The objective was to determine the prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men over 40 years of age and their relationship with frequent pathologies in Primary Care.
Patients and methodsThree hundred two men (40–79 years) were included. Anthropometric medical history, habits and parameters were determined. They were given the international prostate symptomatology questionnaire (IPSS), the male sexual health questionnaire (SHIM) and the Goldberg test for anxiety and depression. The prevalence of erectile dysfunction was determined and the relationship of the different variables obtained by univariate and multivariate analysis was studied.
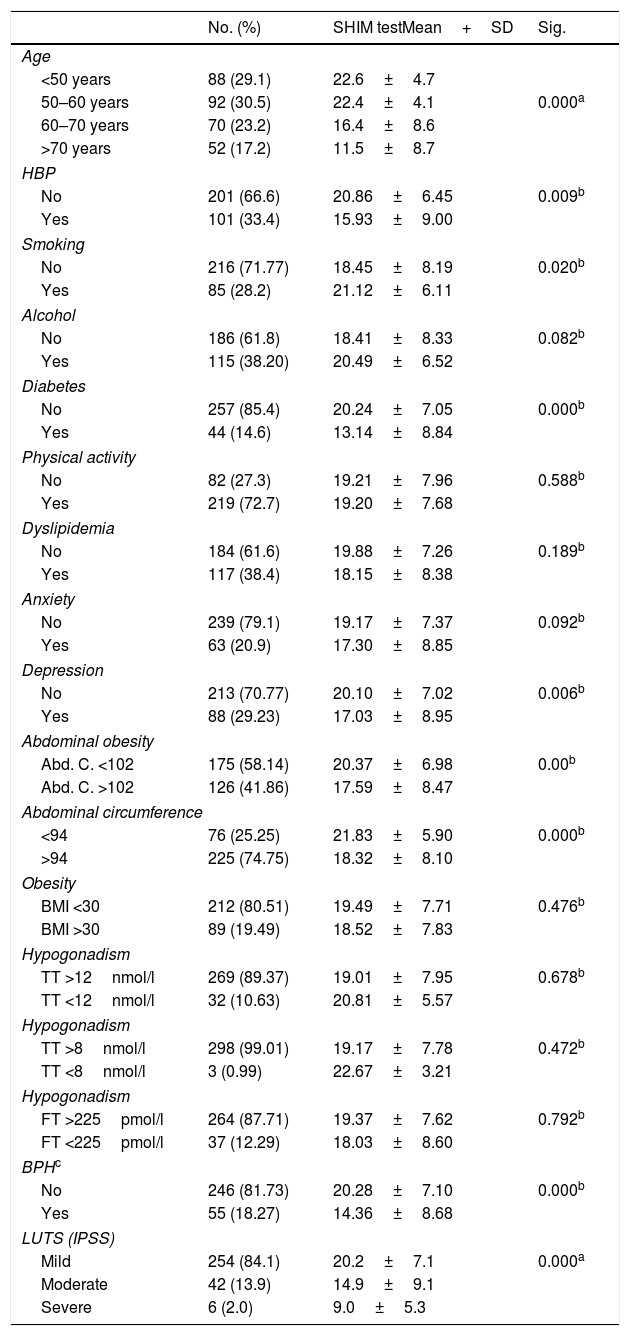
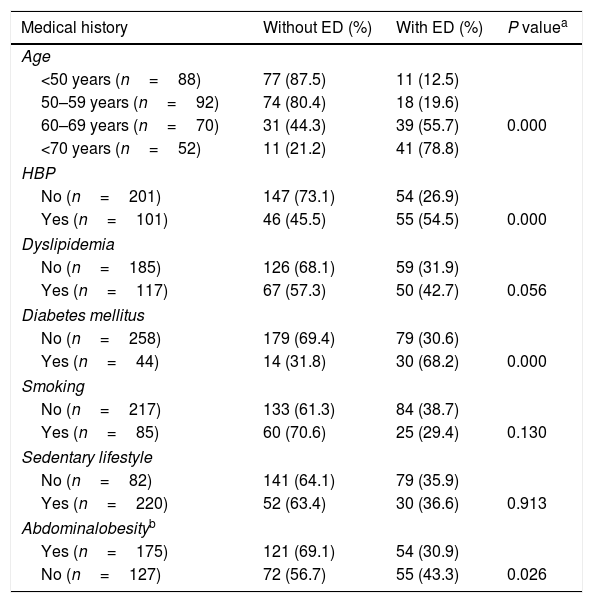
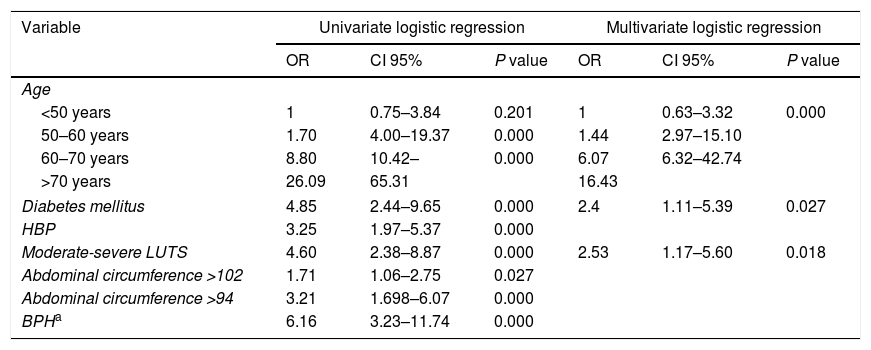
ResultsThe prevalence of erectile dysfunction was 36%. Older patients, smokers, with abdominal obesity, hypertensive, diabetic, at risk of depression or with voiding symptoms had lower scores on the sexual health questionnaire. According to the multivariate analysis, the risk of suffering from erectile dysfunction increased with age, if the person was diabetic, or if there was voiding symptomatology.
ConclusionAge, diabetes mellitus and the presence of voiding symptoms are factors associated with erectile dysfunction in the field of Primary Care.
El objetivo fue determinar la prevalencia de disfunción eréctil en los varones mayores de 40 años, y su relación con enfermedades frecuentes en atención primaria.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron 302 varones (40-79 años). Se determinaron antecedentes médicos, hábitos y parámetros antropométricos. Se les administró el cuestionario internacional de sintomatología prostática (IPSS), el cuestionario de salud sexual del varón (SHIM) y el test de Goldberg para ansiedad y depresión. Se determinó la prevalencia de disfunción eréctil y se estudió la relación de las diferentes variables obtenidas mediante análisis univariante y multivariante.
ResultadosLa prevalencia de disfunción eréctil fue del 36%. Los pacientes de mayor edad, fumadores, con obesidad abdominal, hipertensos, diabéticos, con riesgo de depresión o con síntomas miccionales tenían puntuaciones más bajas del cuestionario de salud sexual. Según el análisis multivariante, el riesgo de padecer disfunción eréctil aumentaba con la edad, si se era diabético o si existía sintomatología miccional.
ConclusiónLa edad, la diabetes mellitus y la presencia de sintomatología miccional son factores asociados a la disfunción eréctil en el ámbito de la atención primaria.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora