Artificial intelligence (AI) allows the optimization of diagnostic processes for hepatitis C virus (HCV) patients. Our objective was to evaluate the clinical, economic, and management benefits of an AI-based clinical decision support system (Intelligen-C strategy).
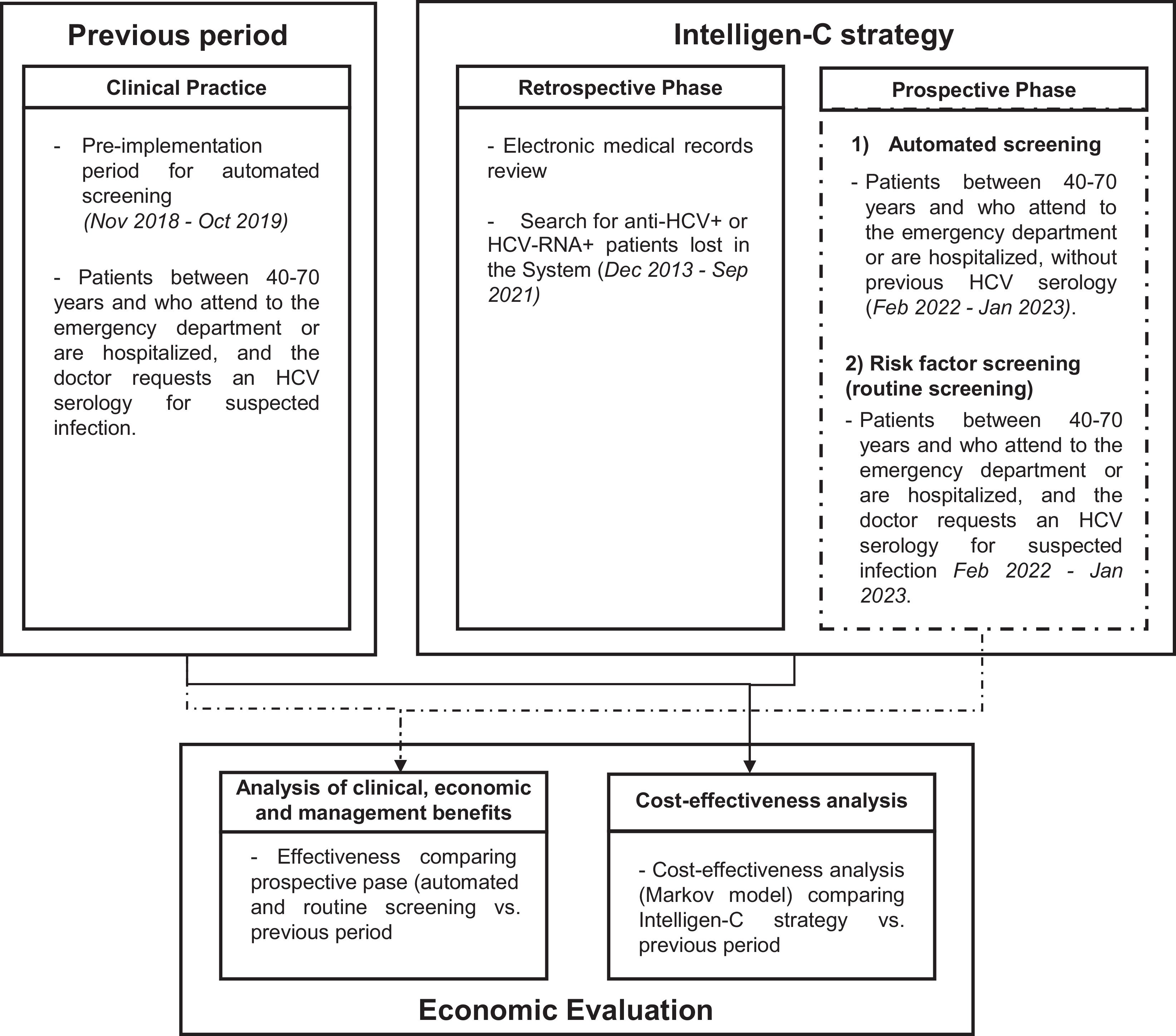
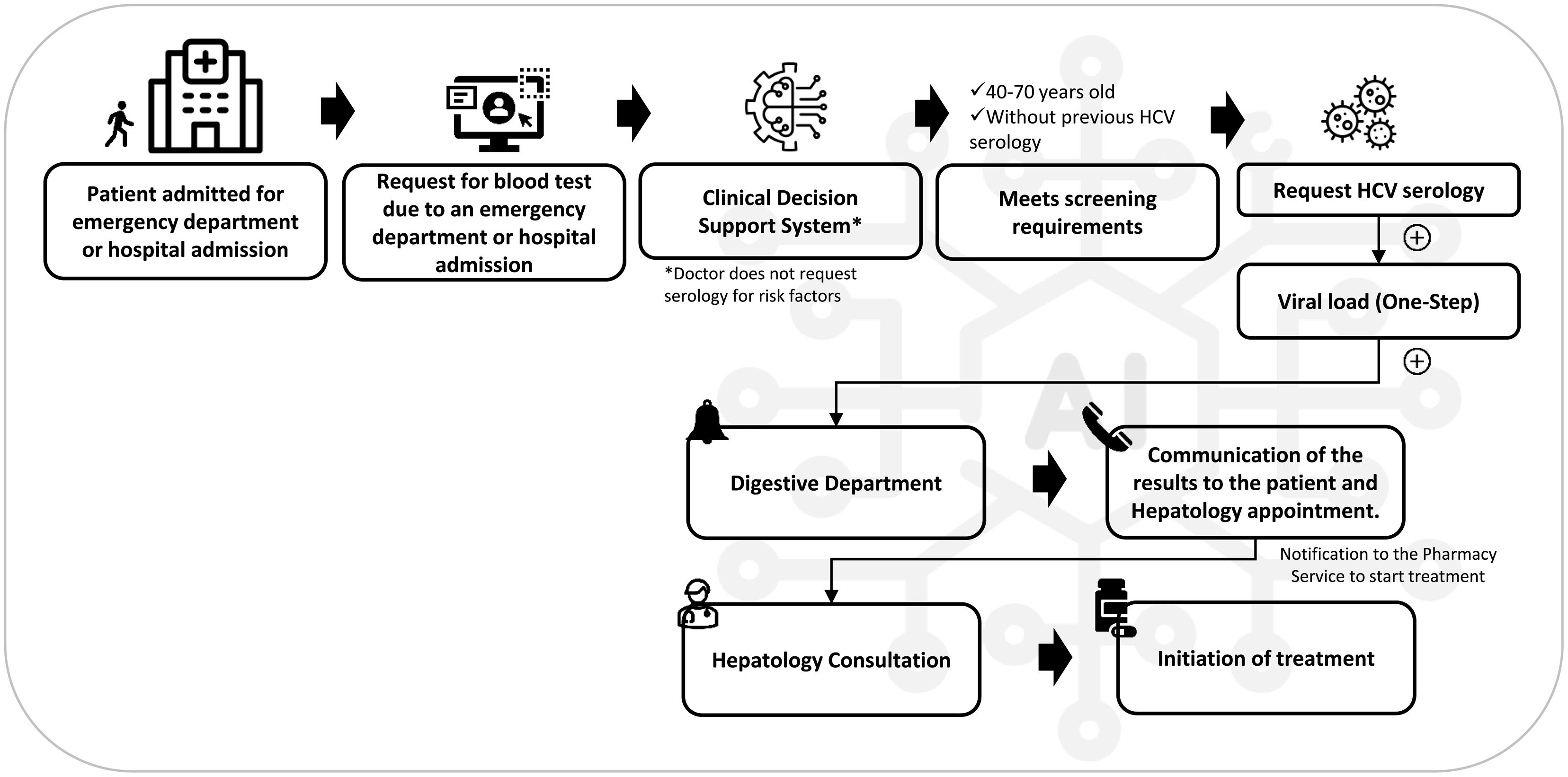
MethodsThe Intelligen-C strategy consisted of (1) a retrospective phase (Dec 2013–Sep 2021), in which medical records were reviewed to search for anti-HCV-positive and/or HCV-RNA+ patients lost in the system, and (2) a prospective phase (Feb 2022–Jan 2023), in which automated screening (40–70 years) and routine testing for risk factors were performed in patients who were admitted to the emergency department or were hospitalized. With the use of automated screening, the system identified patients without an HCV diagnosis among those requiring blood tests and requested HCV serology; if the results were positive, reflex testing for HCV-RNA was performed. If a patient was HCV-RNA+, an alert was generated and sent to the hepatology department. In addition, the prospective phase was compared with the previous period to evaluate its effectiveness and efficiency.
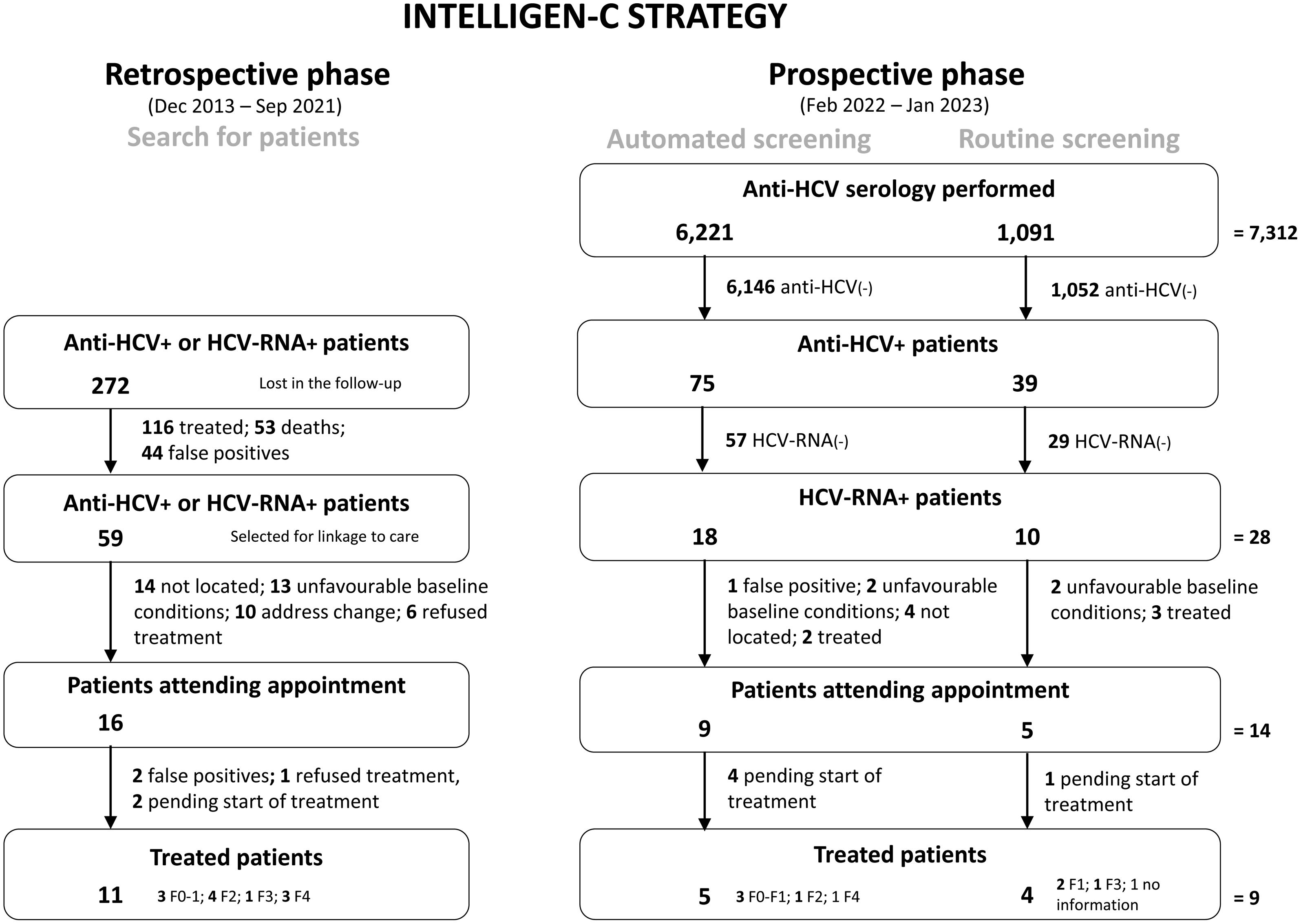
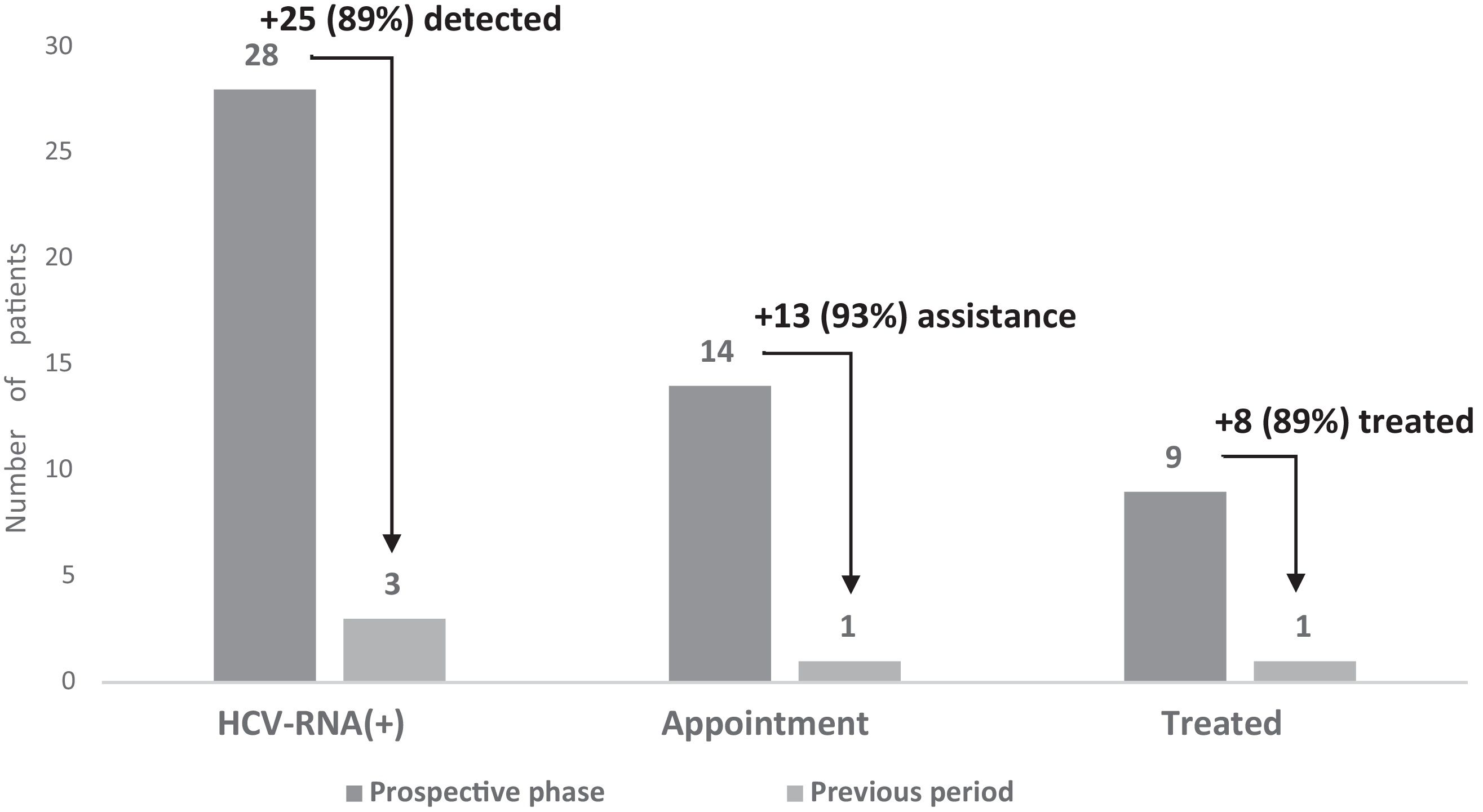
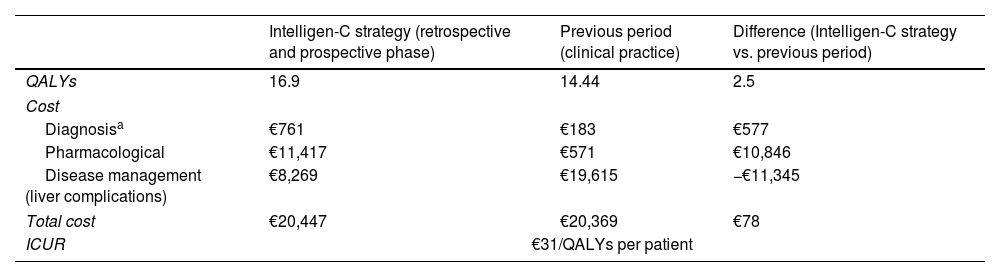
ResultsIn the retrospective phase, the Intelligen-C strategy allowed the identification of 272 anti-HCV- or HCV-RNA+ patients who were lost to follow-up, of whom 11 were treated; in the prospective phase, after 7312 serologies were performed, 28 HCV-RNA+ patients were identified, 14 attended the appointment, and 9 were treated. In the prospective phase vs. the previous period, increased serology (7312 vs. 909), HCV-RNA+ detection (28 vs. 3), and treated patients (9 vs. 1) generated savings to the health system related to medical visits. In addition, Intelligen-C was cost-effective.
ConclusionsThe implementation of the Intelligen-C strategy allowed the identification of patients with undiagnosed infection, facilitated their diagnosis, reduced healthcare processes and associated hospital costs, and proved to be efficient.
La Inteligencia Artificial (IA) permite optimizar los procesos con pacientes con virus de la hepatitis C (VHC). Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar los beneficios clínicos, económicos y de gestión de un sistema de ayuda a la decisión clínica basado en IA (estrategia Intelligen-C) para el cribado automatizado del VHC.
MétodosLa estrategia Intelligen-C consistió en: 1) fase retrospectiva (Dic-2013 a Sep-2021): revisión previa a automatización de historias clínicas para buscar pacientes anti-VHC+/ARN-VHC+ perdidos en el sistema, y 2) fase prospectiva (Feb-2022 a Ene-2023): cribado automatizado (40-70 años) más las pruebas realizadas de rutina por factores de riesgo. En el cribado automatizado el sistema identificó pacientes sin diagnóstico VHC que acudían a urgencias o eran hospitalizados y precisaban analítica, solicitaba una serología VHC y, ante resultados positivos, solicitaba ARN-VHC. Si resultaba ARN-VHC+, se generaba una alerta a Hepatología. Además, se comparó la fase prospectiva de Intelligen-C con el periodo previo para evaluar la eficacia y la eficiencia.
ResultadosLa estrategia Intelligen-C en la fase retrospectiva permitió identificar 272 pacientes perdidos anti-VHC+/ARN-VHC+ (11 fueron tratados). En la fase prospectiva, tras realizar 7.312 serologías se identificaron 28 pacientes ARN-VHC+, 14 acudieron a consulta, 9 tratados. En la fase prospectiva vs. periodo previo aumentaron las serologías (7312 vs. 909) y la detección ARN-VHC+ (28 vs. 3), la vinculación y el acceso a tratamiento (14 vs. 1), generando ahorros al sistema sanitario relacionados con las visitas médicas. Además, la estrategia Intelligen-C resultó ser coste-efectiva.
ConclusionesLa implementación de la estrategia Intelligen-C permitió identificar a pacientes con infección oculta y nuevo diagnóstico, redujo procesos asistenciales disminuyendo costes hospitalarios asociados y demostró ser eficiente.