Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is an alpha-2 adrenergic drug used for short sedation and as an alternative to diazepam (DZP) in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS).
PurposeThis study aims to compare the hemodynamic effect of DZP versus DEX on heart rate (HR) and blood pressure in patients with AWS.
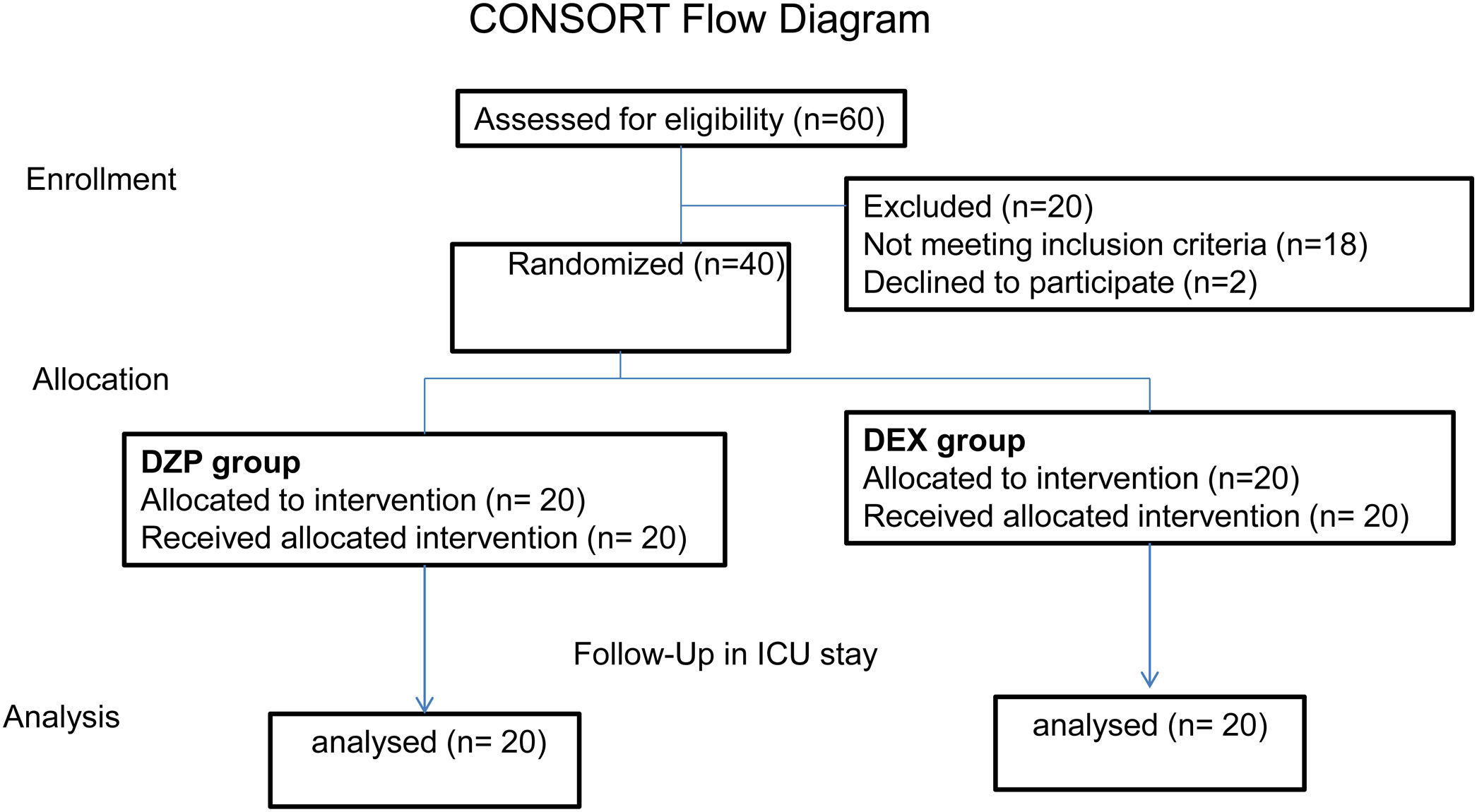
MethodsProspective randomized clinical trial that includes 40 patients with AWS from Mérida, Yucatán, México.
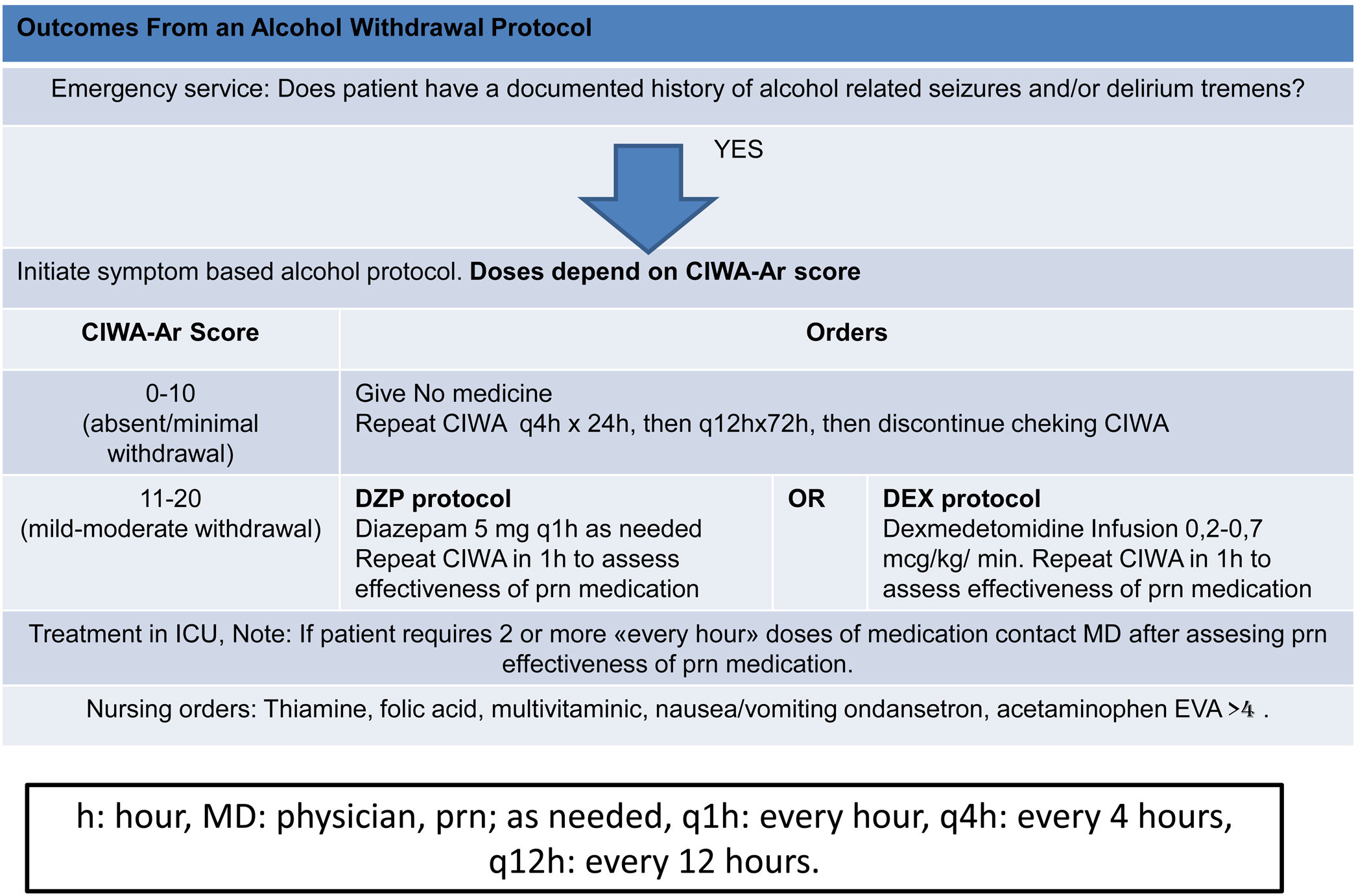
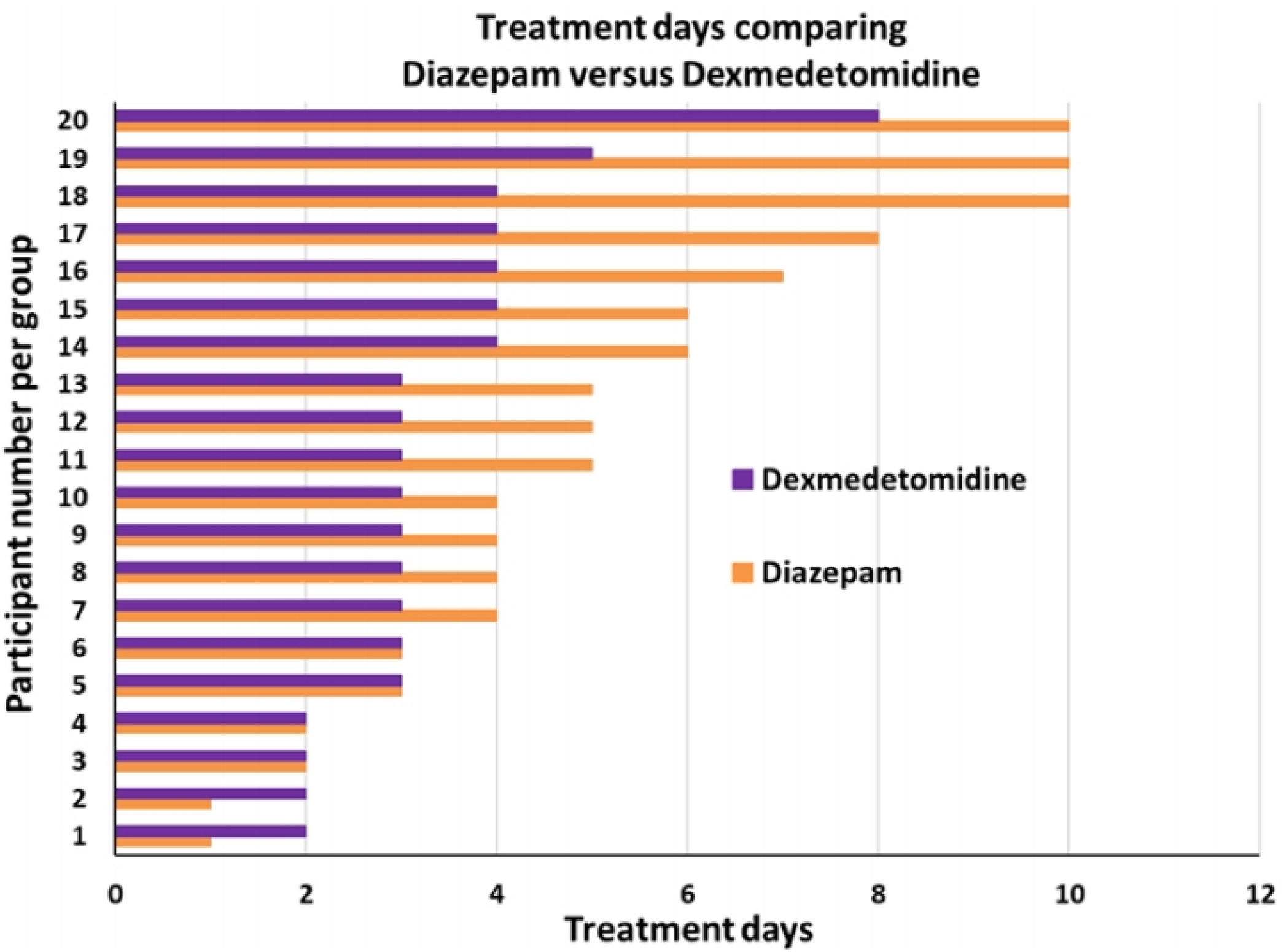
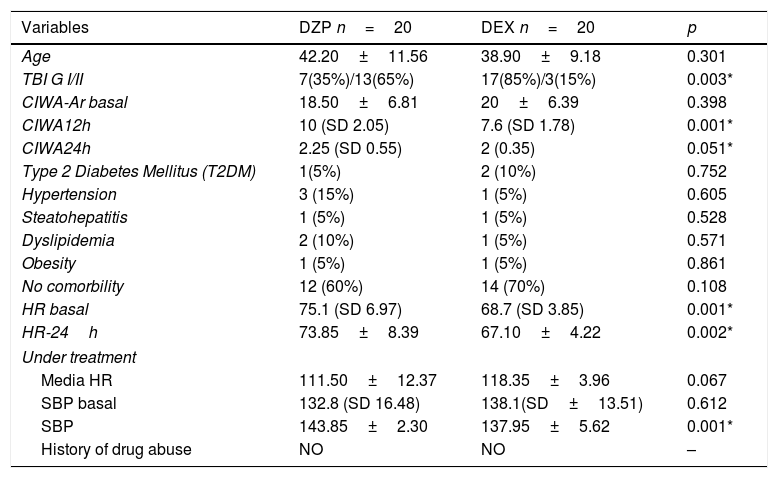
ResultsForty patients were randomly divided into two groups: one group DZP (n=20) patients received diazepam (doses 5–20mg IV) and the other group (n=20) received DEX (dexmedetomidine infusion .2–.7mcg/kg/min). We obtained statistical significance in sedation with the DEX group in the degree of traumatic brain injury I/II (p=.003). The DEX group remained haemodynamically stable in the first 24h, the mean HR (73.85±8.39) was significant comparing both groups (p=.002). In the comparison of the figures for the DEX group with the DZP (143.85±2.30–137.95±5.62) the SBP was significant with a (p=.0001). Furthermore, DEX treatment was shorter.
ConclusionAlthough DEX is not indicated for the routine treatment of AWS, this study proposes a positive effect on HR, SBP and fewer days of treatment compared to the standard DZP treatment for AWS.
Clinical Trials.gov ID: NCT03877120—https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03877120.
La dexmedetomidina (DEX) es un fármaco alfa-2 adrenérgico, utilizado para la sedación corta y como alternativa al diazepam (DZP) en el tratamiento por síndrome de abstinencia por alcohol.
ObjetivosComparar el efecto hemodinámico del DZP versus la DEX en la frecuencia cardíaca (FC) y la presión arterial en pacientes con síndrome de abstinencia del alcohol.
MétodosEnsayo clínico aleatorizado prospectivo en 40 pacientes con síndrome de abstinencia de alcohol, del Hospital General Agustín O’Horán Mérida, Yucatán, México.
ResultadosCuarenta pacientes fueron divididos aleatoriamente en 2 grupos: grupo DZP (n=20) recibió DZP n=20 (dosis: 5-20mg IV) y el otro grupo (n=20) recibió DEX (infusión de DEX: 0,2-0,7μg/kg/min). Obtuvimos significancia estadística en la sedación con el grupo de DEX en el grado de trauma craneoencefálico I/II (p=0,003). El grupo de DEX se mantuvo hemodinámicamente estable en las primeras 24h, la media FC (73; 85±8,39) fue significativa comparando ambos grupos (p=0,002). Las cifras de PAS para el grupo DEX comparada con DZP (143; 85±2; 30-137, 95±5,62) fue significativa con a (p=0,0001). Además, el tratamiento con DEX fue de menor duración.
ConclusiónAunque DEX no está indicado para el tratamiento de rutina de AWS, este estudio propone un efecto positivo hemodinámicamente sobre la FC, la PAS y menos días de tratamiento en comparación con el tratamiento estándar de DZP para el tratamiento del síndrome de abstinencia del alcohol.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora