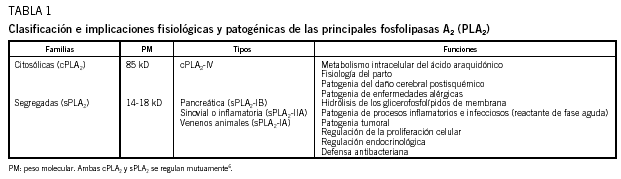
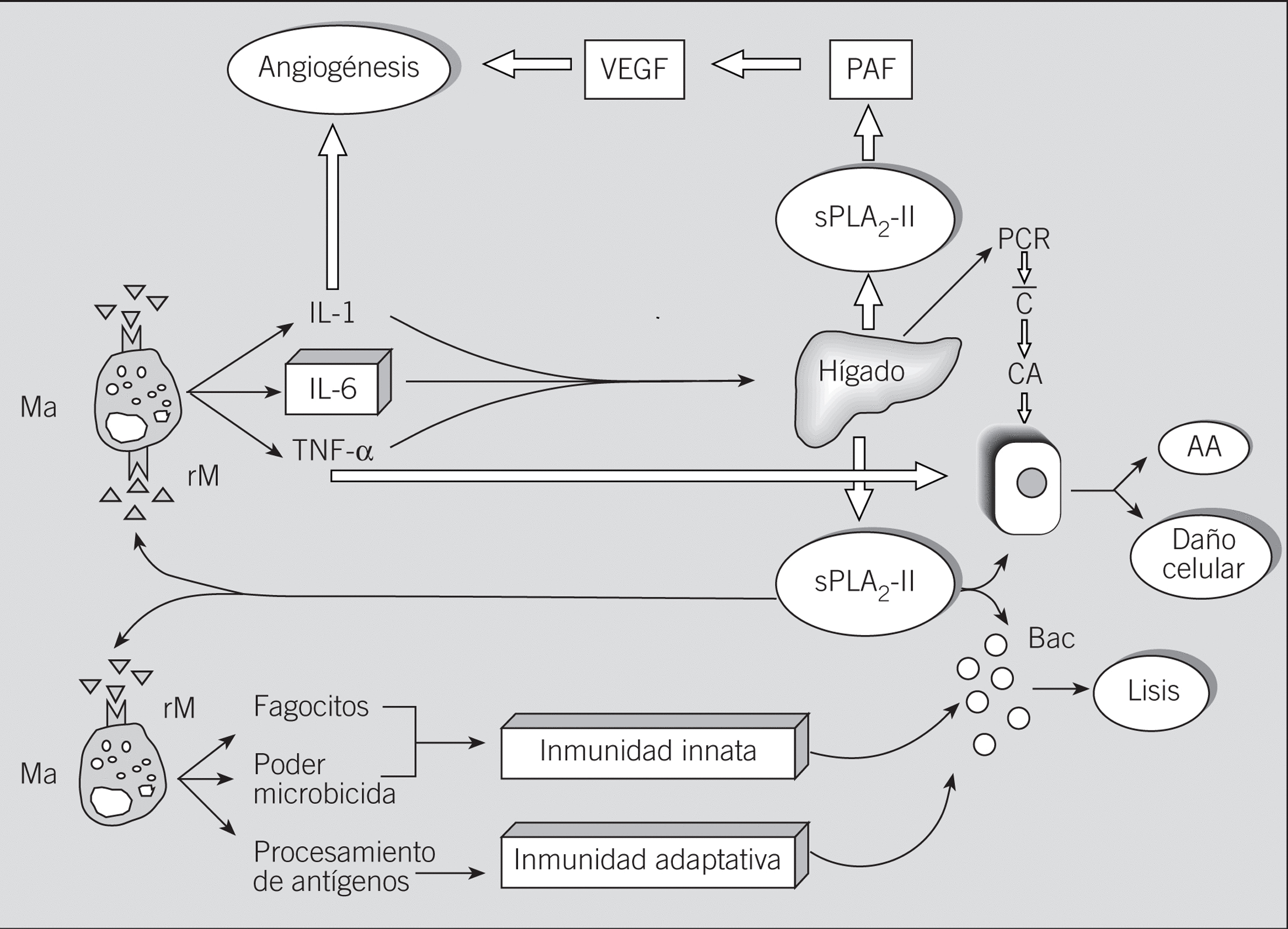
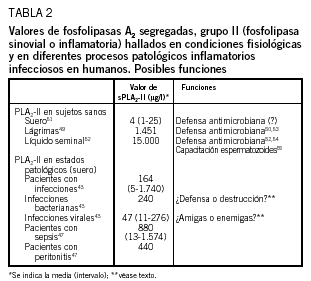
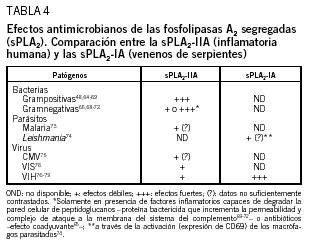
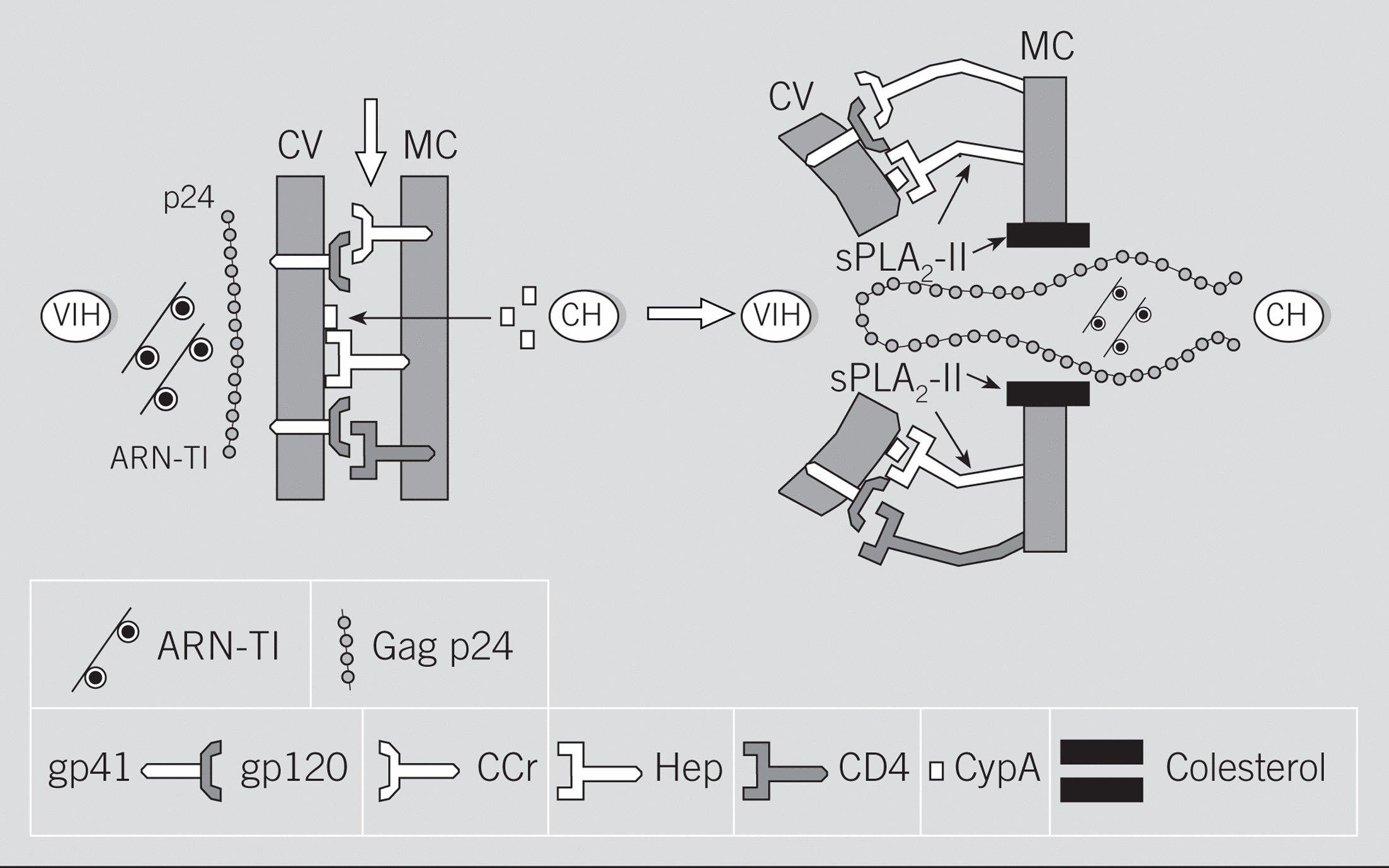
En este artículo se revisan los papeles perniciosos y beneficiosos de las fosfolipasas segregadas A2 (sPLA2). Aunque la sPLA2-II (inflamatoria) humana estuvo inicialmente implicada en la patogenia de la sepsis, del fallo multiorgánico y de otros síndromes relacionados, estudios recientes demuestran también su participación en los mecanismos de resistencia antiinfecciosa del huésped. Así, la sPLA2-II exhibe potentes actividades bactericidas frente a bacterias gramnegativas y grampositivas (en este caso, junto a otros factores inflamatorios). Curiosamente, la sPLA2-IIA no muestra actividad antivirus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH) in vitro, mientras que varias sPLA2-IA aisladas de venenos de abejas y de serpientes sí lo hacen; es el caso de la crotoxina, una sPLA2-IA aislada del veneno de Crotalus durissus terrificus (sPLA2-Cdt). Los efectos anti-VIH in vitro de la sPLA2-Cdt (inhibición de Gag p24) podrían deberse a su capacidad para desestabilizar algunos receptores de anclaje (heparanos) y de penetración (colesterol) del VIH presentes en las células del huésped.
In this paper the authors update on the deletereous or beneficial roles of human and animal secretory phospholipases A2 (sPLA2). Although human sPLA2-IIA (inflammatory) was initially thought as a foe because its pathogenic implication in sepsis, multiorganic failure or other related syndromes, recent data indicates its role in in the antiinfectious host resistance. Thus, sPLA2-IIA exhibits potent bactericidal activities against gram-negative and gram-positive (in this case, together with other endogenous inflammtory factors) bacteria. Surprisingly, human sPLA-IIA does not show in vitro anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) activity, whilst several sPLA2-IA isolated from bee and serpent venons do it: this is the case for crotoxin, a sPLA2-IA isolated from the venon of Crotalus durissus terrificus (sPLA2-Cdt). The mechanism for the in vitro anti-HIV activity of sPLA2-Cdt (inhibition of Gag p24) appears to be related to the ability of the drug to desestabilize ancorage (heparans) and fusion (cholesterol) receptors on HIV target cells.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora