A 36-year-old woman admitted to hospital with a 5-day history of fever and cough on February 11. On January 12, she was confirmed with COVID-19. On admission, her body temperature was 37.9°C. White blood cell count was 4.91×109/L and lymphocytes count was 0.81×109/L. The patient was given antiviral therapy, including lopinavir/ritonavir (lopinavir 400mg/ritonavir 100mg, q12h), arbidol (0.2g, tid) and Lianhua Qingwen Capsule (6.0g, tid).
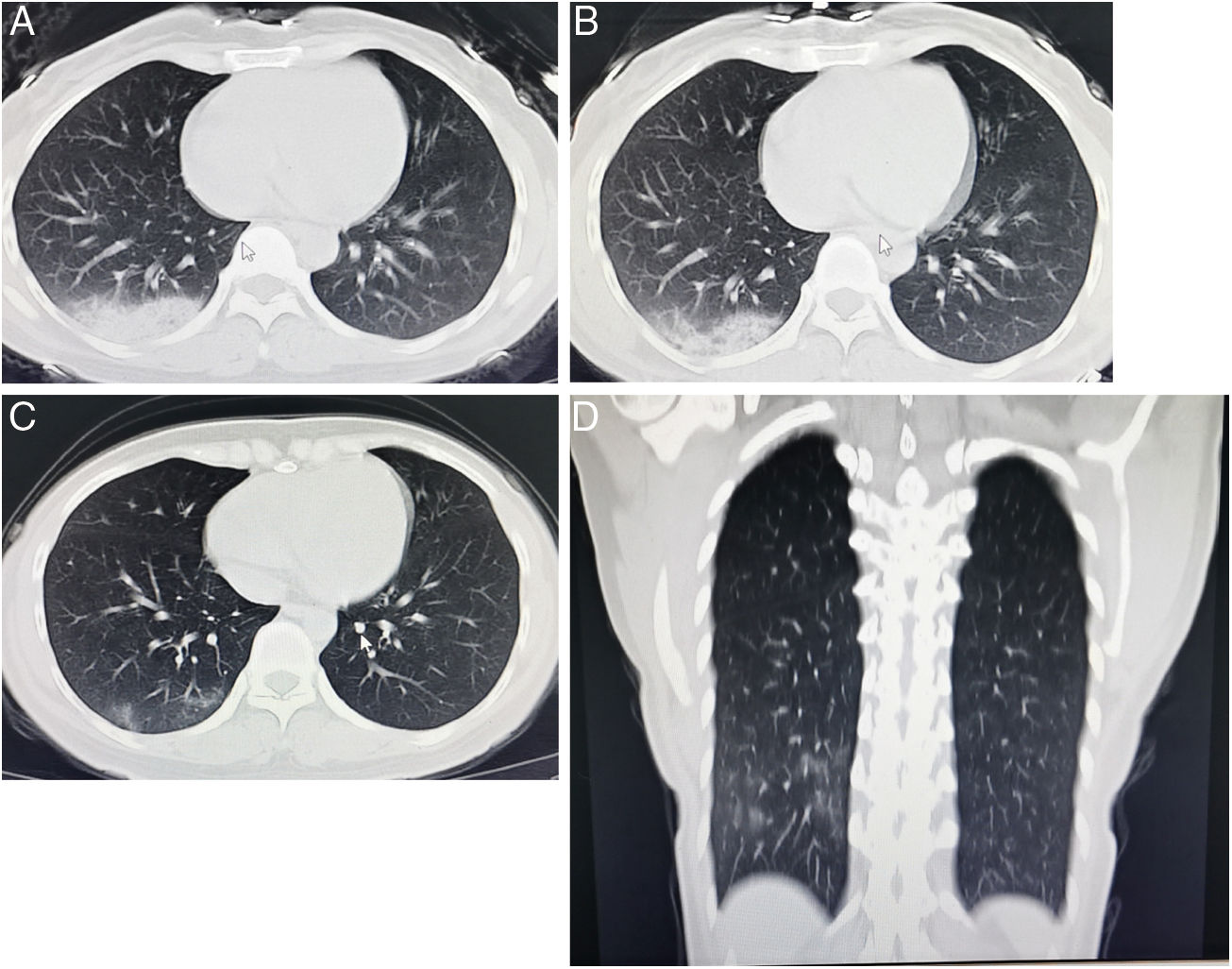
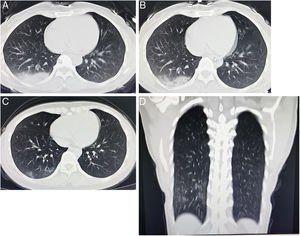
A chest radiograph obtained on day 5 after the onset of symptoms showed multiple high density shadow in the lower lobe 55 and basal segment of the right lung (Fig. 1A). A new CT scan obtained on day 10 showed lesions in the lower lobe of the right lung partially absorbed (Fig. 1B), and a CT scan obtained on day 16 showed evolution to a mixed pattern of ground-glass opacities and consolidation (Fig. 1C). On day 22 a CT scan shown healing of the consolidations and ground-glass opacities (Fig. 1D). On the same day, the throat swab for 2019-nCoV RNA was negative.
A combination of 2019-nCoV RNA tests and chest CT may be helpful for rapid identification of a new case and evaluating therapeutic effect.