Prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease (CKD) is higher than in the general population and predicts a higher mortality risk. The aim of this study is to investigate the occurrence of depressive symptoms among individuals with CKD in conservative treatment and renal replacement therapy (hemodialysis).
MethodsThis is a cross-sectional study conducted at three health centers specialized in CKD care, in Fortaleza-Ceara-Brazil, between June and October 2015. Patients with confirmed diagnosis of CKD were included, in hemodialysis and conservative treatment, older than 18 years. We have applied forms about socio-demographic questionnaire, including questions regarding mental health and the Beck depression inventory.
ResultsA total of 147 patients were interviewed, with mean age of 54±16 years, and 61% were males. Regarding treatment, 65.3% were in hemodialysis and 34.6% in conservative treatment. Previous diagnosis of mental disturbance was reported by 12.9% of patients; 29 (19.7%) had follow-up with Psychologist or Psychiatrist; 61 (41.4%) demonstrated interest in having specialized treatment. According to Beck inventory score, 47 (31.9%) patients presented depressive symptoms, being 22 (14.9%) mild, 14 (9.5%) moderate and 7 (4.7%) severe symptoms. Among patients in hemodialysis, 30 (31.2%) had depressive symptoms, while among patients in conservative treatment, the frequency of depressive symptoms was 25.5% (p=0.2).
ConclusionsThere were a significant number of patients with CKD with depressive symptoms, both in conservative treatment and hemodialysis, with no significant difference between these two groups. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the repercussion of depression in clinical outcome, as well as the impact of preventive and treatment measures.
La prevalencia de la depresión en la enfermedad renal crónica (ERC) es mayor que en la población general y predice un mayor riesgo de mortalidad. El objetivo de este estudio es investigar la ocurrencia de síntomas depresivos entre individuos con ERC en tratamiento conservador y terapia de reemplazo renal (hemodiálisis).
MétodosEste es un estudio transversal realizado en 3 centros de salud especializados en el cuidado de la ERC en Fortaleza, Ceará, Brasil, entre junio y octubre del 2015. Se incluyó a pacientes con diagnóstico confirmado de ERC en hemodiálisis y tratamiento conservador mayores de 18 años. Hemos aplicado cuestionarios sociodemográfico, incluyendo preguntas relacionadas con la salud mental y el inventario de depresión de Beck.
ResultadosFueron entrevistados 147 pacientes, con una edad media de 54±16 años, siendo el 61% varones. En cuanto al tratamiento, el 65,3% estaba en hemodiálisis y el 34,6% en tratamiento conservador. El diagnóstico previo de alteración mental fue reportado por el 12,9% de los pacientes; 29 (19,7%) tuvieron seguimiento con psicólogo o psiquiatra; 61 (41,4%) demostraron interés en recibir tratamiento especializado. De acuerdo con el inventario de Beck, 47 (31,9%) pacientes presentaron síntomas depresivos, siendo 22 (14,9%) leves, 14 (9,5%) moderados y 7 (4,7%) síntomas severos. Entre los pacientes en hemodiálisis, 30 (31,2%) tuvieron síntomas depresivos, mientras que entre los pacientes en tratamiento conservador la frecuencia de síntomas depresivos fue del 25,5% (p=0,2).
ConclusionesHubo un número significativo de pacientes con ERC con síntomas depresivos, tanto en tratamiento conservador como en hemodiálisis, sin diferencias significativas entre estos 2 grupos. Se necesitan más estudios para evaluar la repercusión de la depresión en los resultados clínicos, así como el impacto de las medidas preventivas y de tratamiento.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is currently a Public Health problem, affecting millions of people all over the world, with increasing incidence and prevalence [1]. In the USA there are around 400 cases per million inhabitants [1]. In the last 15 years there was an increase of more than 160% of patients in dialysis in Brazil, and it is estimated that more than 111,000 people are now on dialysis in this country [2].
CKD and its treatment represent a major stress for affected people and require a huge social adaption. Prevalence of depression in end-stage renal disease is higher than in the general population and predicts a higher mortality risk [3]. Previous studies in our region found a frequency of depressive symptoms among patients on hemodialysis between 19 and 68% [4,5]. There are still few studies investigating depression among CKD patients in conservative treatment. In a study conducted in São Paulo, Brazil, with 170 CKD patients, the authors found a slightly higher frequency of depressive symptoms among patients in dialysis, compared to patients under conservative treatment (41.6% vs. 37.3%) [6]. The same authors, in another study have found no significant difference in the prevalence of depression among CKD patients in the different stages of disease [7]. Amira [8], in a study with 118 CKD patients in Nigeria, evidenced a higher prevalence of depression among those on dialysis in comparison to pre-dialytic patients (34.5% vs. 13.3%).
The investigation of depression and other mental disorders among CKD patients is very important because sub-diagnosis is frequent and it may prejudice patients’ adhesion to treatment. It is supposed that patients on dialysis have more psychological distress than those in conservative treatment. The aim of this study is then to search for depressive symptoms among patients with CKD and to investigate if there are significant differences between patients on hemodialysis and those in conservative treatment.
2MethodsThis is a cross-sectional study with patients with CKD followed in three healthcare facilities in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil: two dialysis clinics (PRORIM and PRONTORIM) and one Nephrology outpatients’ clinics (Núcleo de Atenção Médica Integrada, University of Fortaleza), where CKD patients are followed in conservative treatment. Data collection was done between June and October 2015.
All patients with confirmed CKD diagnosis, according to KDIGO criteria (abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for >3 months: albuminuria ≥30mg/24h or ≥30mg/g; urine sediment abnormalities; electrolyte and other abnormalities due to tubular disorders; abnormalities detected by histology structural abnormalities detected by imaging; history of kidney transplantation; glomerular filtration rate <60ml/min/1.73m2) [9] were included. Exclusion criteria were: patients younger than 18 years older and those with severe cognitive deficit that could not answer the questionnaires. Interviewers were conducted before medical consultations (for those on conservative treatment) or during dialysis session (for those on hemodialysis). A socio-demographic questionnaire and the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [10] were applied. The BDI is a multiple-choice instrument with questions about how the subject has been feeling in the last week. Each answer is scored on a scale value of 0–3. Higher total scores indicate more severe depressive symptoms: 0–13: minimal depression, 14–19: mild depression, 20–28: moderate depression, 29–63: severe depression [10].
We have also collected data about patients’ comorbidities, occupation, educational level, previous history of mental disorder (including previous diagnosis of depression), Psychological or Psychiatric treatment and wish to receive specialized treatment and income (socio-economic level). Low income was defined according to Getúlio Vargas Foundation as a family income less than R$ 1115 (Brazilian Real) per month [11].
For the identification of CKD stage, medical records were assessed to estimate glomerular filtration rate based on the most recent serum creatinine through CKD-EPI equation CKD-EPI [12].
Statistical analysis was done with SPSS program version 20 (IBM, USA). In the descriptive analysis we have used summary measures (mean, standard deviation and percentage, where appropriated). For comparing the results between the two groups (dialysis versus conservative treatment) we have used Student t test, chi square test and Fisher exact text. A multivariate regression logistic regression was done to investigate factors associated with depression considering the entire group of patients with CKD. Significant level was set on 5% (p<0.05).
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Fortaleza (Protocol #969.073/2015).
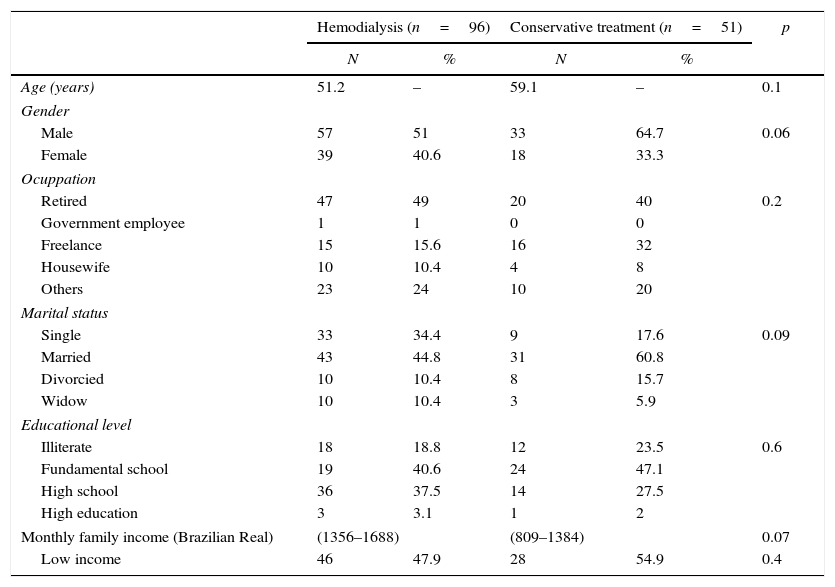
3ResultsA total of 147 patients were included, with mean age 54±16 years (range 21–88 years); 61% were males, 96 (65.3%) were in hemodialysis and 51 (34.6%) were in conservative treatment. Regarding educational level, 50 patients (34%) had finished high school, 63 (42.8%) had elementary school, 30 (20.4%) were illiterate, and 4 (2.7%) had higher education. Patients’ occupations were: retired (45.5%), freelance (21%), housewife (9.5%), government employee (0.6%) and others (23.1%). The majority of patients had low income (47.9%). Social-demographic data is summarized in Table 1.
Socio-demographic characteristics of patients with chronic kidney disease in hemodialysis and conservative treatment. Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, June–October 2015.
| Hemodialysis (n=96) | Conservative treatment (n=51) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age (years) | 51.2 | – | 59.1 | – | 0.1 |
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 57 | 51 | 33 | 64.7 | 0.06 |
| Female | 39 | 40.6 | 18 | 33.3 | |
| Ocuppation | |||||
| Retired | 47 | 49 | 20 | 40 | 0.2 |
| Government employee | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Freelance | 15 | 15.6 | 16 | 32 | |
| Housewife | 10 | 10.4 | 4 | 8 | |
| Others | 23 | 24 | 10 | 20 | |
| Marital status | |||||
| Single | 33 | 34.4 | 9 | 17.6 | 0.09 |
| Married | 43 | 44.8 | 31 | 60.8 | |
| Divorcied | 10 | 10.4 | 8 | 15.7 | |
| Widow | 10 | 10.4 | 3 | 5.9 | |
| Educational level | |||||
| Illiterate | 18 | 18.8 | 12 | 23.5 | 0.6 |
| Fundamental school | 19 | 40.6 | 24 | 47.1 | |
| High school | 36 | 37.5 | 14 | 27.5 | |
| High education | 3 | 3.1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Monthly family income (Brazilian Real) | (1356–1688) | (809–1384) | 0.07 | ||
| Low income | 46 | 47.9 | 28 | 54.9 | 0.4 |
*Fisher exact test and Student t test; significant p<0.05.
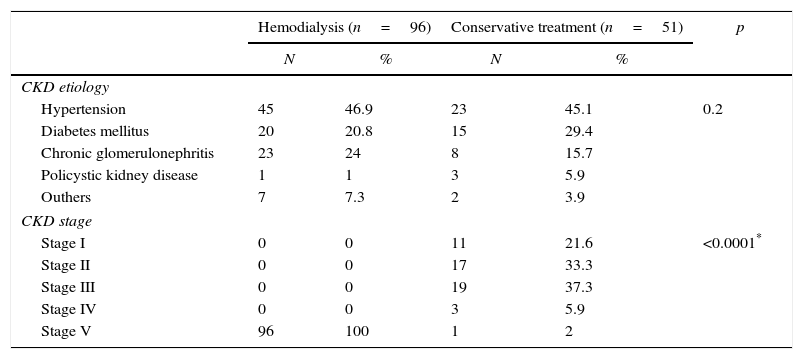
Regarding CKD etiology, 68 patients (46.2%) had hypertension, 35 (23.8%) diabetes, 31 (21%) chronic glomerulonephritis and 1 (0.6%) polycystic kidney disease. Hypertension predominated in both groups (dialysis and conservative treatment). CKD stages were: stage V (65.3%), IV (2%), III (12.9%), II (11.5%) and I (7.4%), as summarized in Table 2. The number of patients in dialysis that were in the list for kidney transplantation was 65 (67.7%) and history of previous kidney transplantation was identified in 6 cases (6.3%).
Clinical characteristics of patients with chronic kidney disease in hemodialysis and conservative treatment. Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, June–October 2015.
| Hemodialysis (n=96) | Conservative treatment (n=51) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| CKD etiology | |||||
| Hypertension | 45 | 46.9 | 23 | 45.1 | 0.2 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 20 | 20.8 | 15 | 29.4 | |
| Chronic glomerulonephritis | 23 | 24 | 8 | 15.7 | |
| Policystic kidney disease | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5.9 | |
| Outhers | 7 | 7.3 | 2 | 3.9 | |
| CKD stage | |||||
| Stage I | 0 | 0 | 11 | 21.6 | <0.0001* |
| Stage II | 0 | 0 | 17 | 33.3 | |
| Stage III | 0 | 0 | 19 | 37.3 | |
| Stage IV | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5.9 | |
| Stage V | 96 | 100 | 1 | 2 | |
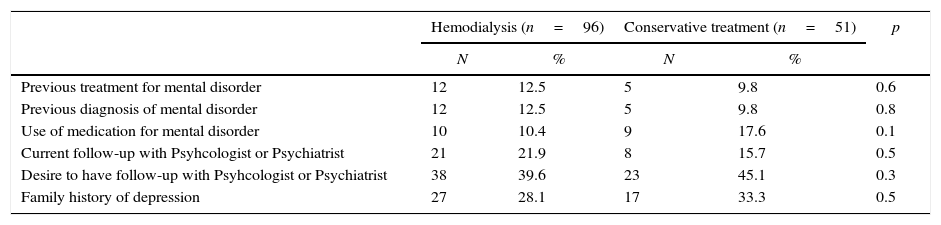
Previous diagnosis of mental disorder was reported by 19 patients (12.9%); 19 (12.9%) reported use of medication for mental disorders; 29 (19.7%) were followed by Psychologist or Psychiatrist; 61 (41.4%) had interest in start treatment with Psychologist/Psychiatrist, and 44 (29.9%) had family history of depression (Table 3).
Mental disorder history and specific treatment among patients with chronic kidney disease in hemodialysis and conservative treatment. Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, June–October 2015.
| Hemodialysis (n=96) | Conservative treatment (n=51) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Previous treatment for mental disorder | 12 | 12.5 | 5 | 9.8 | 0.6 |
| Previous diagnosis of mental disorder | 12 | 12.5 | 5 | 9.8 | 0.8 |
| Use of medication for mental disorder | 10 | 10.4 | 9 | 17.6 | 0.1 |
| Current follow-up with Psyhcologist or Psychiatrist | 21 | 21.9 | 8 | 15.7 | 0.5 |
| Desire to have follow-up with Psyhcologist or Psychiatrist | 38 | 39.6 | 23 | 45.1 | 0.3 |
| Family history of depression | 27 | 28.1 | 17 | 33.3 | 0.5 |
*Fisher exact test; significant p<0.05.
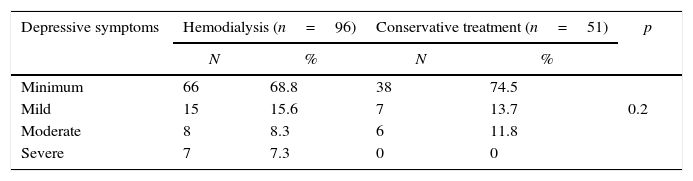
According to Beck Inventory score, 47 (31.9%) had depressive symptoms, and it was mild in 22 cases (14.9%), moderate in 14 (9.5%) and severe in 7 (4.7%). Among patients on dialysis, 30 (31.2%) had depressive symptoms, while in those in conservative treatment this frequency was 25.5% (Table 4).
Depressive symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease in hemodialysis and conservative treatment. Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, June–October 2015.
| Depressive symptoms | Hemodialysis (n=96) | Conservative treatment (n=51) | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Minimum | 66 | 68.8 | 38 | 74.5 | |
| Mild | 15 | 15.6 | 7 | 13.7 | 0.2 |
| Moderate | 8 | 8.3 | 6 | 11.8 | |
| Severe | 7 | 7.3 | 0 | 0 | |
*Fisher exact test; significant p<0.05.
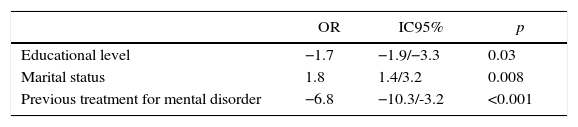
The analysis of logistic regression evidenced that marital status was positively associated with depression, and educational level and previous treatment for mental disorder were negatively associated with depression, as shown in Table 5, which means that married patients had a higher chance of having depression, and those with higher educational level and received previous specialized treatment for mental disorder had a lower chance of having depression.
Factors associated with depression among patients with chronic kidney disease in hemodialysis and conservative treatment. Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil, June–October 2015.
| OR | IC95% | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Educational level | −1.7 | −1.9/−3.3 | 0.03 |
| Marital status | 1.8 | 1.4/3.2 | 0.008 |
| Previous treatment for mental disorder | −6.8 | −10.3/-3.2 | <0.001 |
*Multivariate logistic regression; significant p<0.05.
The present study found a significant number of CKD patients with depressive symptoms, both in dialysis and conservative treatment, with no significant difference, as supposed before. Depression is the most frequent mental disorder in CKD patients on dialysis [4,5], and our study is one of the few to investigate depressive symptoms in CKD patients in conservative treatment.
The way each patient lives and interacts with CKD and its treatment is unique and personal, as it depends on several factors, including psychologic profile, social conditions, family support and others. Disease coping is influenced by patients’ perceptions about treatment and its impact on quality of life. Positive perceptions are associated with rational strategies, such as tracing a goal and knowing different aspects of the disease. Negative perceptions are associated with disease denial, as it did not exist [13]. Significant changes in CKD coping, adopting a pro-active life style and using complimentary therapies to retard dialysis start, are important to improve quality of life [14].
Depression is common not only in CKD, but in other chronic diseases, and it is frequently associated with increased risk of mortality and low adhesion to treatment [3,15]. A recent study with 1621 patients in dialysis in Brazil evidenced that the majority of them (54.5%) considered their health as poor [16]. In another study, population-based cross-sectional study, in South Brazil, there was a higher prevalence of depression among individuals with at least one chronic disease (1.4× higher risk than those without chronic diseases, and 2.2× higher risk among those with two or more chronic diseases) [17]. A significant association between the number of chronic diseases and quality of life was also found among elderly in hemodialysis [18]. The presence of various comorbidities seems to contribute to psychic suffering development, and it is associated with a bad health self-perception [16].
In the present study we have found depressive symptoms in a significant percentage of patients (more than 30% among those in dialysis and 25% among those in conservative treatment). Ferreira and Silva Filho [19], in a study with 130 patients on dialysis, found depressive symptoms in 33.8% of them (21.5% mild, 11.5% moderate and 0.7% severe). Condé et al. [15], in a cross-sectional study with 119 patients (25.2% in hemodialysis, 22.6% in peritoneal dialysis, 26.8% in conservative treatment and 25.2% only with hypertension), detected depression as independent risk factor for death among patients on dialysis. In the present study it was not possible to find association between depression and mortality, as the study period was short and it was not the primary goal. In a previous study from our study group, comparing patients on hemodialysis with and without depression, we found a high prevalence (68.2%), being 49.5% mild, 41.5% moderate and 9% severe. This higher prevalence could be attributable to worse social-conditions of that sample, which direct impact on patients’ quality of life. Varela et al. [20], in a study with 53 patients on peritoneal dialysis, identified 31.4% of them with anxiety symptoms and 35.3% with depression, a frequency similar to that found in the present study. In other studies with dialysis patients, factors associated with depression were: advanced age, female gender, presence of diabetes mellitus, laboratory tests abnormalities (low hemoglobin and albumin levels, high phosphorus levels), dialysis on the morning and educational level [21,22]. Harwood et al. [23] conducted a study to investigate socio-demographic differences in CKD coping and evidenced no significant difference between genders, although women were prone to report higher use of coping strategies.
In the present study, depressive symptoms were similar to the majority of previous studies (around 30%), confirming it as a disease frequently associated with chronic diseases [3,15,24]. Nevertheless, we have found severe depressive symptoms only among patients in dialysis, and these patients could probably have depression, but for the diagnosis of depression we would have to perform a more detailed evaluation of these patients. In our study, the percentage of patients that needs and wants specialized treatment (with Psychologist or Psychiatrist) was also high (more than 40% of interviewers), which evidences a gap in health assistance in CKD in our population. The follow-up of CKD patients by a multidisciplinary team are essential and maybe can prevent mental disorders, or at least decrease its impact on patients’ life.
Low social-economic level, present in the majority of patients in our study, demonstrate that disadvantaged populations commonly have limited access to health care, mainly when specialized care is required. It is also true for other chronic diseases [17]. In general, individuals that are prone to develop CKD had low socio-economic status, low educational level and are frequently unemployed, which per se are factors that can be associated with depression. Barreto et al. [25], in a large multicentric cohort in Brazil (the “ELSA-Brasil” study), found a CKD prevalence of 8.9%, and it was associated with low socio-economic level, black/”pardo” (Brazilian miscegenation)/indigenous race and low educational level. It is believed that financial difficulties faced by these people contribute to development of depressive symptoms or to worsen previous mental disorders.
Despite being largely explores, the issue of depression in CKD is inexhaustible. The increasing incidence of CKD all over the world and prevalence of hemodialysis as the main renal replacement therapy method bring out new requirements for healthcare, such as Psychologist/Psychiatrist careful follow-up, for both patients in conservative or dialysis treatment.
In summary, we have found a high prevalence of depressive symptoms among CKD patients in different modalities of treatment. It was associated with social conditions (low educational levels and marital status) and previous diagnosis of mental disorder (patients with previous diagnosis and treatment for mental disorder had a lower chance of having depressive symptoms) in the entire population studied. Our results also points to a sub-diagnosis of depression and other Psychiatric diseases among patients with CKD. A more careful investigation of mental disorders and more careful approach and follow-up of these patients are urgent required. Further studies, with different designs (such as longitudinal cohort), are also important to better characterize all risk factors for depression in CKD.
5Ethical disclosures5.1Protection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the relevant clinical research ethics committee and with those of the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
5.2Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
5.3Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
6Financial supportThis research was supported by the Edson Queiroz Foundation/University of Fortaleza (UNIFOR).
7Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.