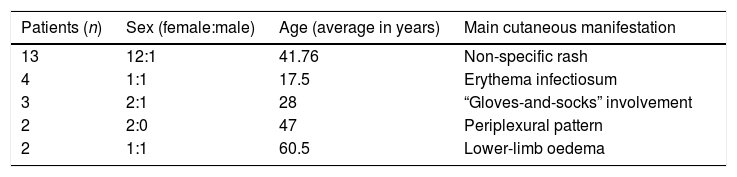Parvovirus B19 (PVB19) infection has a high incidence and worldwide distribution. It has a broad clinical spectrum, with skin, joint and haematological manifestations being the most common. The objective of this study was to determine the epidemiology and clinical–analytical manifestations of acute PVB19 infection.
Patients and methodsA retrospective study of patients with a positive IgM serology for PVB19 (10 years). Forty-six patients were included and their demographic, clinical and analytical characteristics were analyzed.
ResultsPrimary infection was most prevalent in women (ratio 2.2:1) aged 41 (mean age). Joint involvement was the most common manifestation (65%). Skin abnormalities were observed in more than half of patients (24 cases): rash (28%), megalerythema (9%), “gloves and socks” involvement (6.5%), periflexural rash (4%) and oedema (4%). Anaemia was the main haematological alteration (35%). The symptoms were self-limiting and resolved in 1–2 weeks in most patients.
ConclusionsAlthough there is a variable clinical spectrum, polyarthralgias and generalized maculopapular rash with fever and anaemia are the typical and most frequent manifestations of primary infection by PVB19 and are usually self-limiting.
La infección por parvovirus B19 (PVB19) tiene una incidencia elevada y distribución mundial. Su espectro clínico es amplio, destacando las manifestaciones cutáneas, articulares y hematológicas. El objetivo del presente estudio fue estudiar epidemiología y manifestaciones clínico-analíticas de la primoinfección por PVB19.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio retrospectivo (10 años) de pacientes con serología IgM positiva para PVB19. Se incluyeron 46 pacientes y se estudiaron sus características demográficas, clínicas y analíticas.
ResultadosLa primoinfección fue más prevalente en mujeres (ratio 2,2:1), y en edad media de 41años. La afectación articular fue la más frecuente (65%). En más de la mitad de los pacientes (24 casos) se observaron alteraciones cutáneas: exantema (28%), megaloeritema (9%), afectación «en guantes y calcetines» (6,5%), afectación periflexural (4%) y edema (4%). De entre las alteraciones hematológicas destacó la anemia (35%). El cuadro clínico se autolimitó en 1-2 semanas en la mayoría de los pacientes.
ConclusionesA pesar de que existe un espectro clínico variable, las poliartralgias y el exantema maculopapular generalizado junto con fiebre y anemia son las manifestaciones típicas y más frecuentes de la primoinfección por PVB19 y suelen autolimitarse.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora