La identificación de la mutación V617F del gen JAK2 en pacientes diagnosticados de neoplasias mieloproliferativas crónicas (NMPC) es fundamental en el cribado diagnóstico. Nuestro objetivo fue investigar la asociación entre la cuantificación de la mutación V617F (carga alélica JAK2V617F) y el fenotipo clínico al diagnóstico, y definir el papel de la carga alélica en la predicción de complicaciones.
Pacientes y métodosEn el Servicio de Hematología del Hospital Universitario La Paz realizamos un estudio observacional retrospectivo (1987-2011) en 114 pacientes diagnosticados de NMPC y análisis de detección de la mutación V617F: 39 policitemias vera (PV), 71 trombocitemias esenciales y 6 mielofibrosis primarias. El porcentaje de alelos mutados fue evaluado en polimorfonucleares de sangre periférica mediante la técnica quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR, «reacción en cadena de la polimerasa cuantitativa en tiempo real»). En función de si la carga tumoral se encuentra entre 1-50% o es>50% los pacientes fueron diagnosticados de JAK2mut heterocigoto u homocigoto, respectivamente.
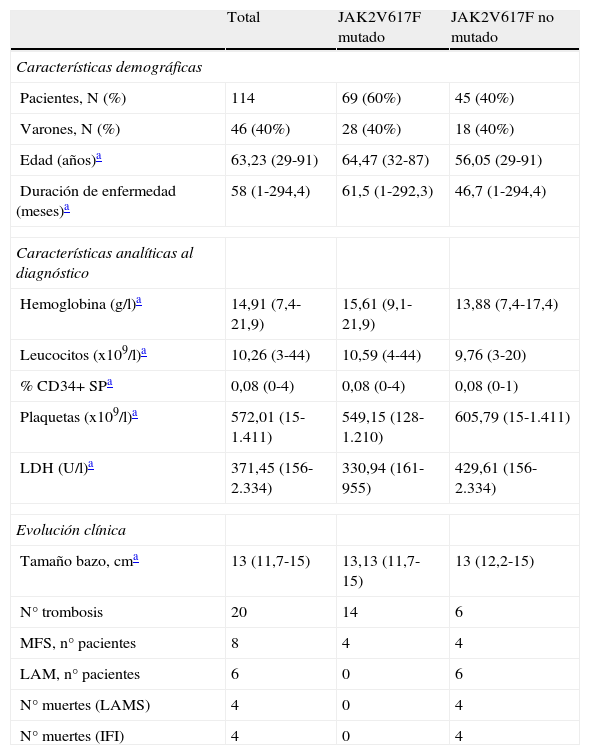
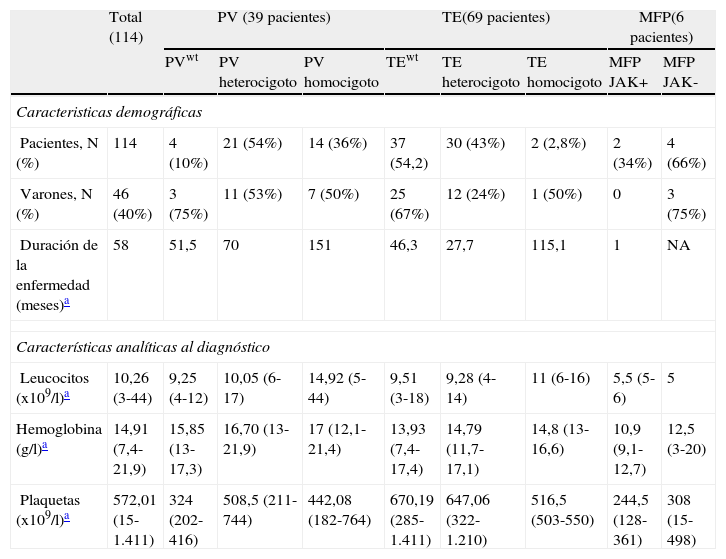
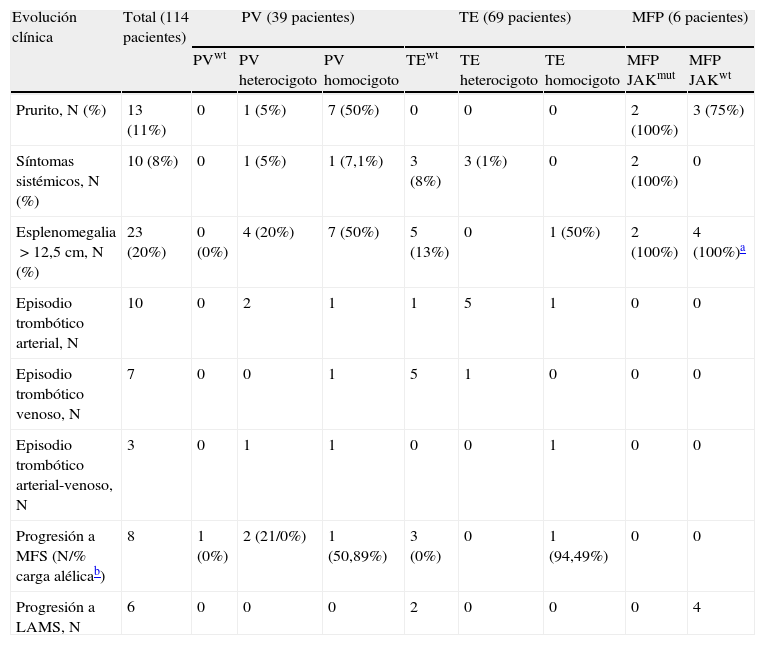
ResultadosSe realizó el análisis cuantitativo por qRT-PCR en los 114 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, detectando la mutación V617F en 69 casos y siendo negativa para los 45 pacientes restantes. Encontramos que la presencia de mutación se asocia con la trombosis, y especialmente con la trombosis arterial. Además, y en la serie completa, la carga alélica homocigótica se asocia con diagnóstico de PV, edad avanzada, leucocitosis, mayor hematopoyesis y esplenomegalia.
ConclusionesLa detección de la mutación V617F está asociada a una mayor incidencia de trombosis, leucocitosis y esplenomegalia. Su identificación nos permitiría una mejor estratificación pronóstica de los pacientes diagnosticados de NMPC.
Our study has investigated the presence of the mutation V617F in the JAK2 gene in patients diagnosed with chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). Furthermore, we determined if JAK2 (V617F) allelic burden associates with a specific clinical phenotype and if its quantification can be used as a marker to predict outcome and complications in patients with MPNs.
Patients and methodsA retrospective observational study was conducted from 1987 to 2011 in the Haematology Department of La Paz University Hospital. The allelic burden was measured in 114 patients diagnosed with MPNs: 39 polycythemia vera (PV) patients, 71 essential thrombocythaemia patients and 6 primary myelofibrosis patients. The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) technology was used to determinate the percentage of mutated alleles in peripheral blood neutrophils. Patients were divided in 2 groups: heterozygous if the result was≤50% of the tested cells, and homozygous if it was positive in>50% of the cells.
ResultsSixty-nine patients were positive for the JAK2 mutation and 45 were negative. Among those positive, the mutation was associated with arterial thrombosis. In addition, we demonstrate in the homozygous group that the V617F mutation is associated to PV, advanced age, leukocytosis, marked haematopoiesis and splenomegaly.
ConclusionsThe presence of V617F mutation is associated with a higher incidence of thrombosis, leukocytosis and splenomegaly. The identification of mutation on the JAK2 gene could help in a better definition of evolution and prognostic stratification of the myeloproliferative disorders.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora