Numerous studies have evaluated the use of ultraviolet-C devices for terminal disinfection in hospitals, however, to date there is little information about the device's final impact on patients. We investigated the effect of an ultraviolet air sterilizer (UVAS) on the clinical outcomes of cardiac surgery patients.
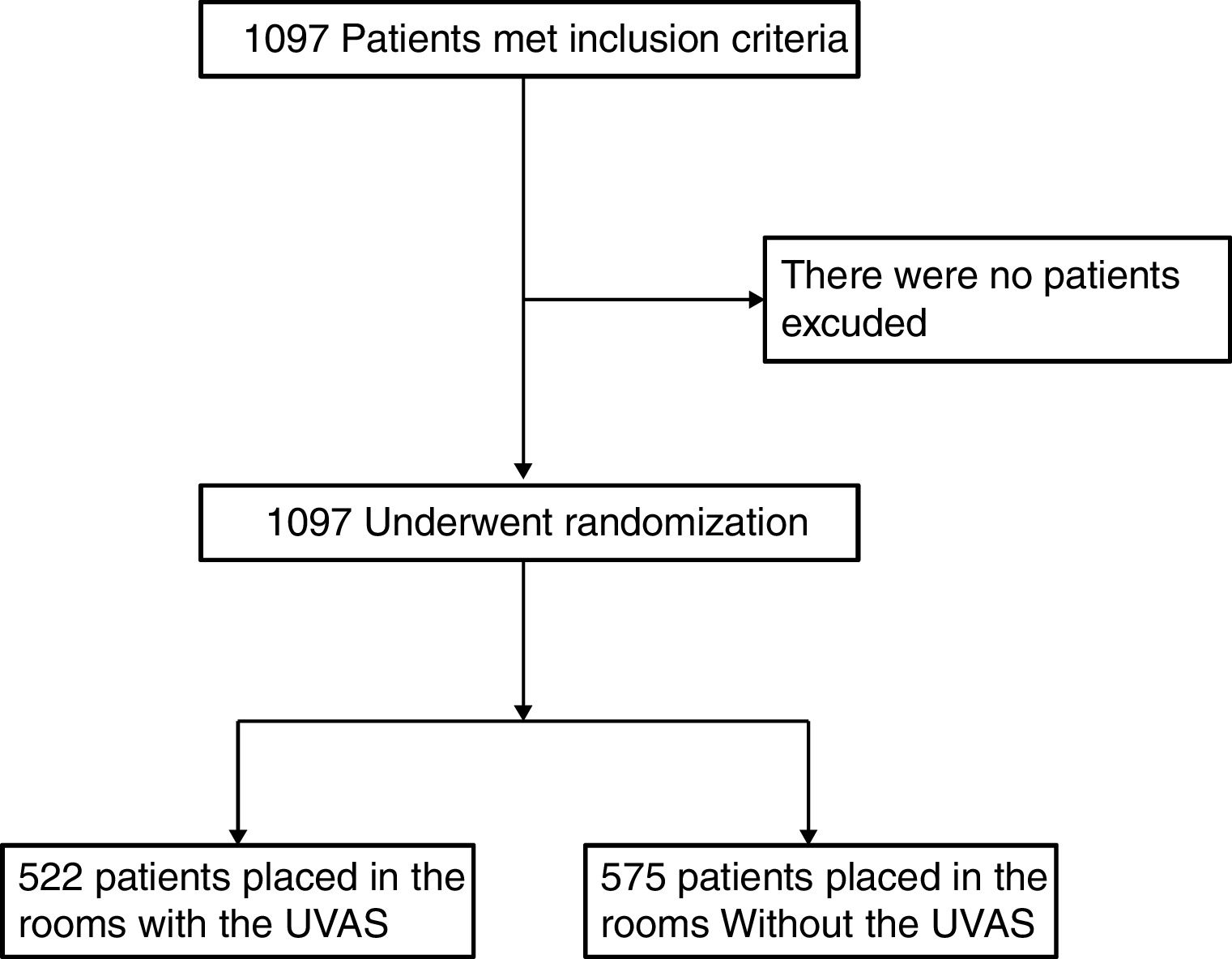
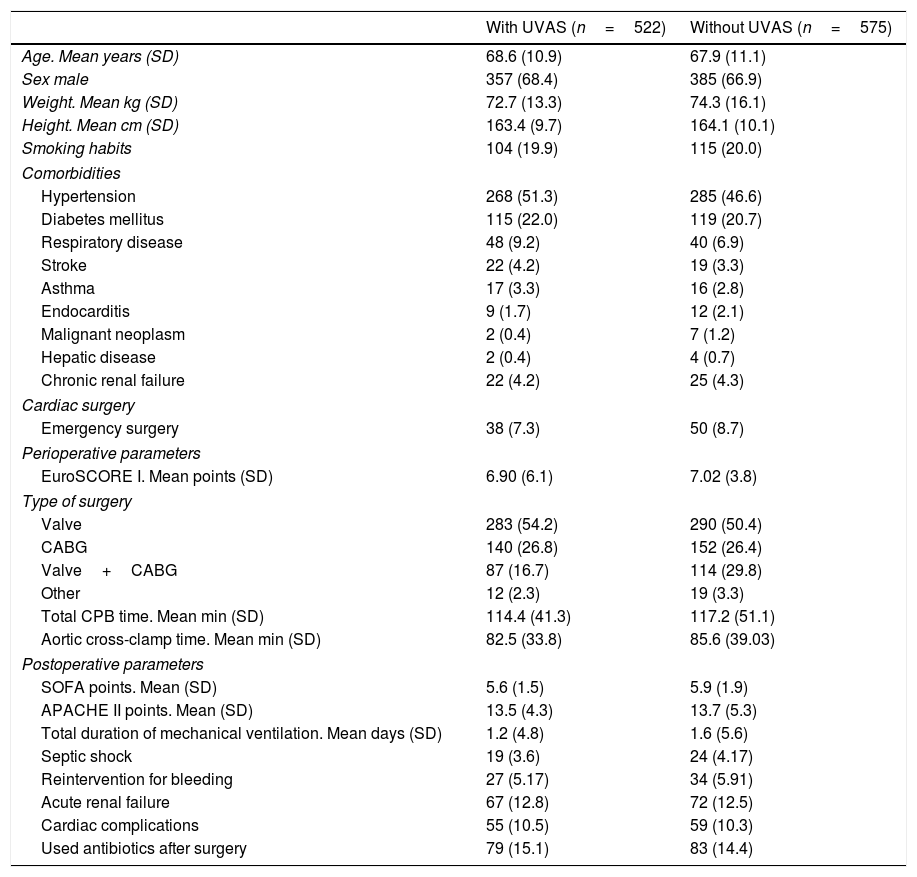
Materials and methodsThis random, prospective and non-interventional study included 1097 adult patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery: 522 stayed in an ICU room with UVAS (Medixair®) and 575 patients ICU room without UVAS and were used as a control. The primary outcome measure was to evaluate the effect of a UVAS on the overall prevalence of nosocomial infections in postoperative cardiac patients in ICUs.
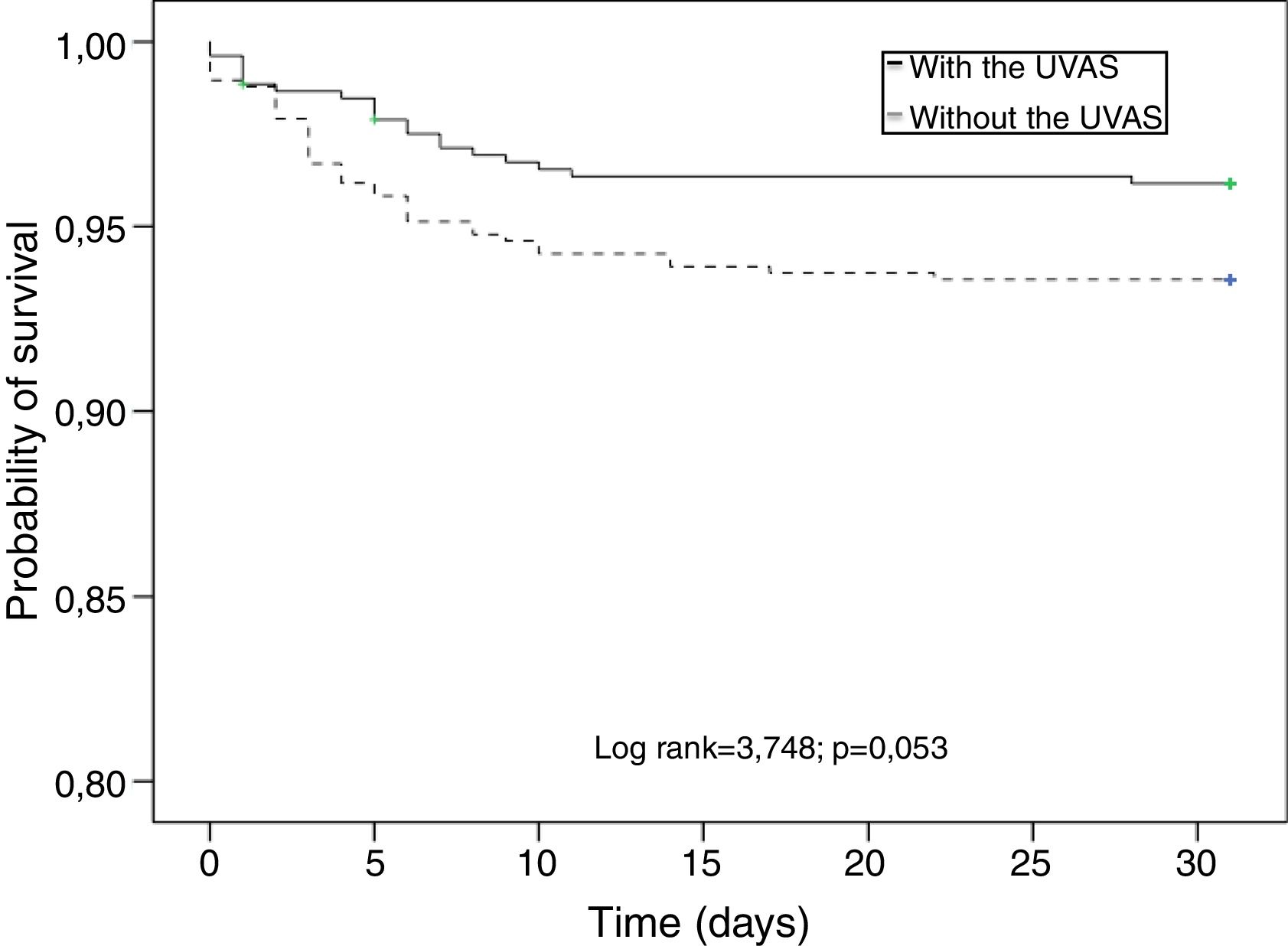
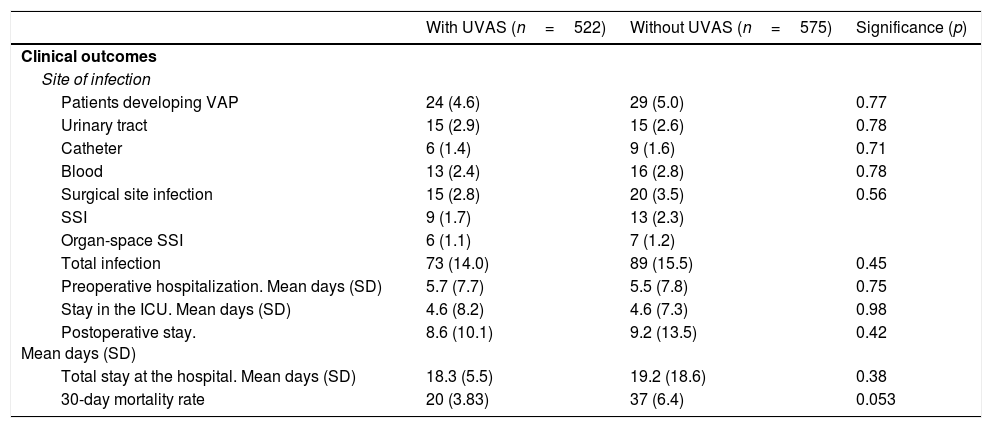
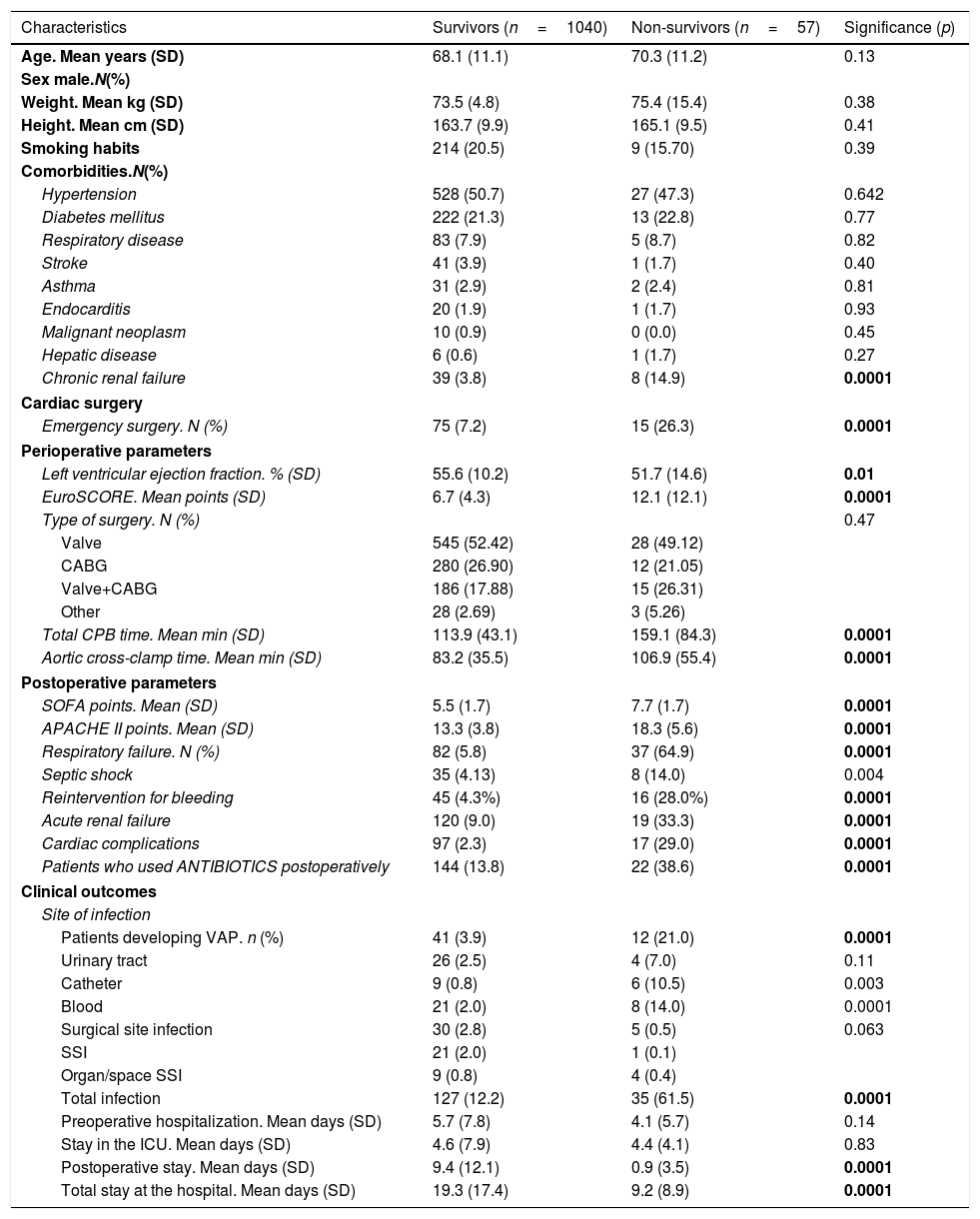
ResultsNo significant differences in ventilator-associated pneumonia (4.6% vs. 5.0%, p=0.77) and total infection (14.0% vs. 15.5%, p=0.45) rates were detected in patients with and without the UVAS. The length of stay in the intensive care unit and at the hospital was similar in both groups, UVAS (4.6 (8.2) days and 18.3 (5.5) days) and without UVAS (4.6 (7.3) days and 19.2 (18.6) days). The 30-day in-hospital mortality rate was 5.3%, no significant differences between groups were observed (p=0.053).
ConclusionNovel ultraviolet-C technology has not been shown to significantly reduce nosocomial infections or mortality rates in cardiac surgery patients.
Numerosos estudios han evaluado el uso de dispositivos ultravioleta C para la desinfección terminal en hospitales; sin embargo, hasta la fecha existen pocos datos sobre el impacto en los pacientes. Hemos evaluado el efecto de un esterilizador de aire ultravioleta (UVAS) sobre las variables clínicas de los pacientes operados de cirugía cardíaca.
Materiales y métodosEste estudio prospectivo, aleatorizado no intervencional incluyó 1.097 pacientes adultos intervenidos de cirugía cardíaca electiva: 522 ingresaron en una habitación de UCI con UVAS (Medixair®) y 575 pacientes en habitación de UCI sin UVAS se utilizaron como control. La variable principal medida fue el efecto del UVAS sobre la prevalencia global de infecciones en el postoperatorio de cirugía cardíaca en UCI.
ResultadosNo hubo diferencias significativas en la neumonía asociada a ventilación mecánica (4,6% vs. 5,0%, p=0,77) e índices totales de infección (14,0% vs. 15,5%, p=0,45) detectados en pacientes con y sin UVAS. La duración del ingreso en UCI y en el hospital fue similar en ambos grupos, UVAS (4,6 [8,2] días y 18,3 [5,5] días) y sin UVAS (4,6 [7,3] días y 19,2 [18,6] días). La mortalidad a 30 días hospitalaria fue del 5,3%, sin diferencias significativas entre los grupos (p=0,053).
Conclusión La nueva tecnología ultravioleta C no ha demostrado disminuir las infecciones nosocomiales ni la mortalidad en pacientes de cirugía cardíaca.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora