No está establecida la estrategia óptima de revascularización coronaria percutánea en pacientes con insuficiencia renal crónica (IRC). Nuestro objetivo fue comparar, en dicho grupo, los resultados clínicos de los stents convencionales y farmacoactivos, e identificar factores pronósticos.
Pacientes y métodoEstudiamos el evento combinado: muerte, infarto no fatal, o revascularización de la lesión tratada tras 24 meses, en 200 pacientes consecutivos con IRC (93 recibieron stents convencionales y 107 farmacoactivos).
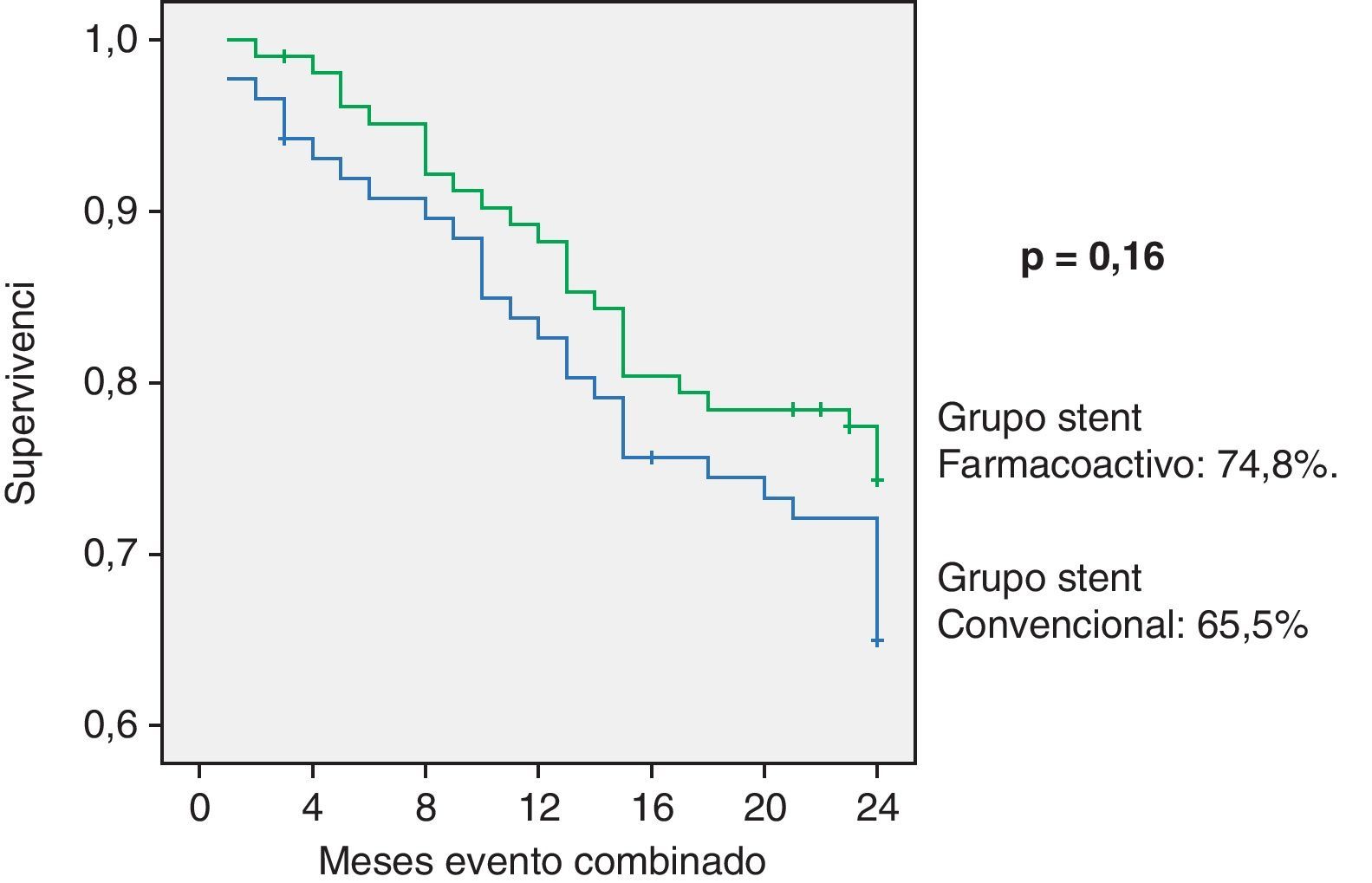
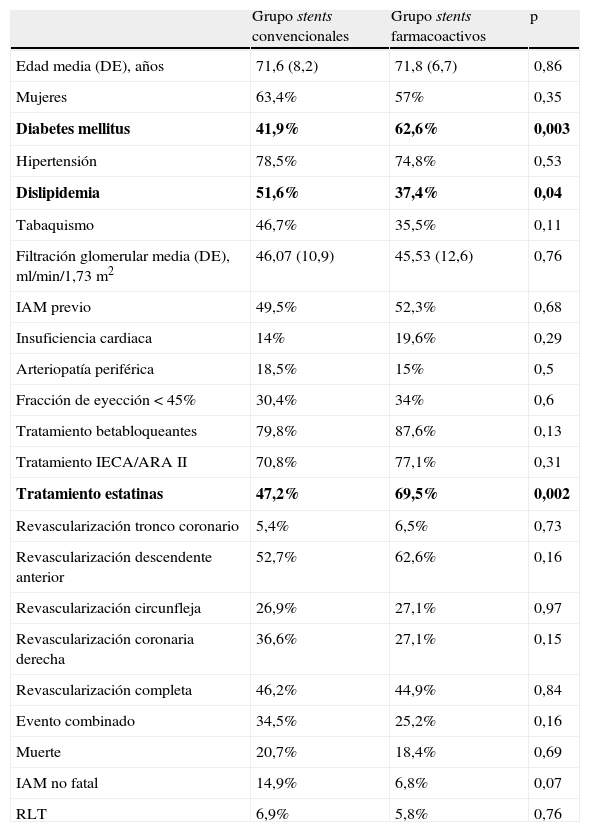
ResultadosEl análisis bivariante no mostró diferencias significativas entre ambos tipos de stent. El análisis multivariable señaló como factores predictores del evento combinado la arteriopatía periférica, la fracción de eyección menor de 45% y el tratamiento con estatinas.
ConclusionesNo alcanzamos evidencia de la superioridad de algún tipo de stent en la revascularización de los pacientes con IRC.
An ideal strategy of percutaneous coronary revascularization in patients with renal insufficiency has not been established yet. Our aim was to compare in this group the clinical results of bare metal stents and drug-eluting stents, and identify predictors.
Patients and methodIn a group of 200 patients with renal disease, 93 received bare metal stents and 107 drug-eluting stents; for over 2 years we studied rates of a combined event: death, non fatal myocardial infarction, or target lesion revascularization.
ResultsWe did not identify differences in the combined event. With multivariate analysis, peripheral arterial disease, left ventricular ejection fraction <45% and treatment with statins were predictor factors.
ConclusionsWe had no evidence of the superiority of any type of stent in the revascularization in patients with chronic renal insufficiency.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora