The aim of our study was to investigate the influence of G-308 promoter variant of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha gene on metabolic changes and weight loss secondary to a high monounsaturated fat vs a high polyunsaturated fat hypocaloric diet in obese subjects.
Patients and methodA sample of 261 obese subjects were enrolled in a consecutive prospective way, from May 2011 to July 2012 in a tertiary hospital. In the basal visit, patients were randomly allocated during 3 months to Diet M (high monounsaturated fat hypocaloric diet) and Diet P (high polyunsaturated fat hypocaloric diet).
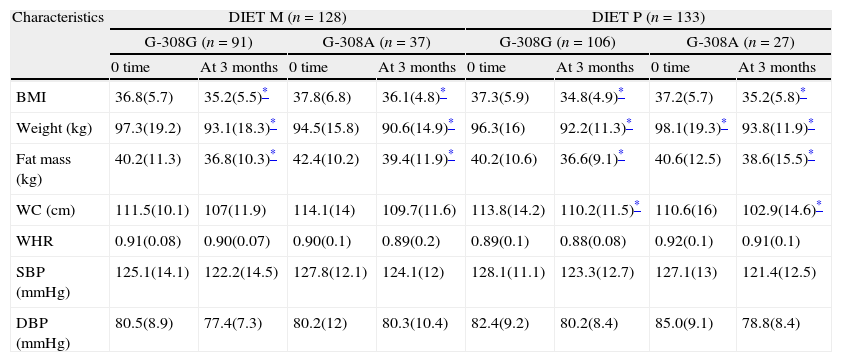
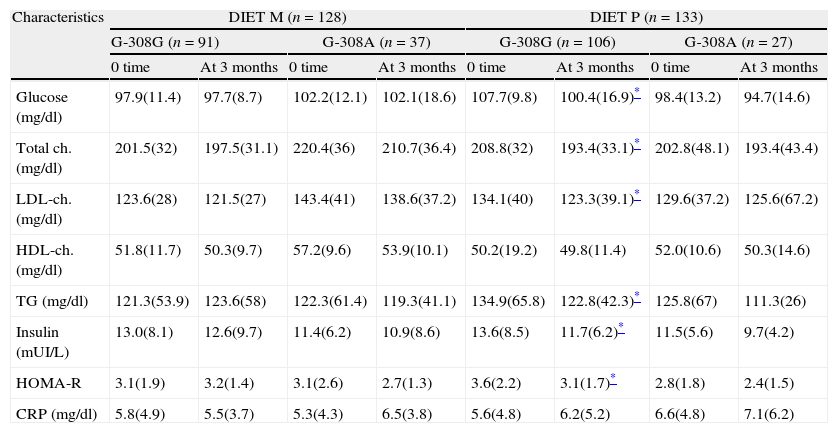
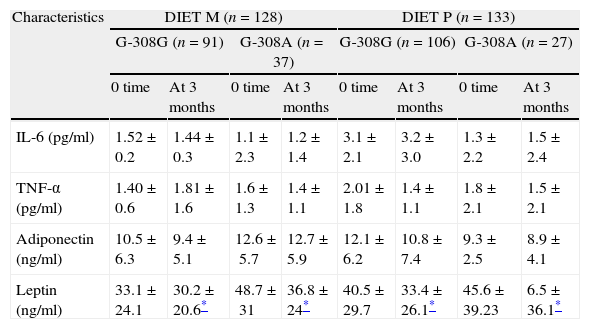
ResultsOne hundred and ninety seven patients (73.2%) had the genotype G-308G and 64 (26.8%) patients had the genotype G-308A. There were no significant differences between the effects (on weight, body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, fat mass) in either genotype group with both diets. With the diet type P and in genotype G-308G, glucose levels (−6.7(22.1)mg/dl vs −3.7(2.2)mg/dl: p=0.02), HOMA-R (−0.6(2.1)units vs −0.26(3.1)units: p=0.01), insulin levels (−1.7(6.6)UI/L vs −0.6(7.1)UI/L: p=0.009), total cholesterol levels (−15.3(31.1)mg/dl vs −8.4(22.1)mg/dl: p=0.01), LDL cholesterol levels (−10.7(28.1)mg/dl vs −3.8(21.1)mg/dl: p=0.008) and triglycerides (−12.1(52.1)mg/dl vs −6.6(43.1)mg/dl: p=0.02) decreased.
ConclusionCarriers of the G-308G promoter variant of TNF alpha gene have a better metabolic response than A-308 obese with a high polyunsaturated fat hypocaloric diet.
El objetivo de este estudio es investigar la influencia de la variante G-308 del promotor del gen TNF-α sobre los cambios metabólicos y pérdida de peso secundaria a una dieta hipocalórica rica en grasas monoinsaturadas frente a una dieta rica en grasas poliinsaturadas.
Pacientes y métodoUna muestra de 261 obesos fue reclutada de una manera prospectiva consecutiva, desde mayo de 2011 a julio de 2012 en un hospital terciario. En la visita basal fueron aleatorizados a recibir las siguientes dietas durante al menos 3 meses: dieta M (rica en grasa monoinsaturada) y dieta P (rica en grasa poliinsaturada).
ResultadosCiento noventa y siete (73,2%) obesos presentaron el genotipo G-308G, y 64 (26,8%), el genotipo G-308A. No hubo diferencias significativas en la mejoría de peso, IMC, circunferencia de la cintura y masa grasa con ambas dietas y en ambos genotipos. Tras la dieta P y con el genotipo G-308G, los niveles de glucosa (−6,7 [22,1] vs. −3,7 [2,2] mg/dl; p=0,02), HOMA-R (−0,6 [2,1] vs. −0,26 [3,1] unidades; p=0,01), insulina (−1,7 [6,6] vs. −0,6 [7,1] UI/l; p=0,009), colesterol total (−15,3 [31,1] vs. −8,4 [22,1] mg/dl; p=0,01), colesterol LDL (−10,7 [28,1] vs. −3,8 [21,1] mg/dl; p=0,008) y triglicéridos (−12,1 [52,1] mg/dl vs. −6,6 [43,1] mg/dl; p=0,02) disminuyeron.
ConclusiónLos portadores del genotipo G-308G presentan mayores beneficios metabólicos tras la pérdida de peso generada por la dieta rica en grasas poliinsaturadas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora