Identificar bases de datos de interacciones medicamentosas de antirretrovirales y valorar su calidad estructural.
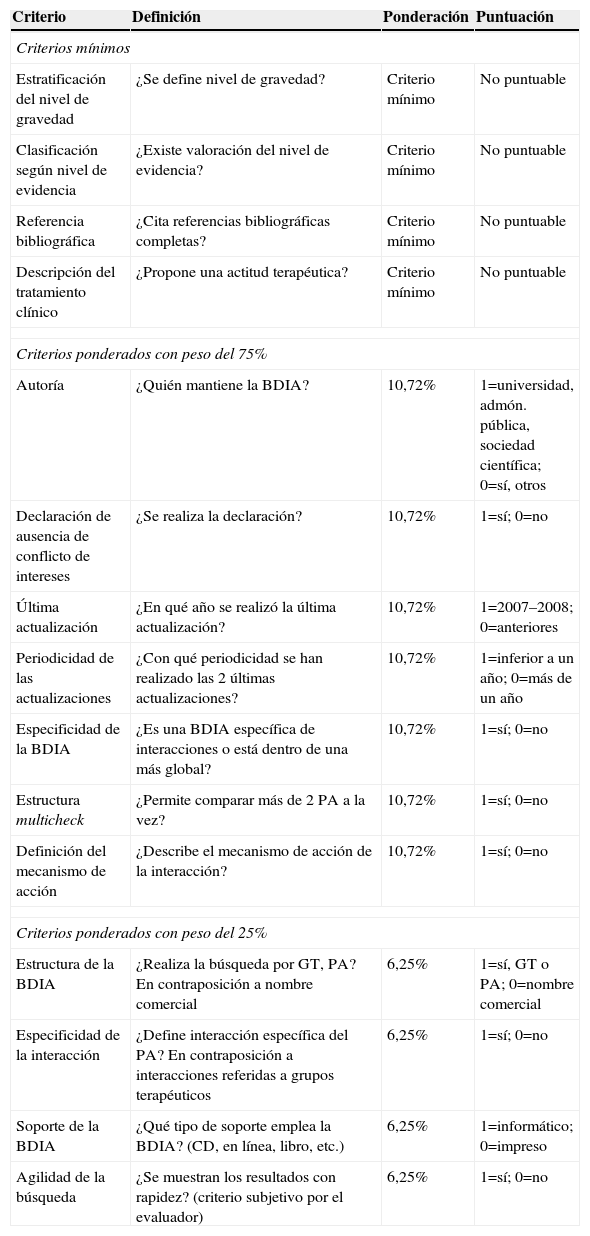
Material y métodoSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica en Medline y literatura médica gris. Las bases de datos identificadas se sometieron a criterios de exclusión y de calidad estructural (4 criterios de calidad mínima: estratificación según nivel de gravedad, clasificación según nivel de evidencia, referencia bibliográfica de datos y descripción del tratamiento clínico) y 11 criterios que aportaban peso ponderal. Se analizó el grado de cumplimiento en cada base de datos de los criterios definidos y el grado de cumplimiento de cada criterio en todas las bases de datos.
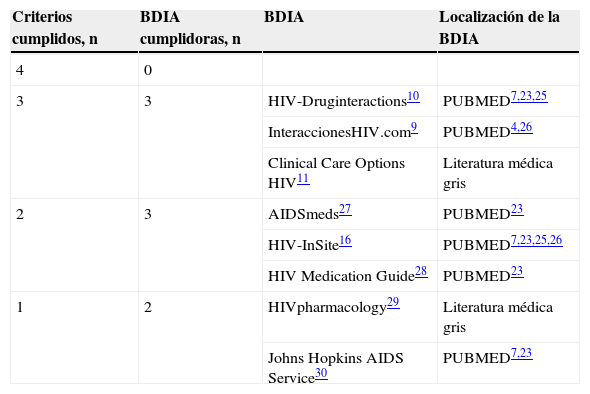
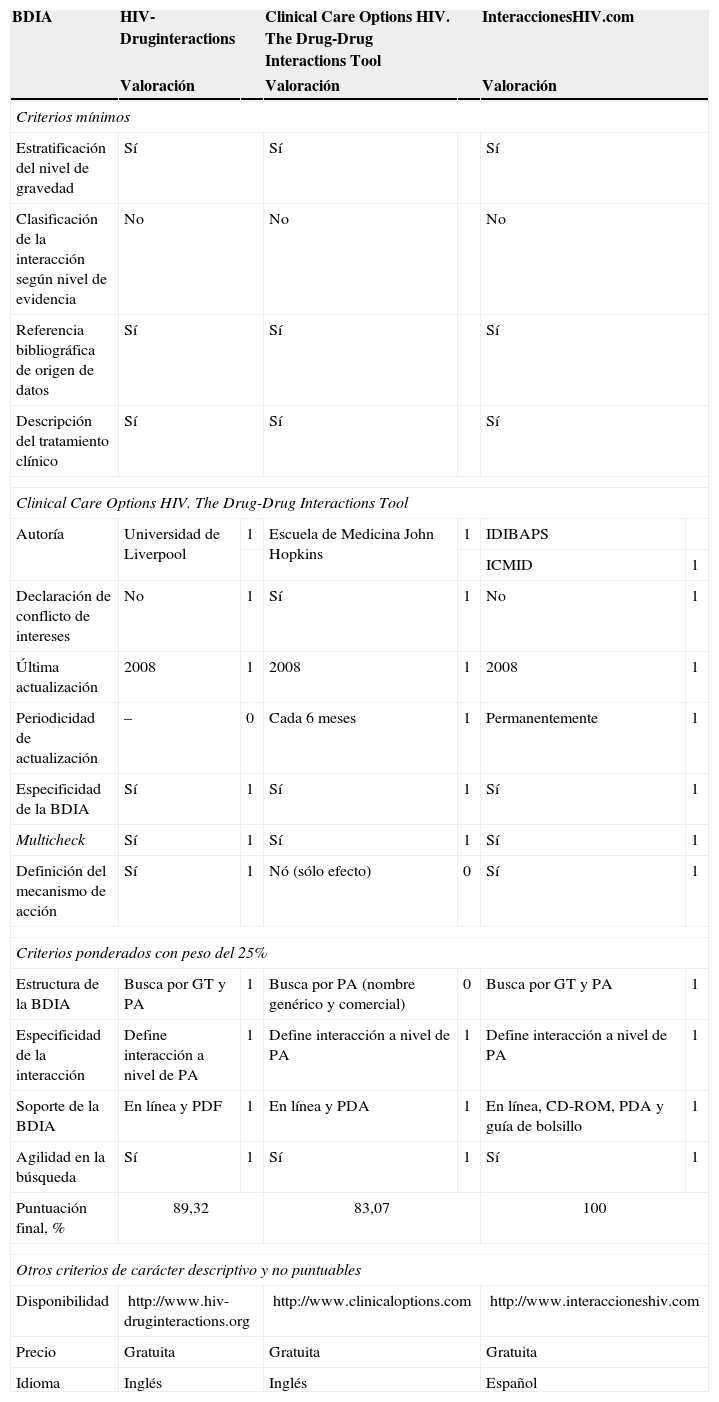
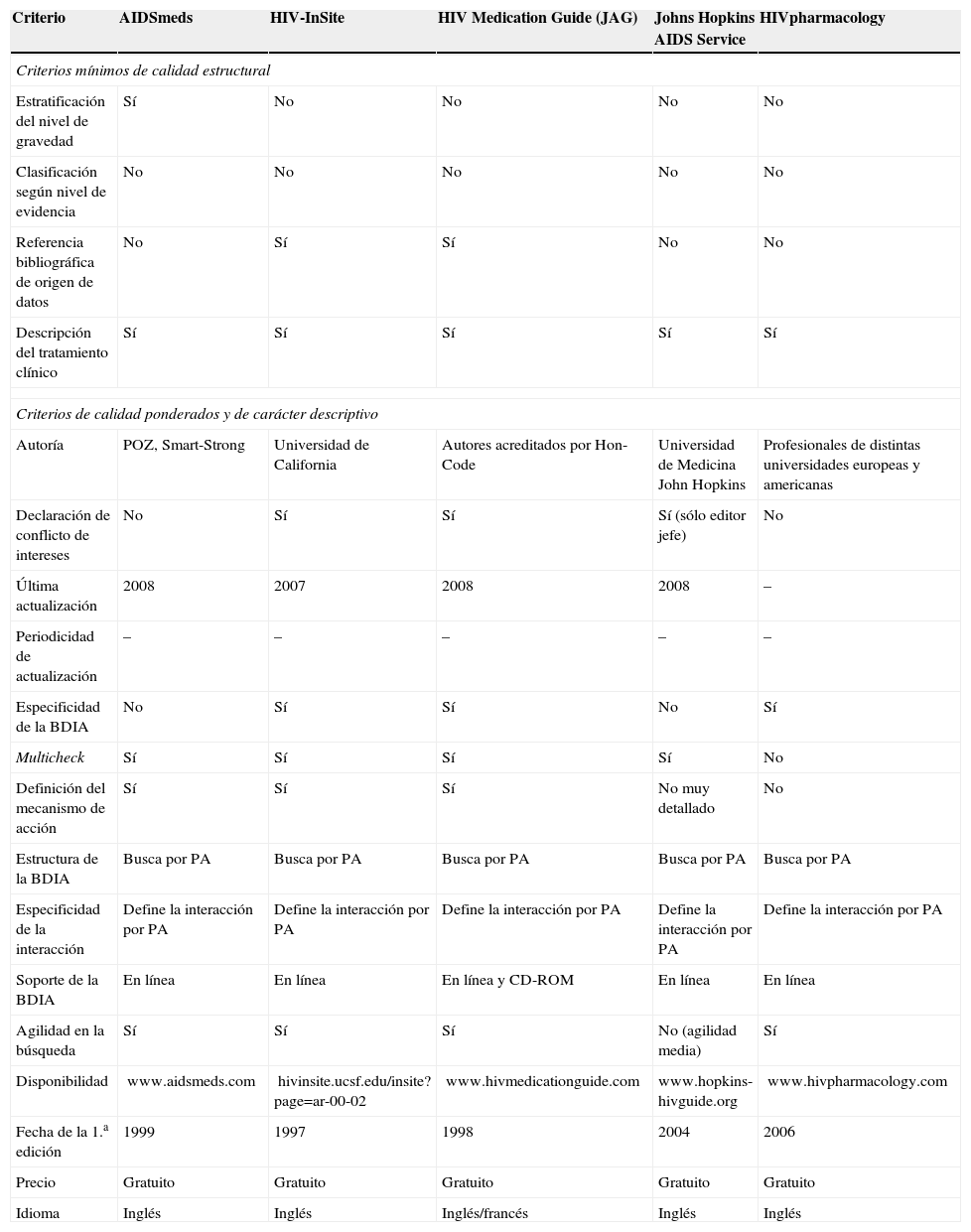
ResultadosSe identificaron 81 bases de datos, de las que 8 se incluyeron en el análisis. Sólo 3 de ellas cumplían 3 de los 4 criterios mínimos: HIV-Druginteractions, Clinical Care Options HIV (the Drug-Drug Interactions Tool) e InteraccionesHIV.com. Todas las bases de datos incluidas se presentan en soporte informático, proporcionan información por principio activo y describen tratamiento clínico. De ellas, 7 documentan el mecanismo de acción de la interacción y presentan estructura multicheck, lo que agiliza la búsqueda, 4 estratifican según nivel de gravedad y declaran no tener conflicto de intereses y 5 facilitan las referencias bibliográficas en las que se basa. Ninguna de ellas clasifica su información según nivel de evidencia.
ConclusionesExiste una gran cantidad de bases de datos disponibles sobre interacciones de antirretrovirales. El conocimiento de su calidad en cuanto a características formales ayudará a disponer de información contrastada.
To identify antiretrovirals drug interaction databases (ADID) and evaluate its structural quality.
Material and methodA literature search in Medline and a grey literature search were conducted. The identified ADID underwent scrutiny based on exclusion criteria and structural quality (4 minimum quality criteria: stratification by level of severity, classification by level of evidence, bibliographic data, description of the clinical management) and 11 criteria that provide the relative importance (specific weight). We analyzed the degree of compliance of the criteria in each ADID and the degree of compliance of each criterion in all ADID.
ResultsWe identified 81 databases but only 8 of them were included for the analysis. Only 3 of them reached the minimum criteria: HIV-Druginteractions, Clinical Care Options HIV (The Drug-Drug Interactions Tool) and InteraccionesHIV.com. All the databases included are presented on computerized support, organized by active drug and describe clinical management; 7 of them inform about the interaction mechanism of action and have multicheck structure that speeds up the search; 4 declare they have no conflict of interest and stratifies by level of severity; 5 contain bibliographic reference; none of them classifies by level of evidence.
ConclusionsThere are many antiretroviral interaction databases available. The knowledge about their quality structure will help provide appropriate information.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora