To determine whether the urgent embolization of a cerebral aneurysms and posterior surgery on cerebral hematomas is safe and efficacious in patients with hematomas and signs of intracranial hypertension due to the rupture of cerebral aneurysms.
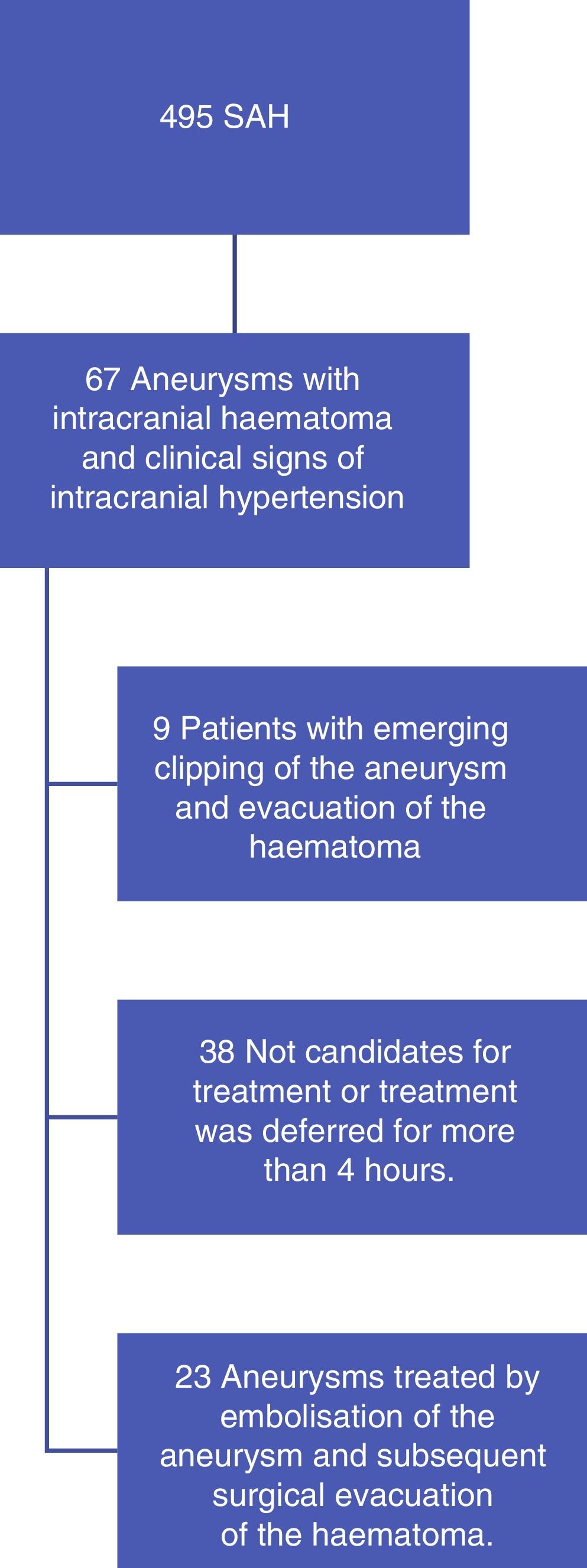
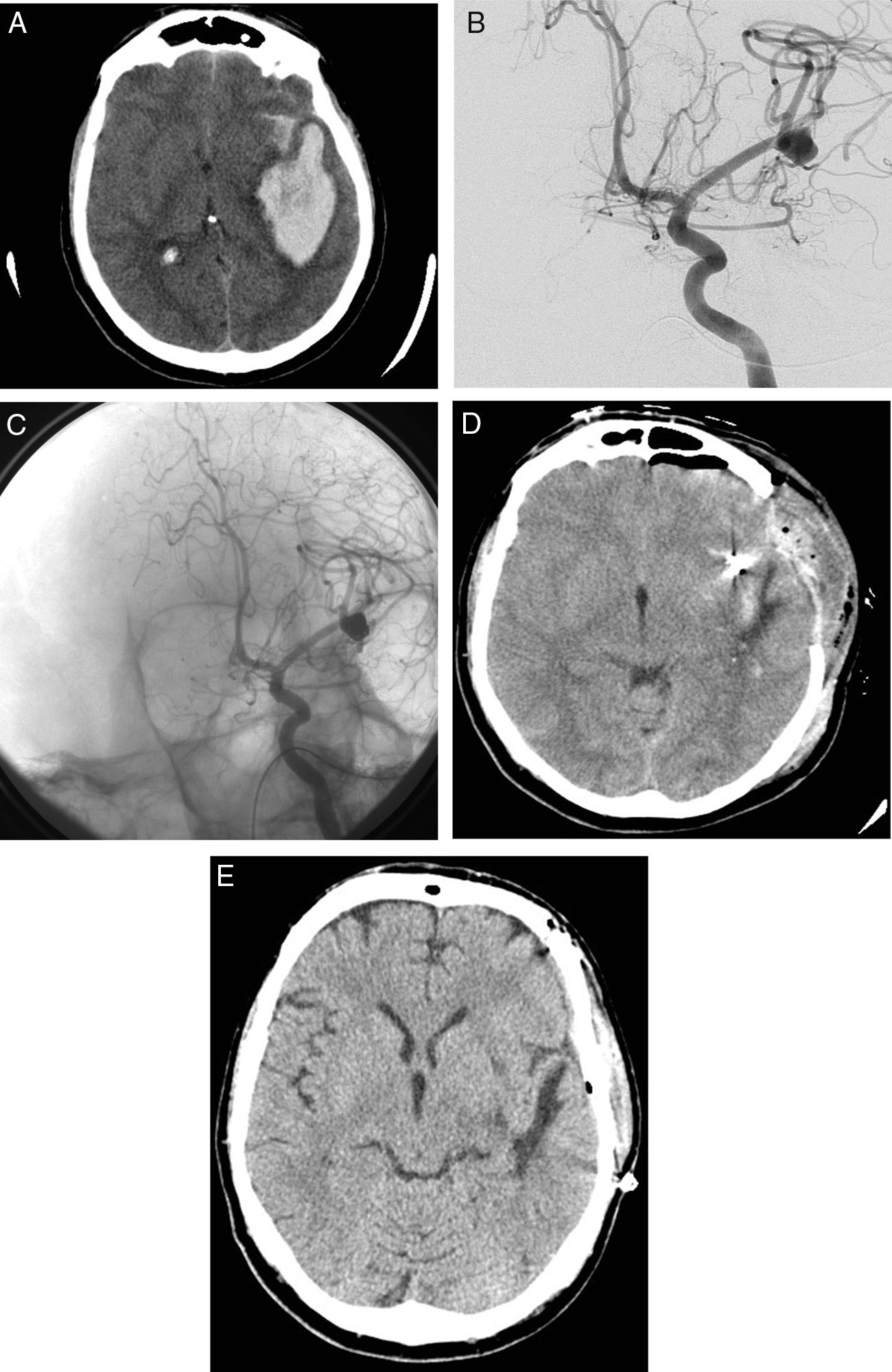
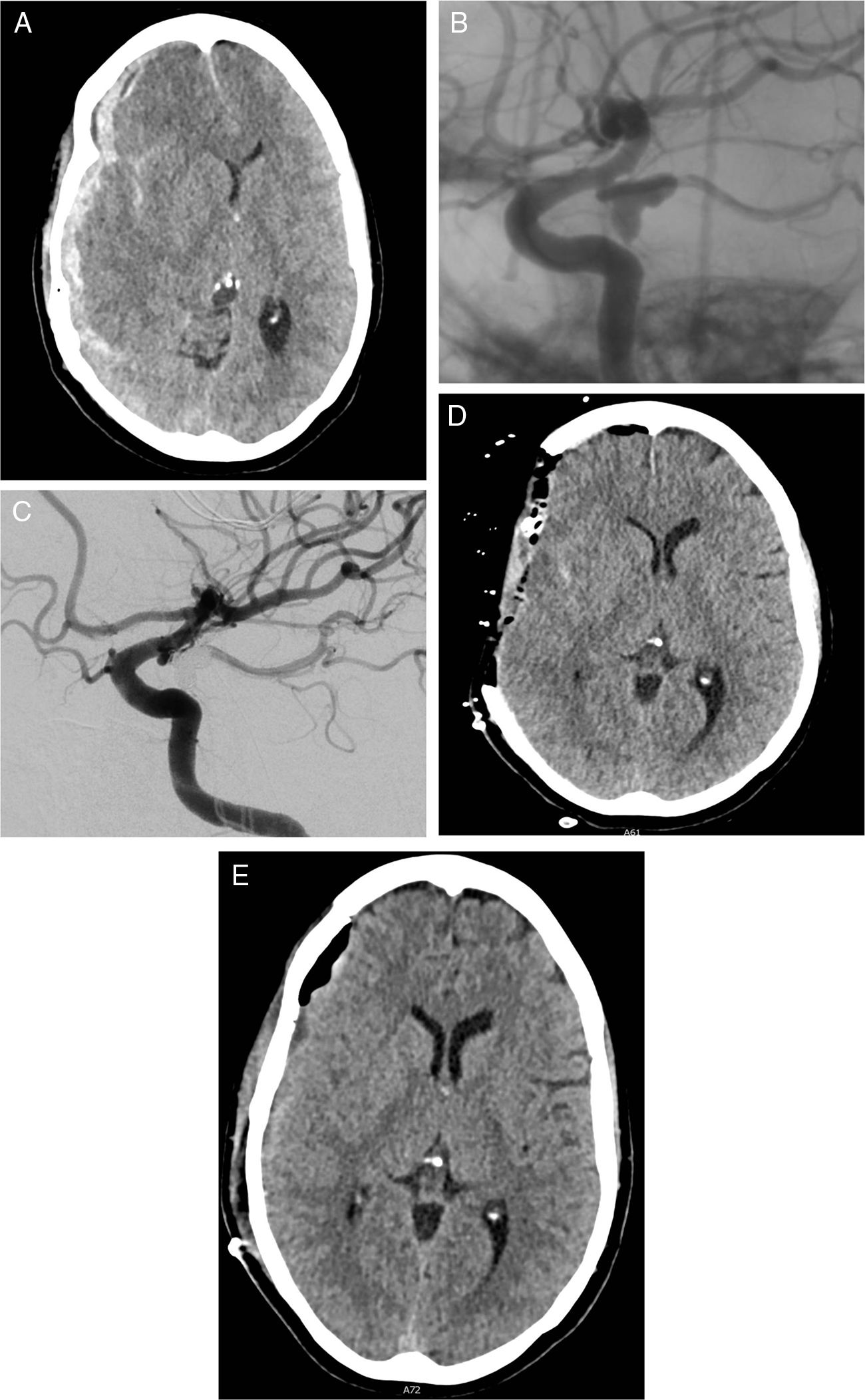
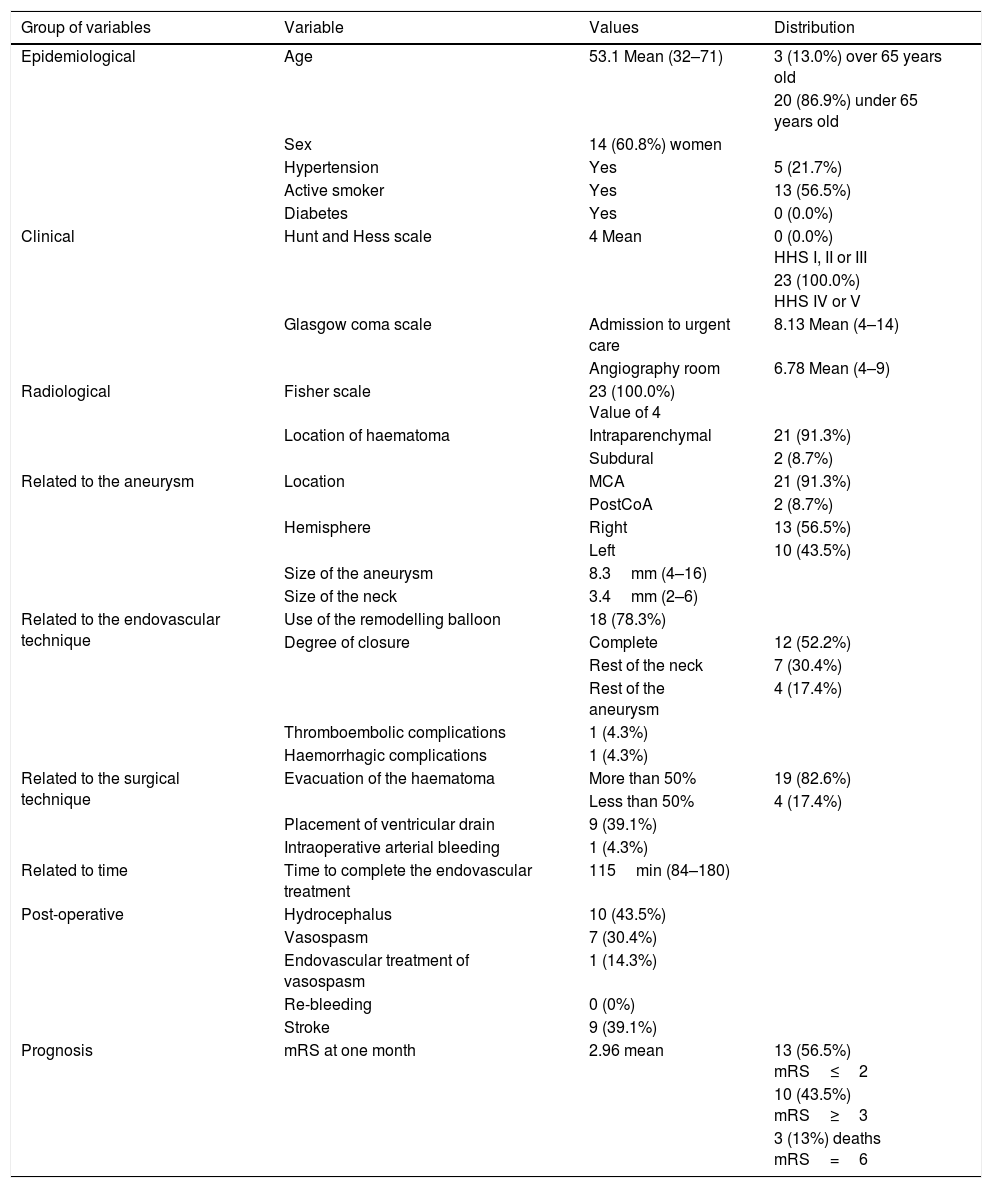
MethodsWe included 23 consecutive patients in poor clinical condition due to an intracranial hematoma caused by a ruptured cerebral aneurysm who were treated with both embolization and surgery within 4h of the onset of symptoms. All patients had clinical signs of intracranial hypertension and/or altered levels of consciousness, including coma due to rostrocaudal deterioration. We evaluated the efficacy of the combined technique by determining the degree of closure of the aneurysms and the patients’ prognosis one month after the procedures; we evaluated safety by analyzing the complications of the treatments.
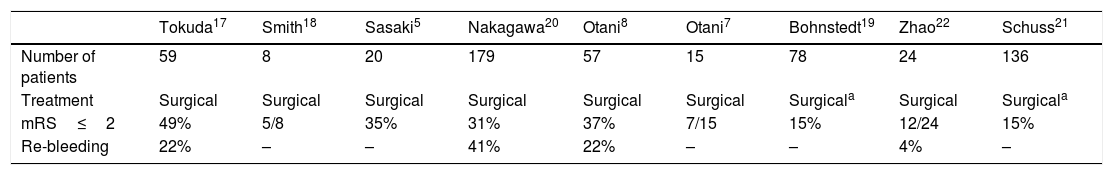
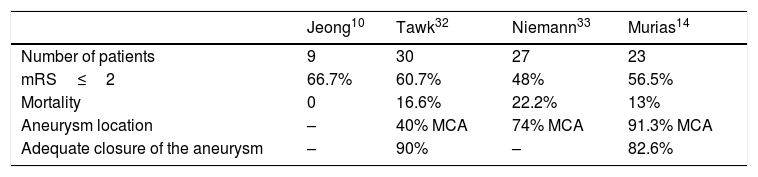
ResultsAll but two of the patients (21/23; 91.3%) had an aneurysm of the middle cerebral artery. All patients scored 4 on the Fisher scale and were classified as Hunt and Hess IV or V. The mean time from the identification of the aneurysm on computed tomography to embolization was 115min. A balloon remodelling technique was used in 18 (78%) patients; embolization achieved adequate closure in 19 (82.6%) patients. During surgery, a ventricular drain was placed in 9 (39.1%) patients. One month after treatment, 13 (56.5%) patients were functionally independent and 3 (13%) had died. No episodes of rebleeding were observed.
ConclusionIn our experience, combined treatment including embolization of the aneurysm and surgical decompression with evacuation of the hematoma is a safe and effective alternative to surgical treatment alone.
Valorar si la técnica de embolización urgente del aneurisma cerebral y posterior cirugía del hematoma es segura y eficaz en pacientes con hematoma y signos de hipertensión intracraneal por rotura de aneurisma cerebral.
MétodosSe incluyeron 23 pacientes consecutivos con aneurisma cerebral roto y mal estado clínico debido a un hematoma intracraneal, ambos tratamientos completados en las primeras 4 horas del inicio de la clínica. Todos los pacientes presentaban signos clínicos de hipertensión intracraneal y/o alteración del nivel conciencia, incluido coma por deterioro rostrocaudal. Se valoró la eficacia de la técnica mediante el grado de cierre de los aneurismas y el pronóstico de los pacientes un mes después, y la seguridad, mediante el análisis de las complicaciones de los tratamientos.
ResultadosEl 91,3% de los pacientes tenía un aneurisma localizado en la arteria cerebral media (ACM). Todos los pacientes presentaban un valour de 4 en la escala de Fisher y de IV-V en la escala de Hunt y Hess. El tiempo medio desde la identificación del aneurisma en la tomografía computarizada hasta la embolización del aneurisma fue de 115 minutos. Se usó balón de remodelling en el 78% de los casos, con el que se logró un cierre adecuado en el 82,6% de los pacientes. Durante la cirugía se colocó un drenaje ventricular en 9 (39,1%) pacientes. Al mes, 13 (56,5%) pacientes eran independientes, con una mortalidad del 13%. No existieron resangrados.
ConclusiónEn nuestra experiencia, el tratamiento combinado mediante embolización del aneurisma y descompresión quirúrgica con evacuación del hematoma es segura y efectiva, y es una alternativa al tratamiento quirúrgico aislado.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora