Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer with high metastasis rate and mortality. Although the emergence of immunotherapy has brought hope for treatment, the mortality rate of melanoma is still increasing year by year. The underlying mechanism of melanoma tumor progression and metastasis is urgently needed to be clarified. Recently chemokines have been found to play an important role in tumor progression in addition to their immunocytochemical chemotaxis.
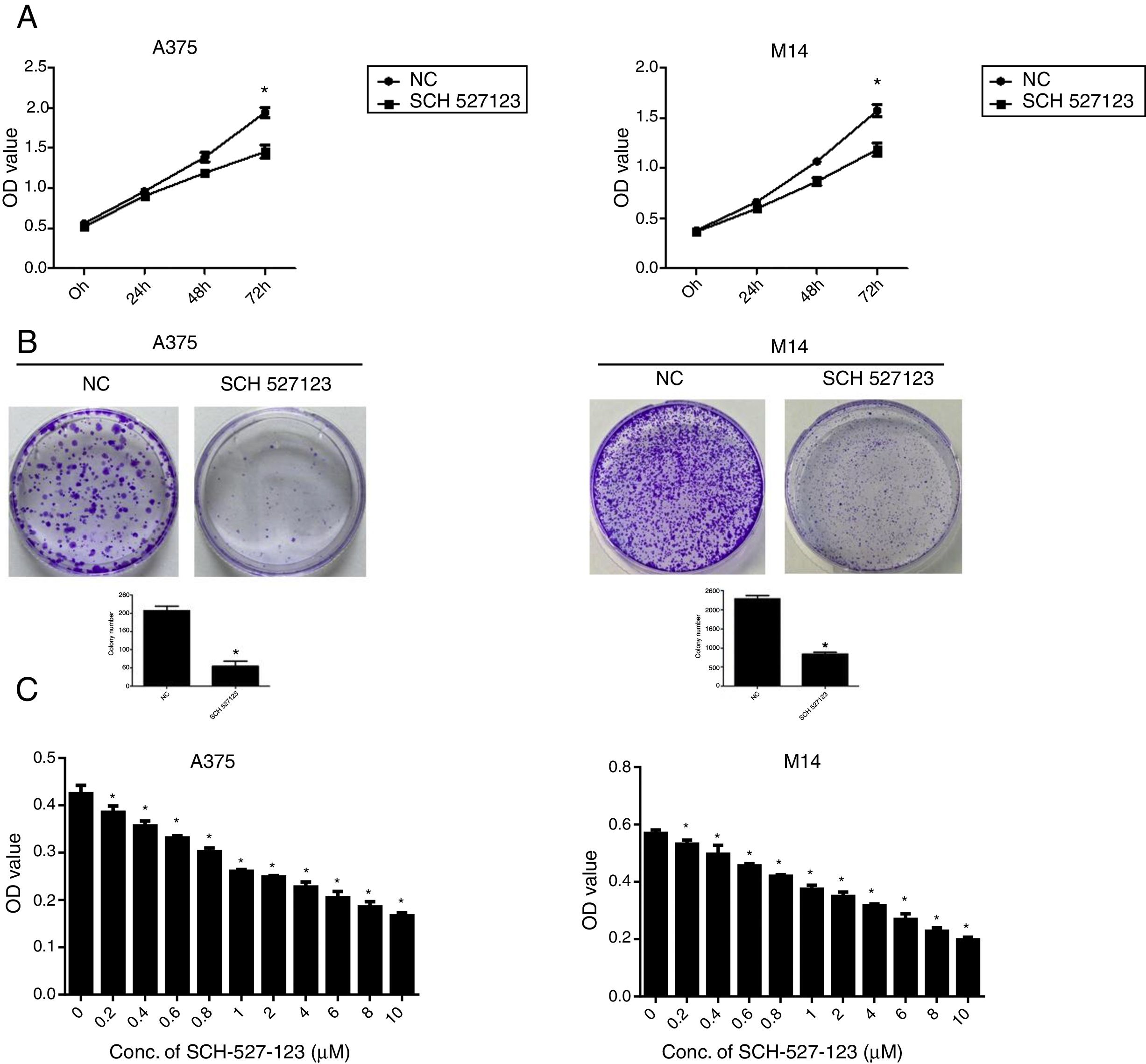
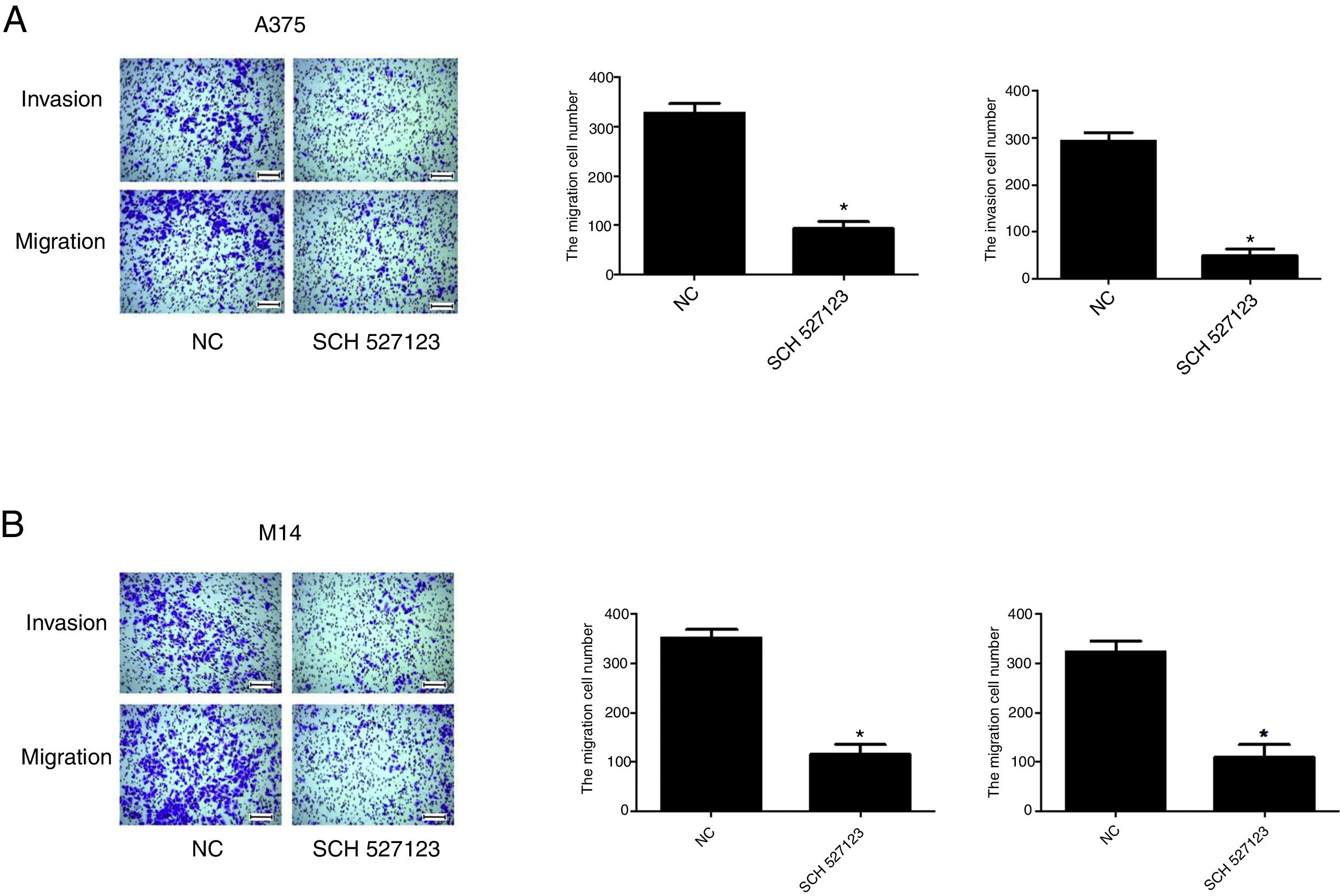
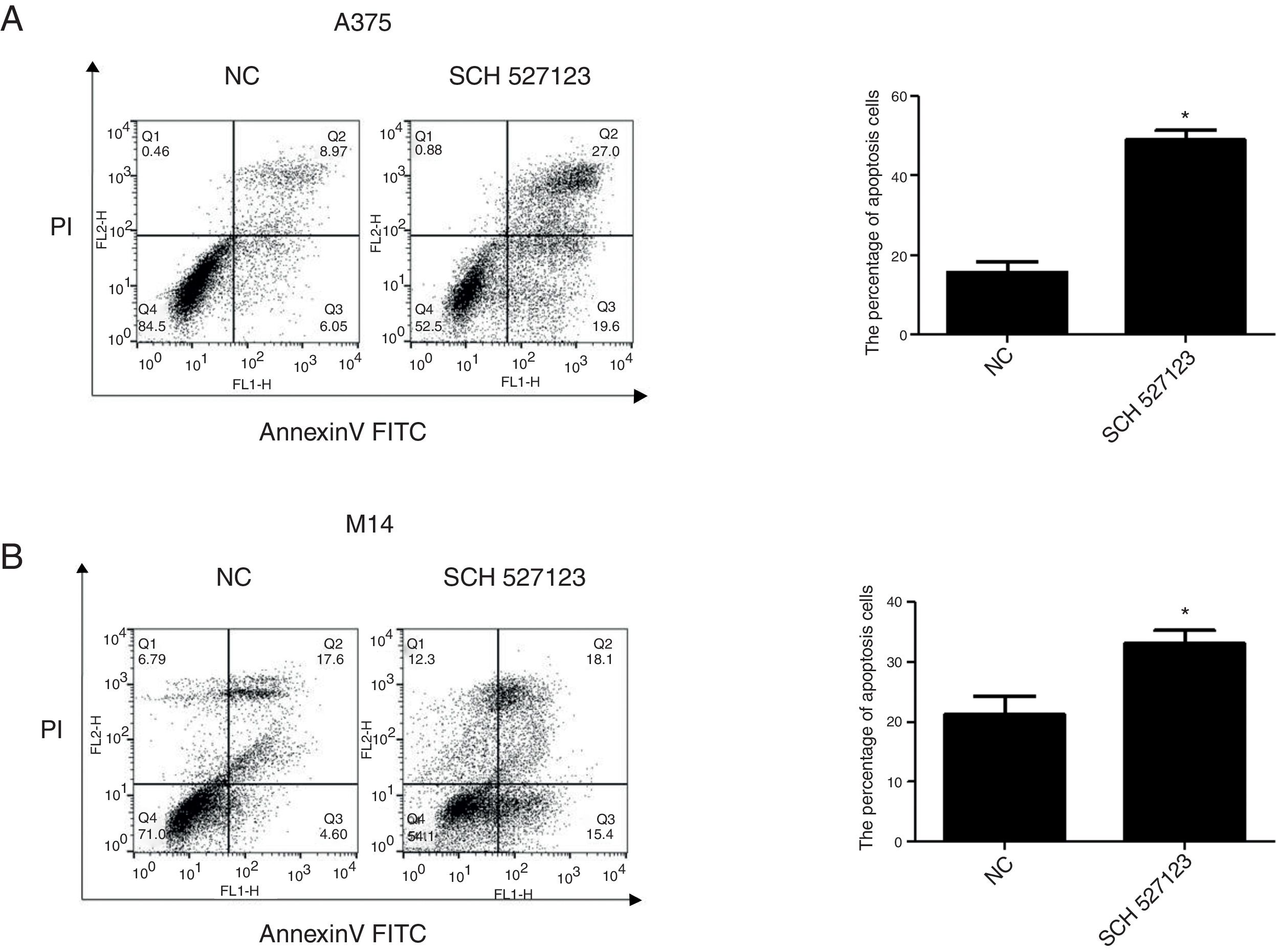
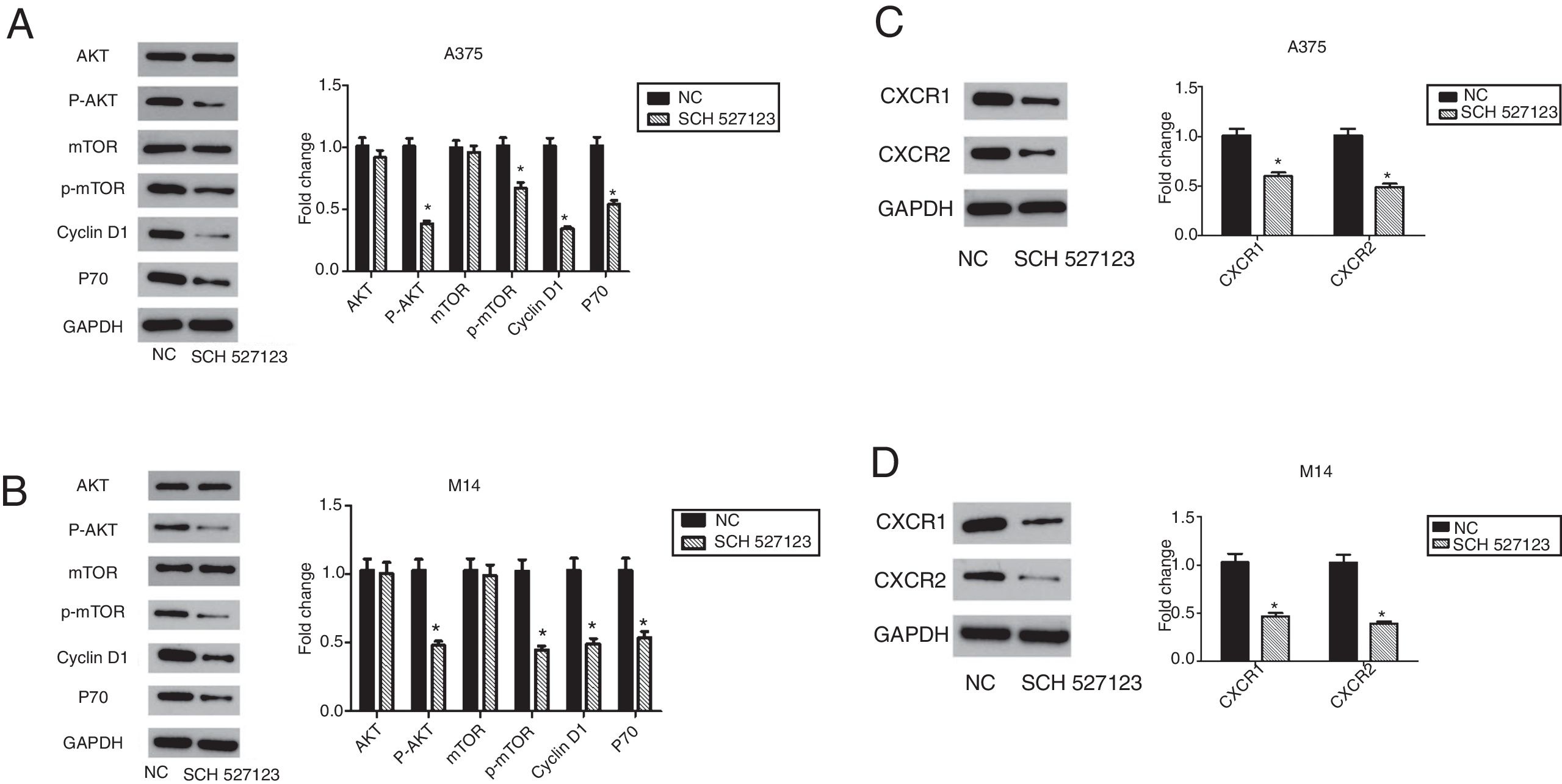
MethodsIn this study, human melanoma cell lines A375 and M14 were treated with SCH-527123, a small molecule antagonist of CXCR1 and CXCR2. The effects of treatment with SCH-527123 on melanoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion were evaluated in vitro by CCK-8, colony formation and transwell assays. Apoptosis was also detected by flow cytometry staining with annexin V and propidium iodide (PI). The molecular mechanisms of antagonist mediated were detected by western blot.
ResultsThe results showed that SCH-527123 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion of melanoma cell lines and promoted apoptosis. The expression of CXCR1 and CXCR2 was downregulated after treatment with SCH-527123. PI3K/AKT pathway and downstream signaling were also inhibited at molecular level owing to treated with SCH-527123.
ConclusionIn conclusion, our study demonstrated that SCH-527123, a small-molecule antagonist for CXCR1 and CXCR2 inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion in melanoma via PI3K/AKT pathway.
El melanoma es el cáncer de piel más peligroso, con una alta tasa de metástasis y mortalidad. Aunque la inmunoterapia ha traído esperanza para el tratamiento, la tasa de mortalidad del melanoma sigue aumentando año tras año. Es de crucial importancia aclarar el mecanismo subyacente de la evolución y la metástasis del melanoma. Recientemente se ha descubierto que las quimiocinas juegan un importante papel en la evolución tumoral.
MétodosEn el presente estudio, las líneas celulares de melanoma humano A375 y M14 se trataron con SCH-527123, un inhibidor de molécula pequeña de CXCR1 y CXCR2. Los efectos del tratamiento con SCH-527123 sobre la proliferación, migración e invasión de células de melanoma se evaluaron in vitro mediante CCK-8, formación de colonias y ensayos Transwell. También se detectó apoptosis mediante citometría de flujo con tinción con anexina V y yoduro de propidio (PI). Los mecanismos moleculares del antagonista fueron detectados por Western blot.
ResultadosLos resultados mostraron que SCH-527123 inhibió la proliferación, migración e invasión de líneas celulares de melanoma y promovió la apoptosis. La expresión de CXCR1 y CXCR2 disminuyó después del tratamiento con SCH-527123. La vía de señalización de la PI3K/AKT también se inhibió a nivel molecular debido a que se trataron con SCH-527123.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio demostró que SCH-527123, un inhibidor de molécula pequeña para CXCR1 y CXCR2 inhibió la proliferación celular, la migración y la invasión del melanoma a través de la vía PI3K/AKT.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora