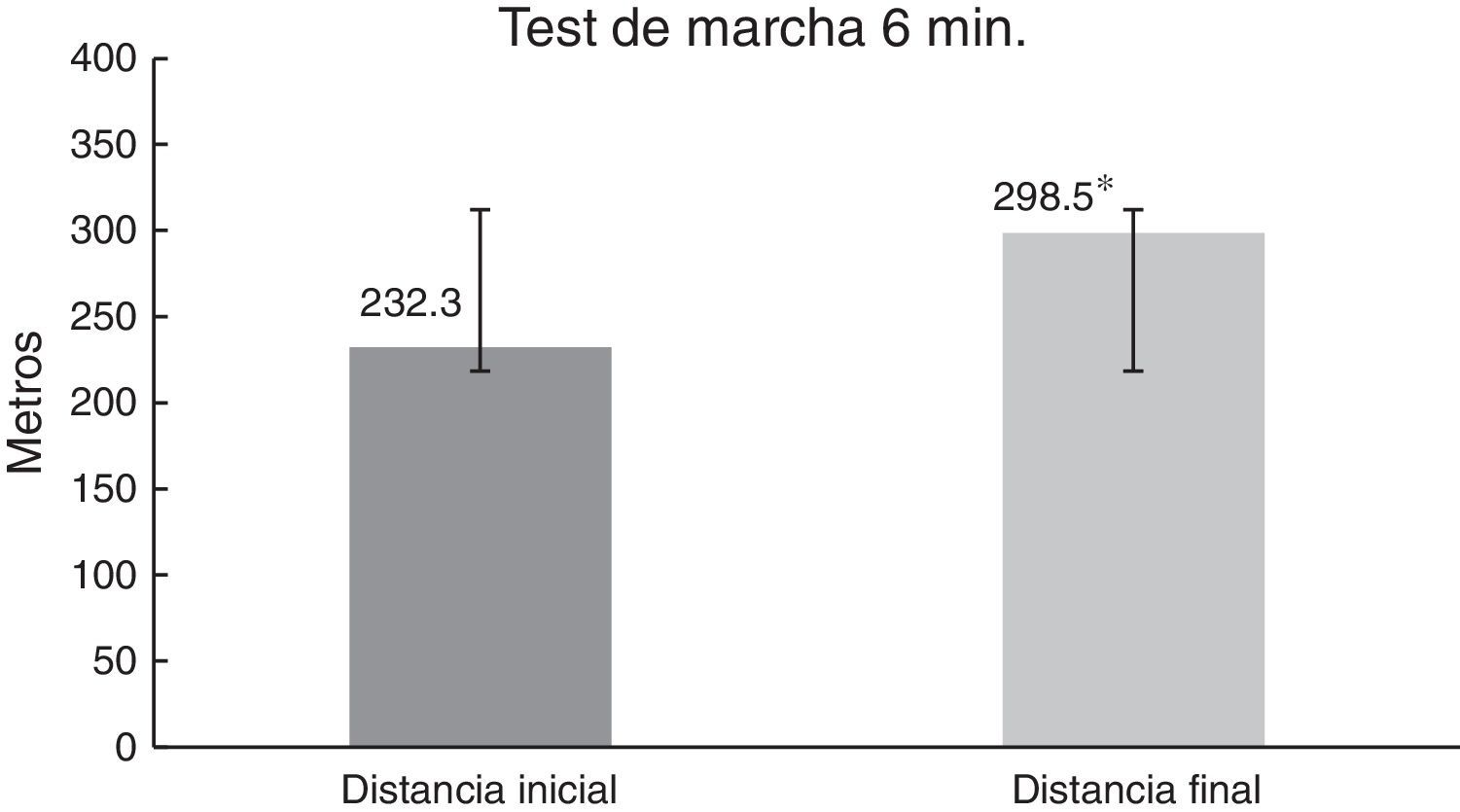
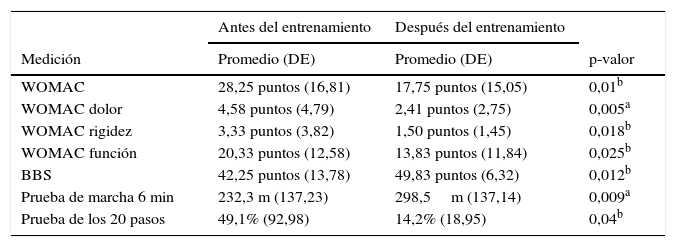
ResultadosPostratamiento se observa una reducción en la puntuación del cuestionario WOMAC y un aumento en los valores de la escala de Berg Balance y prueba de marcha de 6 minutos; estos cambios en la puntuación de las variables medidas presentaron una importancia estadística con una p<0,05.
ConclusionesSe observan cambios funcionales al evaluar un entrenamiento fisioterapéutico que utiliza realidad virtual en mayores de 60 años con artroplastia total de cadera.
The objective of this study is to describe the changes in the WOMAC questionnaire score, the Berg Balance Scale, and the six-minute walk test, after taking part in a physiotherapy training that includes virtual reality in this patient group.
Material and methodThe present prospective, descriptive study was conducted on a series of cases in the Hospital Clínico San Borja Arriarán (Chile). Using a convenience sampling, 12 patients were selected with a diagnosis of total hip arthroplasty. There were 10 physiotherapy sessions, which included the virtual reality as part of the treatment. The outcome measures were: functionality, using the WOMAC questionnaire; risk of falling, using the Berg Balance Scale; difference of weight load in ERIA, using Wii Fit™ Plus game, and distance travelled in the six-minute walk test. There were no losses of participants.
ResultsPost-treatment there was a reduction in the WOMAC questionnaire score, and an increase in the values of the Berg Balance Scale, and six-minute walk test. These changes in the scores of the variables measured were statistically significant with a P<.05.
ConclusionsFunctional changes were observed in the assessment of a physiotherapy training that uses virtual reality in patients older than 60 years with total hip arthroplasty.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora