Family practice is the specialty with the highest number of doctors and covers all of Portugal, but, as far as we know, no studies have been carried out on the attitudes and practices of Portuguese family practice doctors about breaking bad news. However, the attitude of these doctors may have a high impact on patients.
ObjectiveTo study the practice of family physicians on breaking bad news.
MethodsA questionnaire, specifically developed for this survey, was given to 196 doctors about 10% of the family physicians of Northern Portugal.
ResultsOne hundred fifty-nine (81%) of them participated in this study. The median age was 43 (26–64) and 108 (68%) of them were female. One hundred and seven (67%) doctors disclosed on principle the diagnosis and that rate rose to 81% when patients requested the disclosure. One hundred and two (64%) proactively questioned patients about their wish to know the diagnosis and then decided whether to convey it or not. Forty-seven 47 (30%) doctors disclosed the prognosis on principle and that rate rose to 48% when patients requested the disclosure. Seventy-three (46%) often questioned patients proactively about their wish to know the prognosis and then decided whether to convey it or not. One hundred and two (64%) doctors frequently include patients in treatment decisions. Physicians think that the disclosure may affect hope but may also give patients more control of the situation.
ConclusionFamily practitioners disclose the diagnosis of a chronic life-threatening disease often, especially at patients’ request. General practitioners do not disclose the prognosis of a life-threatening disease often, even at patients’ request.
The disclosure of information about diagnosis and mainly about prognosis of life-threatening diseases is one of the most difficult parts of being a doctor.1–3 However, most patients want to know what is happening to them and what their future is likely to be,4 although not all studies bear out this statement.5 There are many differences between countries all over the world with regard to diagnosis and prognosis disclosure practices. Even in Europe there are differences between countries, with doctors from Northern European countries being more prone to disclosure than Southern and Eastern European doctors.6–11
Family physicians play a very important role in public health systems. In fact, they are the base of national health services, which most people resort to in all phases of life to maintain their health and when they need help. Even when other specialties are needed, contact with the general practitioner or the family doctor is maintained. Usually they cover most of the national territories. Therefore, they come into contact with patients with a wide range of different diseases including life-threatening ones, such as cancer or organ failure. Some years ago, we carried out surveys on the practice of doctors at an oncological center about information disclosure,12 and on patients’ preferences and experiences with the disclosure of cancer diagnosis.13 Both studies were carried out in the Porto Center of the Portuguese Institute of Oncology. However, relative to what doctors in other specialties concerning this topic do, no studies have been carried out in Portugal, as far as we know, and general practitioners with such wide ranging activities have a great influence on the entire health system. Therefore, their practice and opinions are certainly very important, which is why we have carried out this study.
MethodsMost family medicine trainees in Northern Portugal do a one-month internship in our palliative care department. Some of these doctors, one per family practice center, were the researchers responsible for conducting the study in their center.
A questionnaire was specifically developed for this survey, based on one of the previous studies indicated above. It was evaluated by ten clinicians and modified according to their suggestions. Then the questionnaire was circulated by all the researchers involved in this survey and some of them also suggested further adjustments to the questionnaire.
The questionnaire included questions about demographic data, on informing patients and their families of diagnoses and prognoses for life-threatening diseases and involvement in treatment decisions. The questions were answered using a verbal rating scale (always, often, sometimes, rarely, never).
All family doctors dealing with patients autonomously willing to participate were included.
The variables were analyzed by proportions and means. To evaluate the existence or not of associations between categorical variables, the chi-square test was used. The level of significance was deemed to be 0.05. SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) version 24.0 statistical software was used to analyze the data. Missing data were omitted, an approach usually called listwise deletion or complete case analysis.
The protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Northern Portuguese Health Authority and authorized by the medical directors at each center.
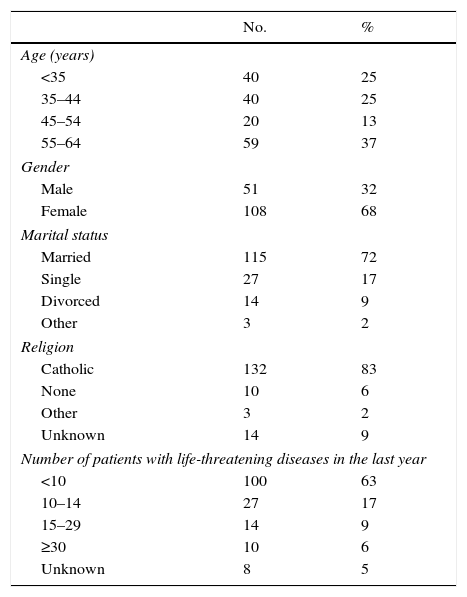
ResultsThe study was carried out in January 2013. The questionnaire was sent to 20 family health centers all over Northern Portugal. The questionnaire was delivered to 196 doctors from the about 1800 working in that region. Of these doctors, 159 (81%) participated in this study, with a range of participation between 56% and 100% of the doctors working in each center. The median age was 43 (26–64) and 108 (68%) of them were female. One hundred thirteen (71%) were married and 132 (83%) were Roman Catholic (Table 1).
Demographic data.
| No. | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| <35 | 40 | 25 |
| 35–44 | 40 | 25 |
| 45–54 | 20 | 13 |
| 55–64 | 59 | 37 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 51 | 32 |
| Female | 108 | 68 |
| Marital status | ||
| Married | 115 | 72 |
| Single | 27 | 17 |
| Divorced | 14 | 9 |
| Other | 3 | 2 |
| Religion | ||
| Catholic | 132 | 83 |
| None | 10 | 6 |
| Other | 3 | 2 |
| Unknown | 14 | 9 |
| Number of patients with life-threatening diseases in the last year | ||
| <10 | 100 | 63 |
| 10–14 | 27 | 17 |
| 15–29 | 14 | 9 |
| ≥30 | 10 | 6 |
| Unknown | 8 | 5 |
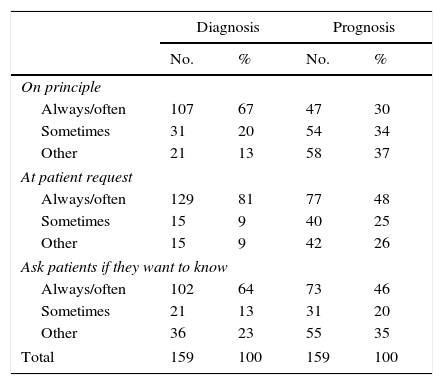
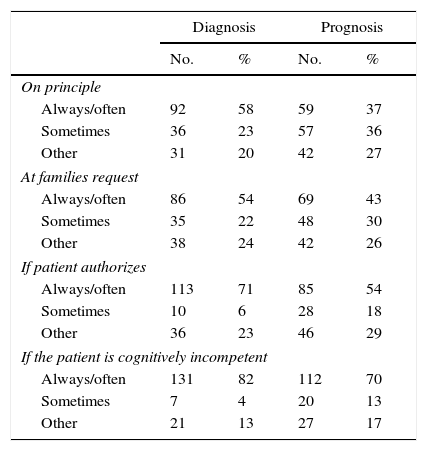
One hundred seven (67%) doctors disclosed the diagnosis on principle often or always, with a significant difference between genders: 78% of men vs. 62% of women (p=0.04). That rate rose to 81% when patients requested the disclosure. One hundred two (64%) proactively questioned patients about their wish to know the diagnosis and then decided whether to convey it or not (Table 2). Sixty-one 61 (38%) would use the term cancer often but only 11 (7%) used that word always. In this case, dividing doctors by the median age, we found that the younger ones used the term cancer more frequently than the older ones: 39 (49%) vs. 22 (28%) (p=0.02). One hundred nineteen (75%) used euphemisms at least sometimes. The word most used was tumor, 86 (54%), followed by lump, 41 (26%). 92 (58%) disclosed the diagnosis to families on principle often to always, with the older ones doing it more frequently: 53 (67%) vs. 39 (49%) (p=0.02). This percentage increases to 82% if the patient is cognitively incompetent (Table 3). For 85 (54%) the disclosure is psychologically deleterious often to always, and for 117 (74%) the disclosure has a detrimental effect on patients’ hope. On the other hand, 90 (57%) think that the disclosure gives patients control of the situation often to always and another 57 (36%) answered sometimes. In the experience of 37 (23%) doctors, families frequently ask them not to disclose the diagnosis to the patient and another 84 (53%) answered that families sometimes do that. On taking families’ opinions into account, 61 (38%) do so often to always and 75 (47%) do so sometimes.
Diagnosis and prognosis disclosure to patients.
| Diagnosis | Prognosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | |
| On principle | ||||
| Always/often | 107 | 67 | 47 | 30 |
| Sometimes | 31 | 20 | 54 | 34 |
| Other | 21 | 13 | 58 | 37 |
| At patient request | ||||
| Always/often | 129 | 81 | 77 | 48 |
| Sometimes | 15 | 9 | 40 | 25 |
| Other | 15 | 9 | 42 | 26 |
| Ask patients if they want to know | ||||
| Always/often | 102 | 64 | 73 | 46 |
| Sometimes | 21 | 13 | 31 | 20 |
| Other | 36 | 23 | 55 | 35 |
| Total | 159 | 100 | 159 | 100 |
Diagnosis and prognosis disclosure to families.
| Diagnosis | Prognosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | |
| On principle | ||||
| Always/often | 92 | 58 | 59 | 37 |
| Sometimes | 36 | 23 | 57 | 36 |
| Other | 31 | 20 | 42 | 27 |
| At families request | ||||
| Always/often | 86 | 54 | 69 | 43 |
| Sometimes | 35 | 22 | 48 | 30 |
| Other | 38 | 24 | 42 | 26 |
| If patient authorizes | ||||
| Always/often | 113 | 71 | 85 | 54 |
| Sometimes | 10 | 6 | 28 | 18 |
| Other | 36 | 23 | 46 | 29 |
| If the patient is cognitively incompetent | ||||
| Always/often | 131 | 82 | 112 | 70 |
| Sometimes | 7 | 4 | 20 | 13 |
| Other | 21 | 13 | 27 | 17 |
Fourty-seven (30%) doctors disclose the prognosis on principle often or always and 54 (34%) do so sometimes. The rate of doctors who often disclose the prognosis rose to 48% when patients requested the disclosure. Seventy-three (46%) often questioned patients proactively about their wish to know the prognosis and then decided whether to convey it or not (Table 2). When disclosing the prognosis, 120 (76%) doctors do not try to give a precise time to death (e.g. 3 months) but they try to give an idea which would be useful. Fifty-nine (37%) disclosed the prognosis to families on principle often to always and 57 (36%) do so sometimes; 23 (15%) doctors only do that with the patients’ authorization. The percentage of doctors who disclose the prognosis often to always increases to 70% if the patient is cognitively incompetent (Table 3). For 69 (43%) the disclosure is psychologically deleterious often to always and another 72 (45%) answered sometimes. For 43 (27%) the disclosure has a detrimental effect on patients’ hope often to always; the older ones have that opinion more often than the younger ones: 29 (37%) vs. 14 (18%) (p=0.023). On the other hand, 69 (43%) think that the disclosure gives patients control of the situation often to always and another 61 (38%) answered sometimes. Forty-five (28%) doctors answered that families frequently ask them not to disclose the prognosis to the patient; the older ones gave that answer more often than the younger ones: 28 (35%) vs. 17 (21%). Fifty (31%) take the families’ opinion into account often to always and 85 (54%) do so sometimes.
Treatment decisionOne hundred eleven (70%) doctors say that patients often ask questions about the treatment they will be submitted to. One hundred two (64%) doctors include patients in treatment decisions often or always. One hundred four (65%) doctors say that families often ask questions about treatment. The families are usually included in treatment decisions by 52 (33%) of the doctors and this rate rises to 72% if the patient is cognitively incompetent. Only 13 (8%) think that the involvement of the patients in treatment decisions has a negative psychological impact, while 106 (67%) think that the involvement gives patients’ control of the situation.
Physicians’ demographic variables had no significant influence on their attitudes about the involvement of patients and families in treatment decisions.
DiscussionIn this study, 67% of the family physicians disclose the diagnosis of a life-threatening disease such as cancer on principle. This percentage is much higher than the 31% of oncologists in the study carried out about 13 years ago.12 The percentage of patients who are proactively questioned about their desire for information is also reasonable. This topic cannot be directly compared with the former study, but the results suggest that that practice was not common. Even if the usual practice now is to disclose more often, most doctors avoid the word cancer, using euphemisms. Curiously, the term most used was tumor, which seems to be close to cancer. The scientific literature on this topic is contradictory with some authors favoring the use of euphemisms14 while others are against their use.1 However, those opinions are based on clinical experience and good sense not on research.
With regard to prognosis, fewer physicians convey it systematically. The results of an earlier study carried out in our hospital, although not questioned directly on prognosis disclosure, suggested that prognosis is addressed less often than diagnosis.13 This aspect seems to be universal.15,16 In fact, doctors seem more reluctant to discuss a poor prognosis than a poor diagnosis. The impact that a poor prognosis may have on patients could be an explanation, but the uncertainty about prognostication, requests from family members to withhold information and the lack of proper training in communication also play a role.15–17 However, the results of this study, surprisingly, show that doctors deemed the negative impact of diagnosis disclosure higher than that of prognosis. It is not clear why this is so. The opinion on the negative psychological impact of breaking bad news is not supported by most studies which indicate that non-disclosure has a higher probability of negatively influencing the patients’ mental health than the disclosure,4,18 but there are exceptions.19
Most doctors when disclosing the prognosis do not give a precise time to live but a general idea that can be useful for patients. This seems to be a wise attitude because the precise time that a particular patient has to live is something that nobody really knows. Therefore, trying to give a precise date for death is doomed to failure.
Many families try to prevent the disclosure of diagnosis and prognosis and many family physicians take their opinion into account. This is not rare in many countries such as those of Southern Europe.7–9 Family doctors disclose diagnosis and prognosis to families often, mainly when the patient is cognitively incompetent. However, the disclosure is not as high as it was in the former study12 when practically all families were informed. The practice of informing patients about their situation seems, however, to be generally improving.20
Patients and families ask questions on treatment often and doctors mainly include patients in treatment decisions. Families are included mainly when the patient is cognitively incompetent.
Regarding the influence of gender and age on disclosure practice, women disclose the diagnosis less often than men for unclear reasons. But what seems to be occurring is a trend of younger doctors to see the communication of bad and sad news to patients in a more positive way than the older ones.
ConclusionGeneral practitioners disclose the diagnosis of a chronic life-threatening disease often, especially at patients’ request. It is also frequent to disclose the diagnosis to family members mainly when patients are cognitively impaired. General practitioners do not disclose the prognosis of a life-threatening disease often, even at patients’ request, especially the older ones. Most doctors take the families’ request not to disclose the prognosis into account. They think that the disclosure may affect hope but may also give patients more control of the situation.
The practice of informing patients about their situation seems to be improving, mainly among younger doctors.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
This work was supported in part by the North Portugal Section of the Portuguese League against Cancer.