Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSP) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by persistent infection with measles virus.1 It is characterised by progressive cognitive and motor impairment and associated with myoclonus.1,2 The condition is rarely observed in adult patients; when this does occur, SSP manifests with atypical symptoms.3
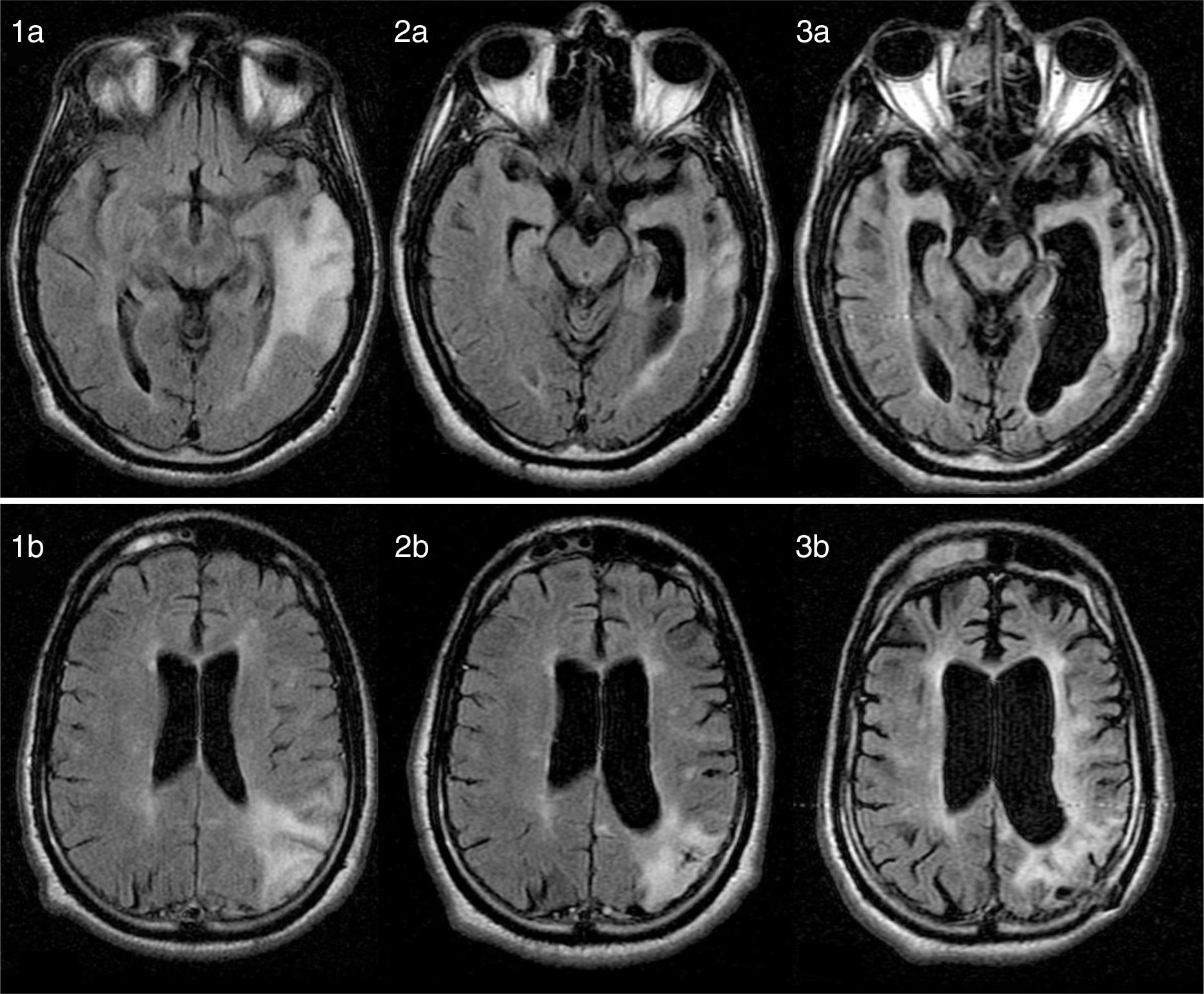
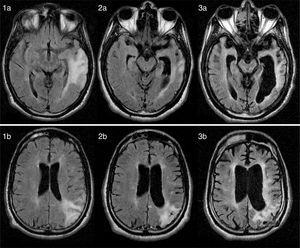
We present the case of a 25-year-old man with no relevant medical history who developed behavioural alterations and cognitive deficits over the course of 3 years due to SSP. The initial neurological examination revealed inattention, impaired executive function, poor language fluency, motor perseveration, predominantly right-sided ideomotor apraxia, asomatognosia, agraphaesthesia, and right hemiparesis. A brain MRI scan revealed an extensive left-sided cortico-subcortical temporoparietal lesion, as well as other smaller lesions in the bilateral subcortical white matter on T2-weighted and FLAIR sequences; lesions showed no contrast uptake and the results of a cerebral angiography study were normal (Fig. 1: 1a and 1b). Serial electroencephalography revealed diffuse slowing, with theta rhythm in posterior regions and no periodic activity.
(1a and 1b) Axial FLAIR MR images (12 months after symptom onset) showing diffuse hyperintensities in cortical and subcortical regions of the parietal and temporal lobes. (2a/b, 3a/b) Axial FLAIR MR images (26 months and 8 years after symptom onset, respectively) revealing disease progression, with severe cerebellar and brainstem atrophy and a diffuse, extensive lesion to the periventricular white matter.
We excluded prion disease, autoimmune encephalopathy, inflammatory vasculopathy, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. The results from serology tests and autoimmune studies were negative. A lumbar puncture yielded the following results: one red blood cell, 51mg/dL glucose, 54mg/dL proteins, and a high IgG index (1.74) with presence of oligoclonal bands. Results from CSF polymerase chain reaction for Tropheryma whippelii and herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, and JC viruses; syphilis serology; and 14-3-3 protein determination were all negative. Radiological studies and CSF anti-neuronal antibody determinations revealed no tumours.
The clinical, imaging, and laboratory findings led to suspicion of SSP; diagnosis was confirmed by high anti-measles virus antibody titres in the serum and CSF (1:10 and 1:134, respectively). The patient had no history of infection or exposure to measles virus and had been vaccinated against the virus. In the following 6 months, the patient's clinical symptoms worsened progressively: he displayed myoclonus in the form of periodic supraversion eye movements and refractory tonic-clonic seizures. A follow-up MRI scan revealed severe cerebellar and brainstem atrophy (Fig. 1: 2a, 2b, 3a, and 3b). The patient is currently in a vegetative state, displaying akinetic mutism.
SSP typically presents during the first and second decades of life; only 100 cases of adult-onset SSP are described in the literature.4 Incidence of the condition decreased by 90% after the introduction of the measles vaccine into the vaccination schedule.5 A causal relationship between measles vaccination and SSP has not been determined. The cases of SSP described in patients vaccinated against measles virus are thought to be due to subclinical measles infection within the first year of life.1
As in our case, most cases of adult-onset SSP are not associated with a history of infection or exposure to measles virus.3 Atypical symptoms are also more frequent in adult-onset SSP.2,3 Our patient experienced progressive motor and cognitive impairment without generalised myoclonus or periodic EEG activity; these findings are typical in advanced stages of the disease.3 High anti-measles virus antibody titres in the serum and CSF confirm the diagnosis of SSP due to their high sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value.1,2 Death usually occurs 1-3 years after symptom onset; there is currently no effective treatment for the condition.2 A combination of intrathecal interferon alfa and oral isoprinosine has shown an efficacy of 30% to 35% in clinical trials.6,7 Our patient did not start treatment due to the advanced stage of the condition.
In conclusion, a diagnosis of SSP must be considered in young patients with progressive cognitive impairment. Atypical symptoms are frequent in adult-onset SSP, especially in cases with compatible serology and imaging findings.
Please cite this article as: Martins R, Peres J, Casimiro C, Valverde A. Demencia rápidamente progresiva en adulto joven como forma de presentación de panencefalitis esclerosante subaguda. Neurología. 2018;33:206–207.