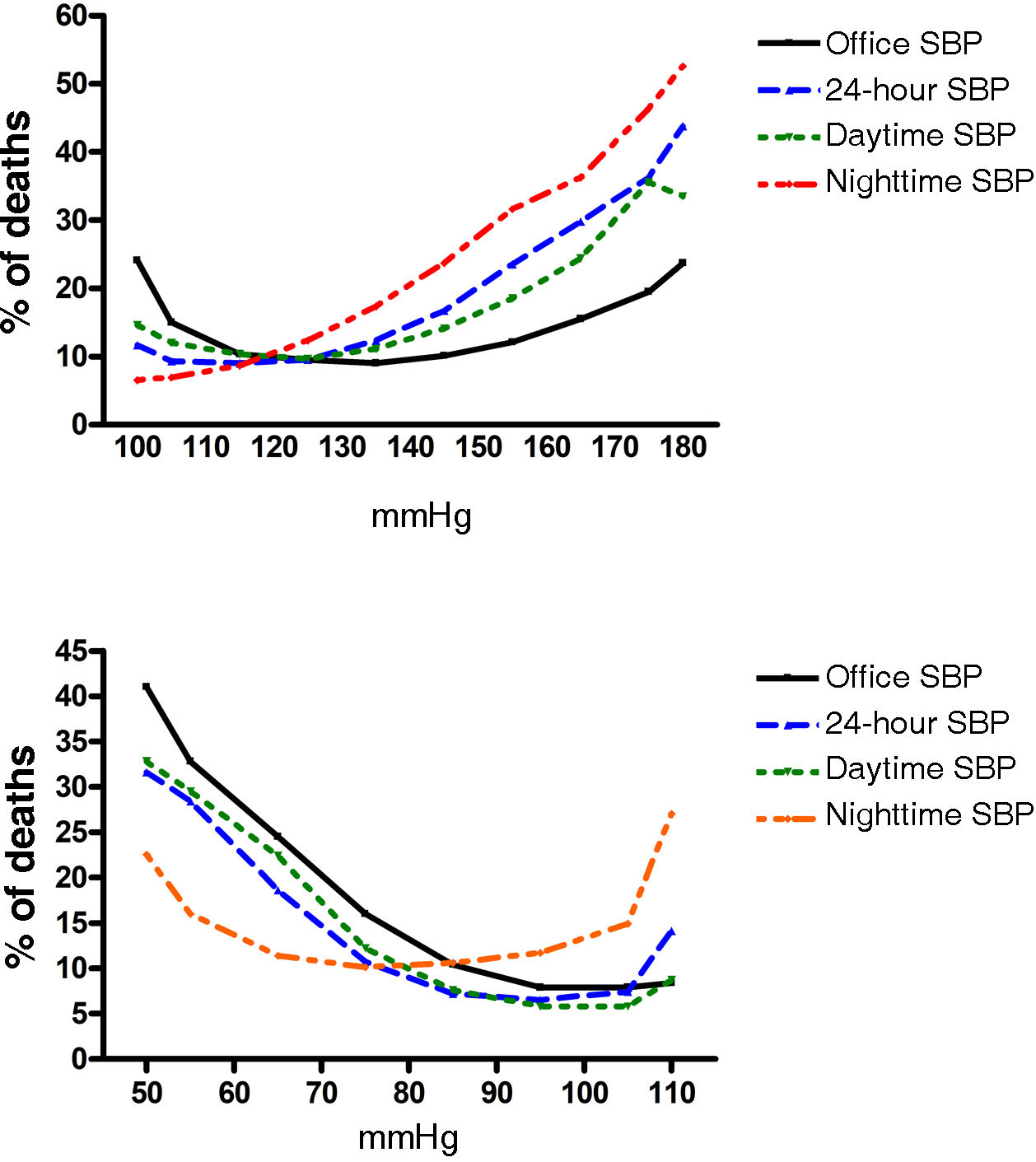
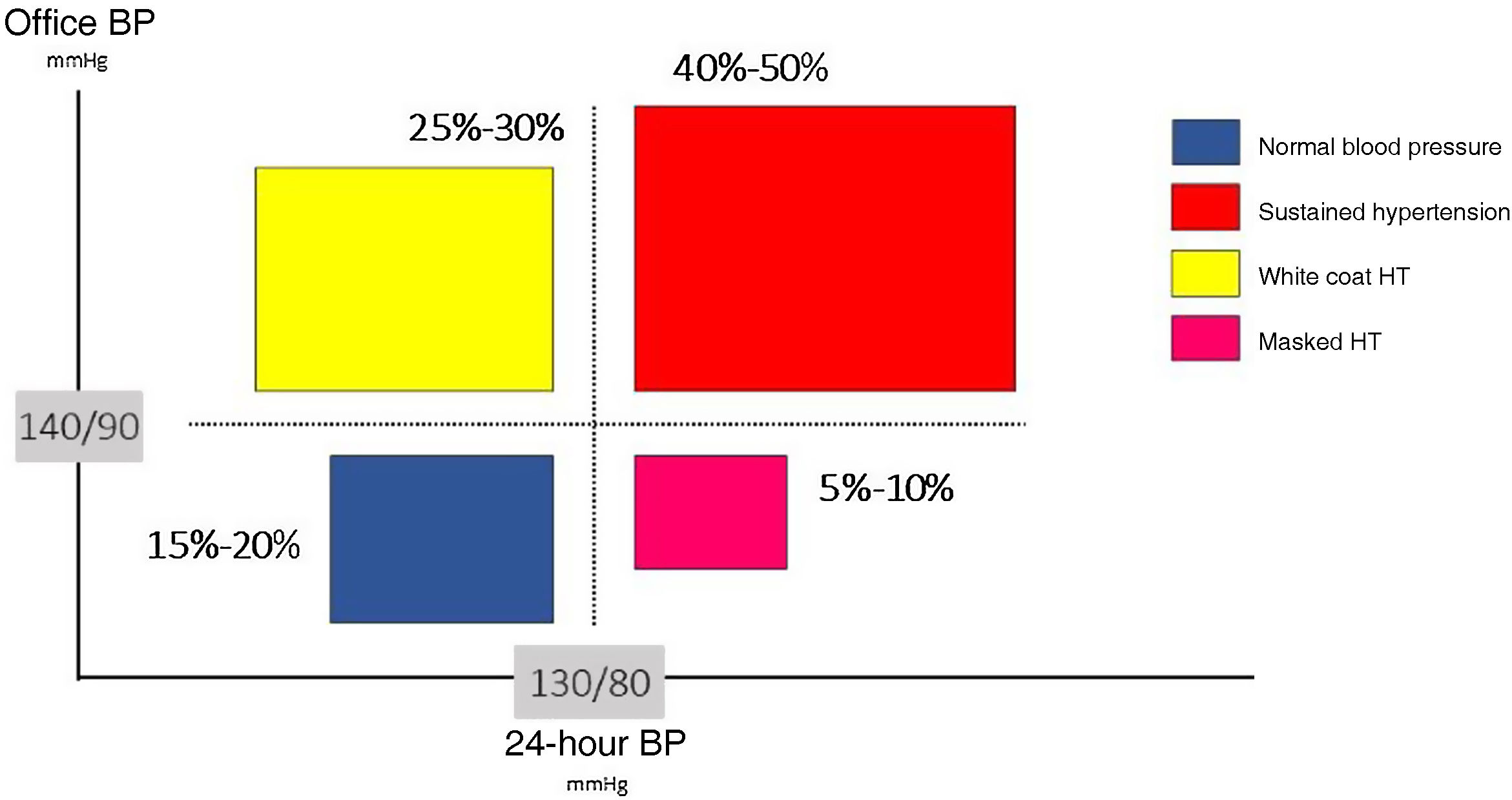
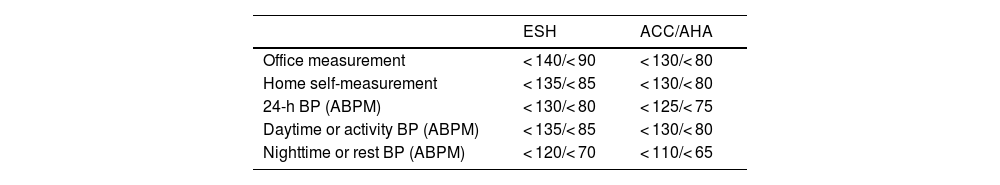
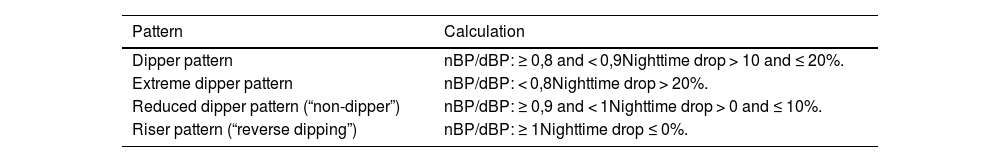
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) is considered the best method for obtaining a reliable estimation of the true blood pressure. Average values obtained during the whole 24-h period, or during daytime and nighttime periods are better correlated with the risk of mortality and cardiovascular disease compared to clinic or office blood pressure. Indeed, nighttime blood pressure, a measure only obtained through ABPM, is the most powerful risk predictor. ABPM is complementary to clinic blood pressure measurement and allows the definition of blood pressure phenotypes, such as “white-coat or masked hypertension, when clinic and ABPM measurements show discrepancy in normal values. Additional potentially relevant features include blood pressure variability, such as nocturnal blood pressure decline, morning surge or short-term variability, as determined by standard deviation or the coefficient of variation.
La Monitorización Ambulatoria de la Presión Arterial (MAPA) permite obtener una medida más exacta y fiable de la presión arterial. Los valores obtenidos en los periodos de 24 horas, diurno y nocturno se correlacionan mejor con la morbimortalidad cardiovascular, comparados con la presión clínica. La presión nocturna es el estimador con una relación más estrecha con el riesgo. La MAPA complementa a la medida clínica y, además de los valores medios de presión, permite definir los fenotipos de hipertensión de “bata blanca” y de hipertensión enmascarada, cuando hay discordancia en la normalidad de valores de presión clínica y obtenida por MAPA. Otros elementos de interés se refieren a la variabilidad de las cifras de presión durante el periodo de monitorización, incluyendo el descenso nocturno de presión, el incremento matutino o la inestabilidad de los valores, medida mediante la desviación estándar o el coeficiente de variación.