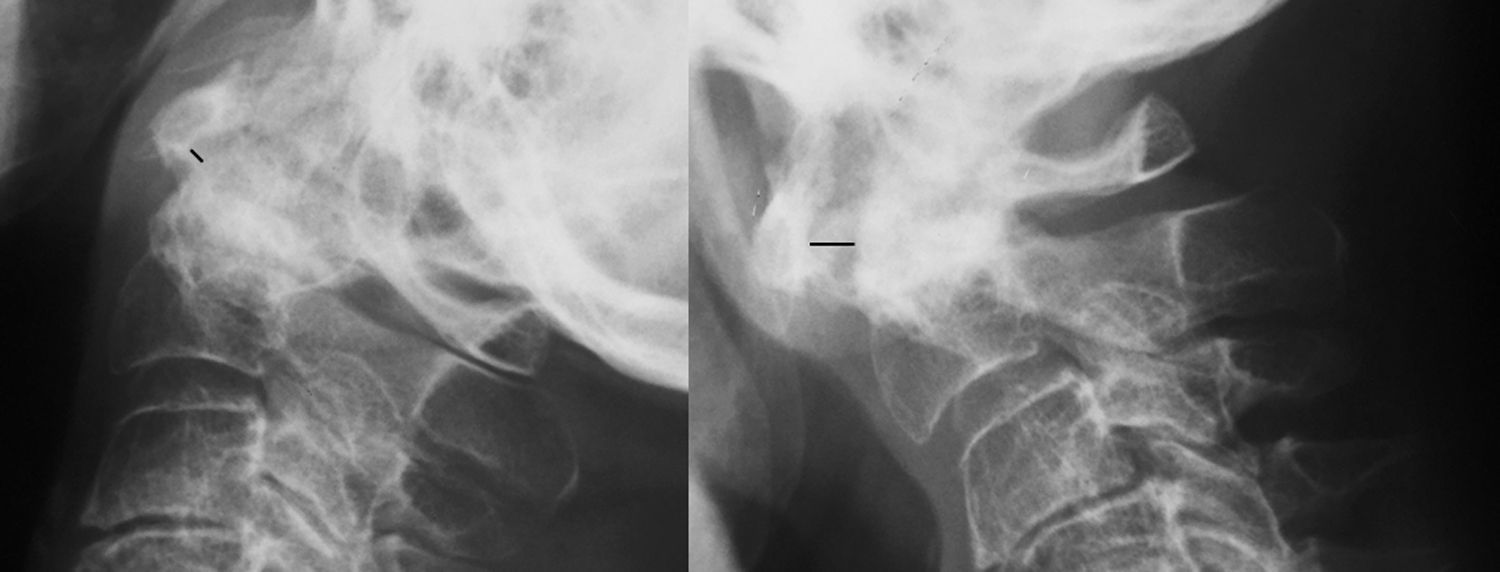
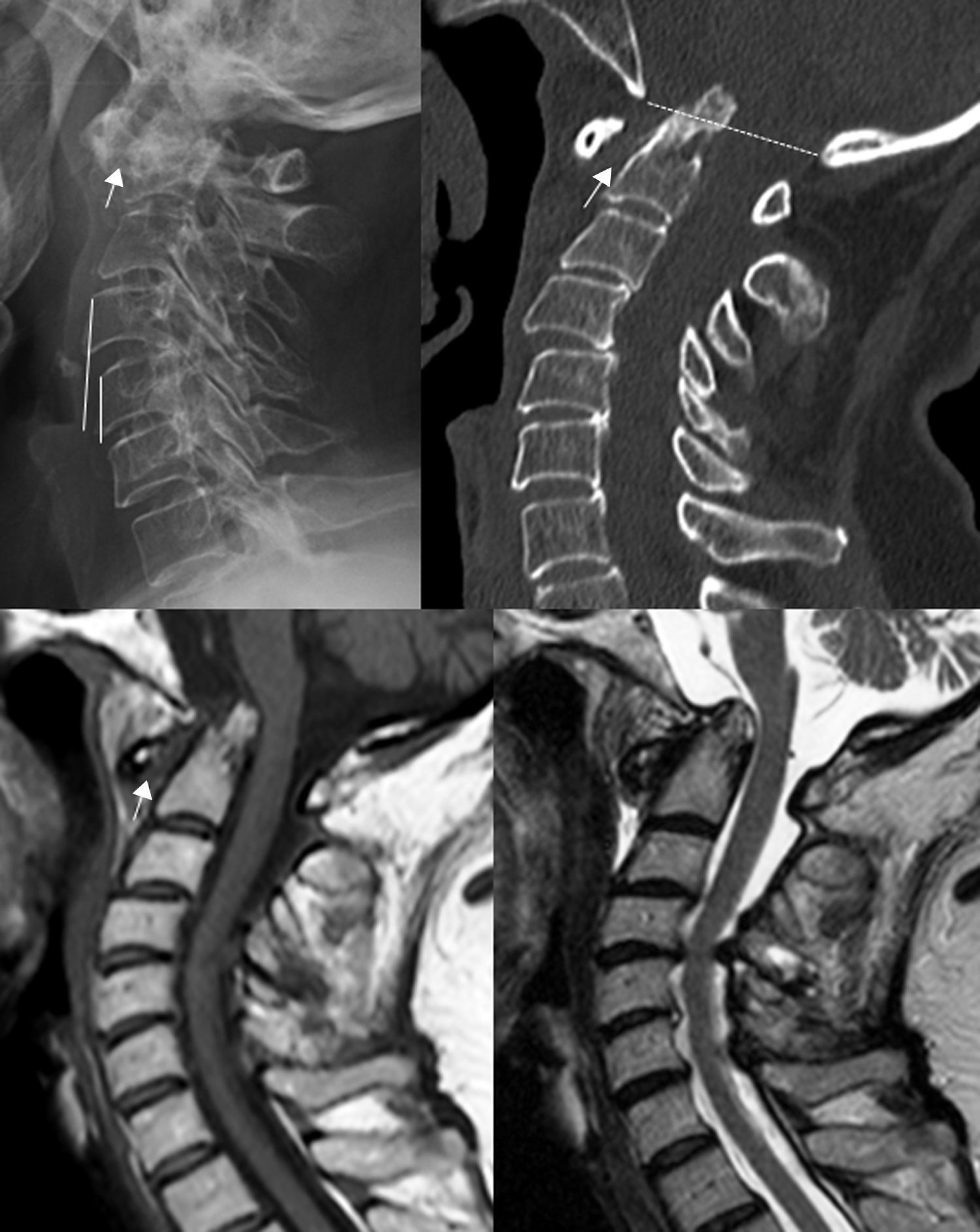
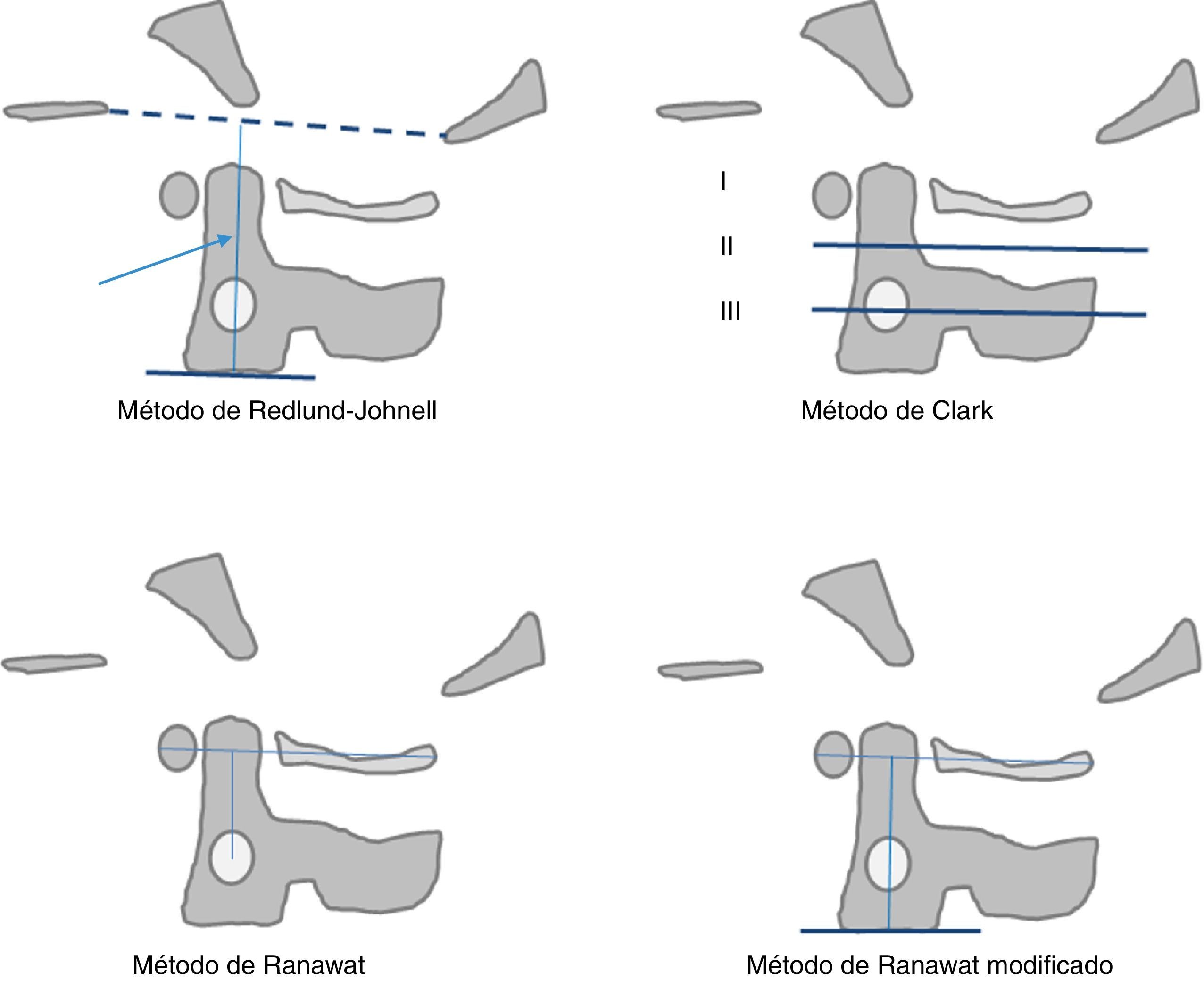
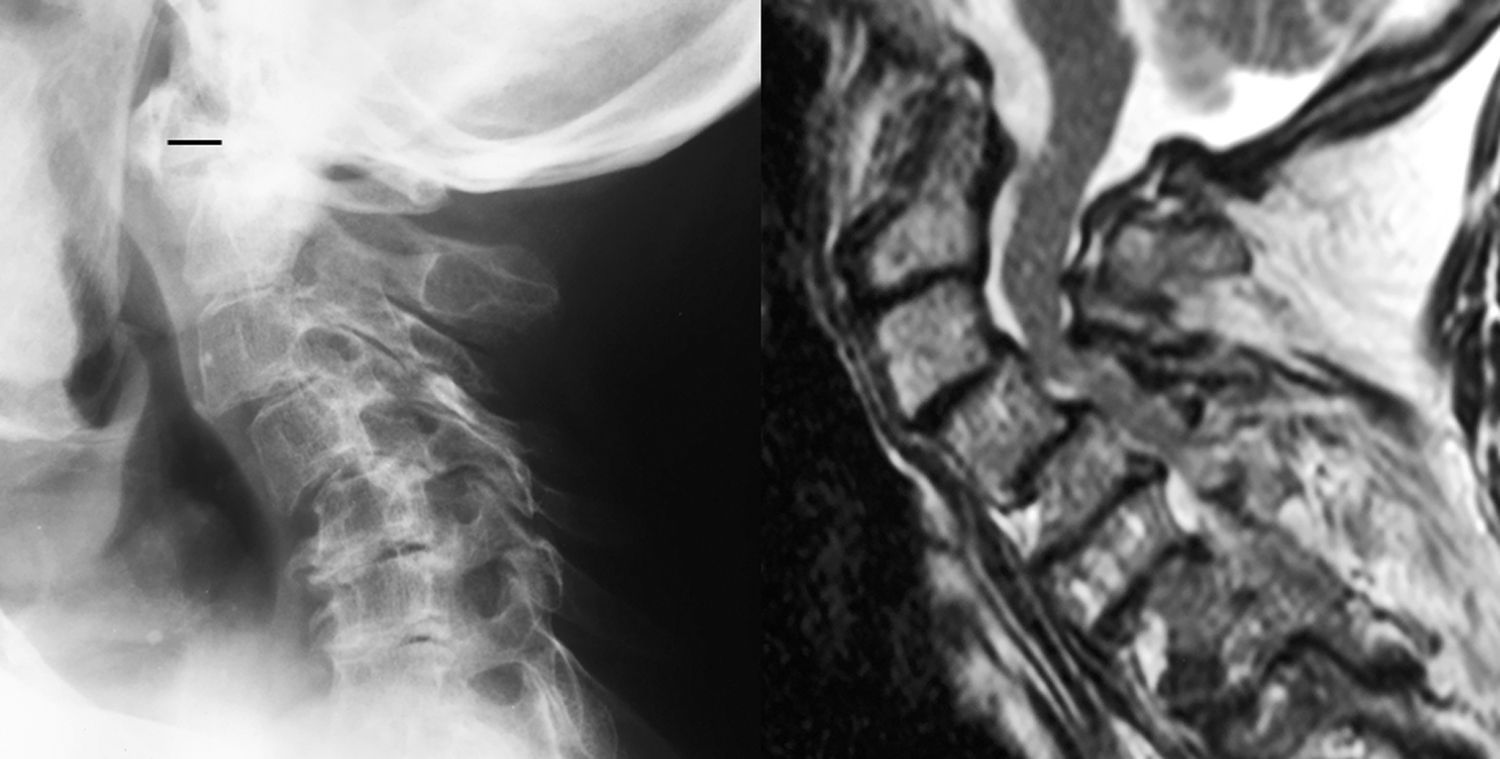
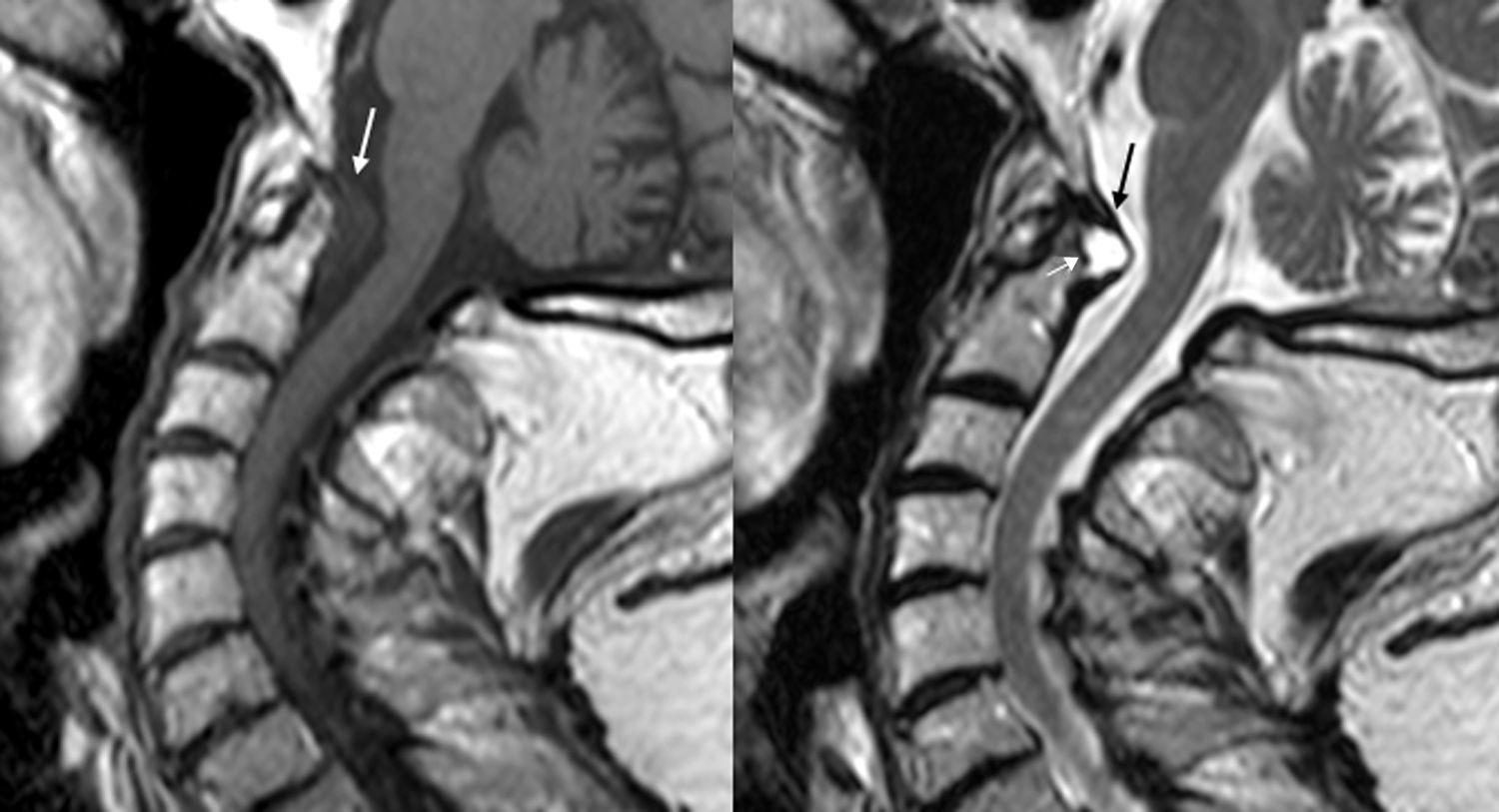
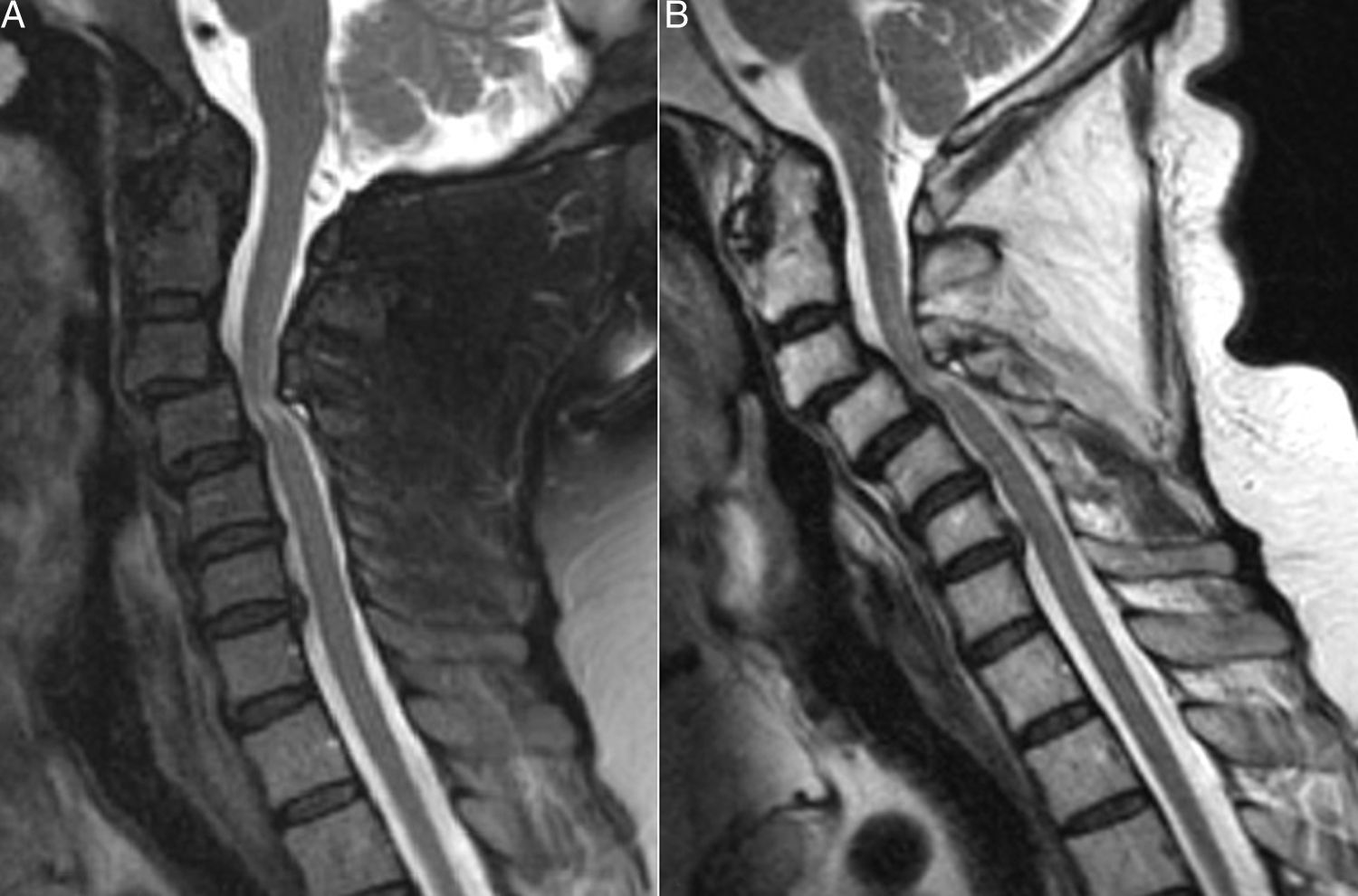
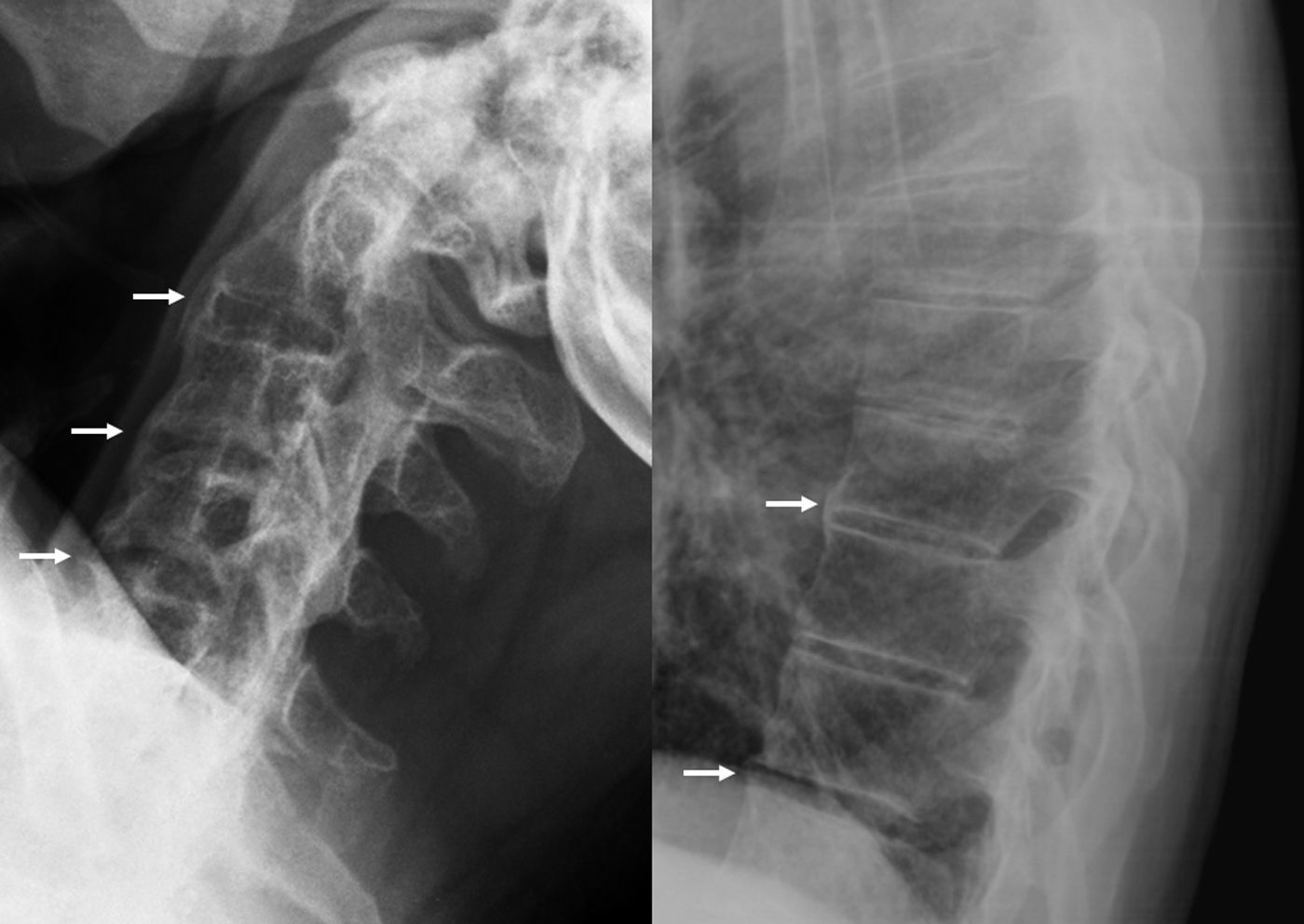
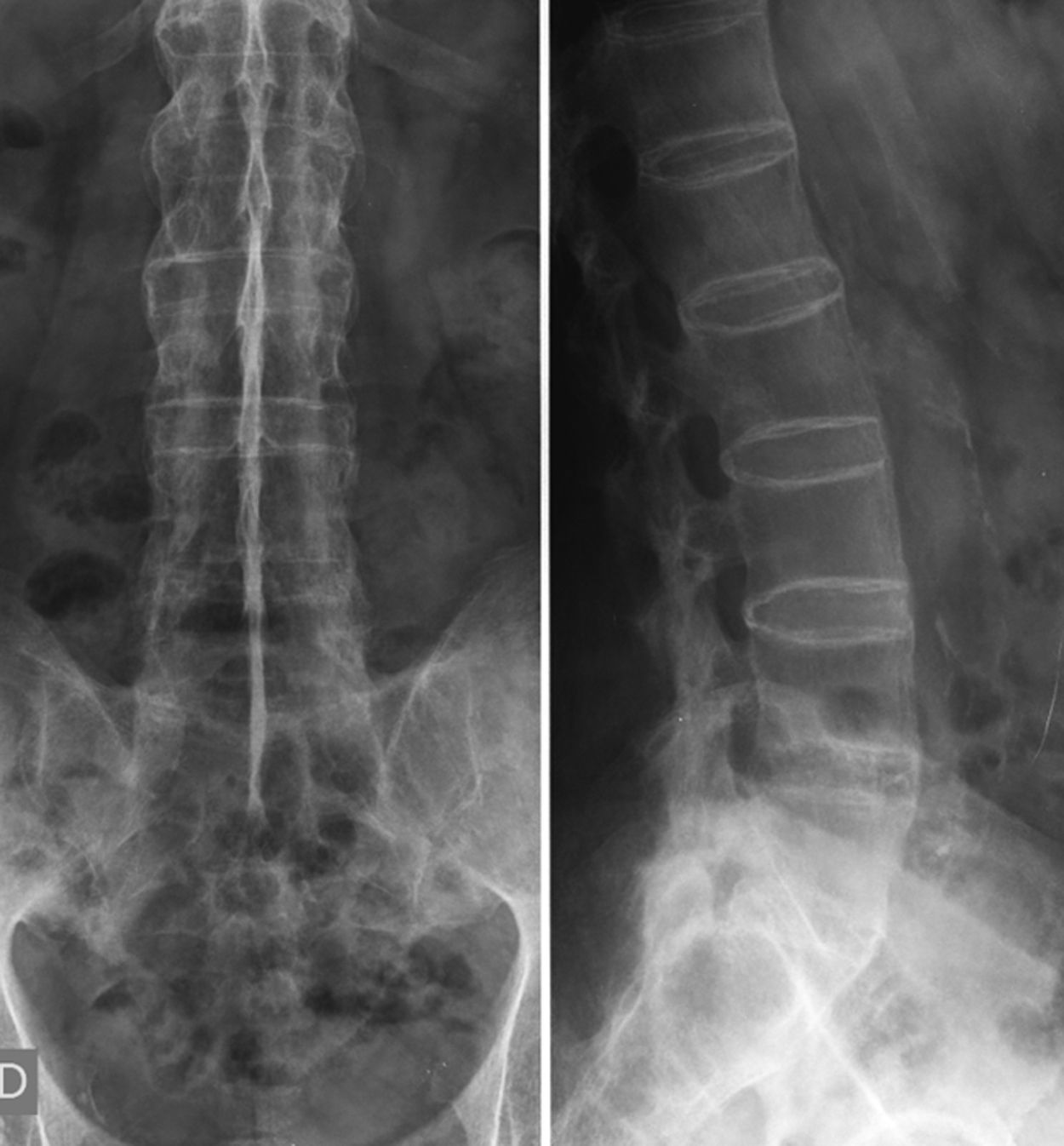
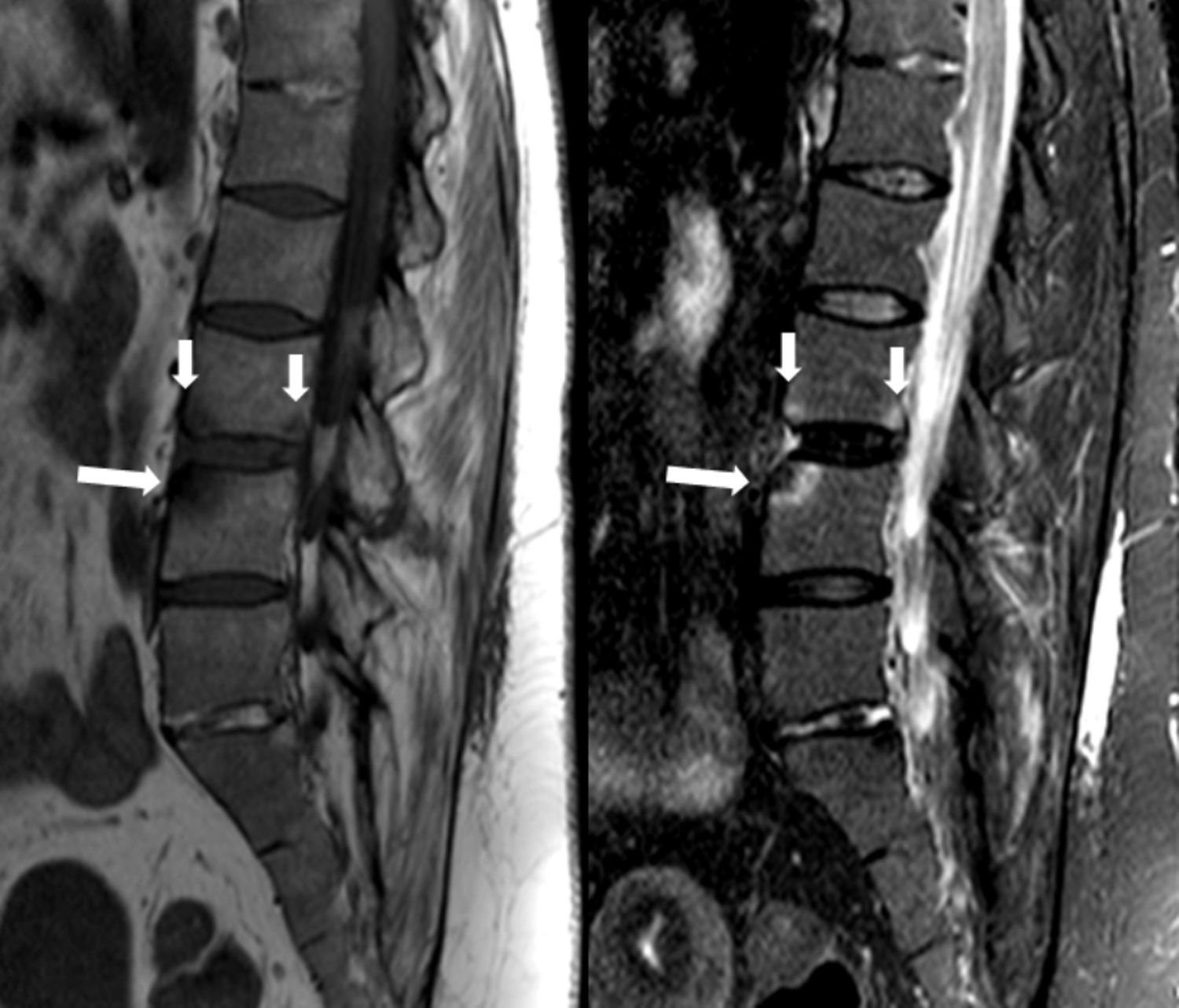
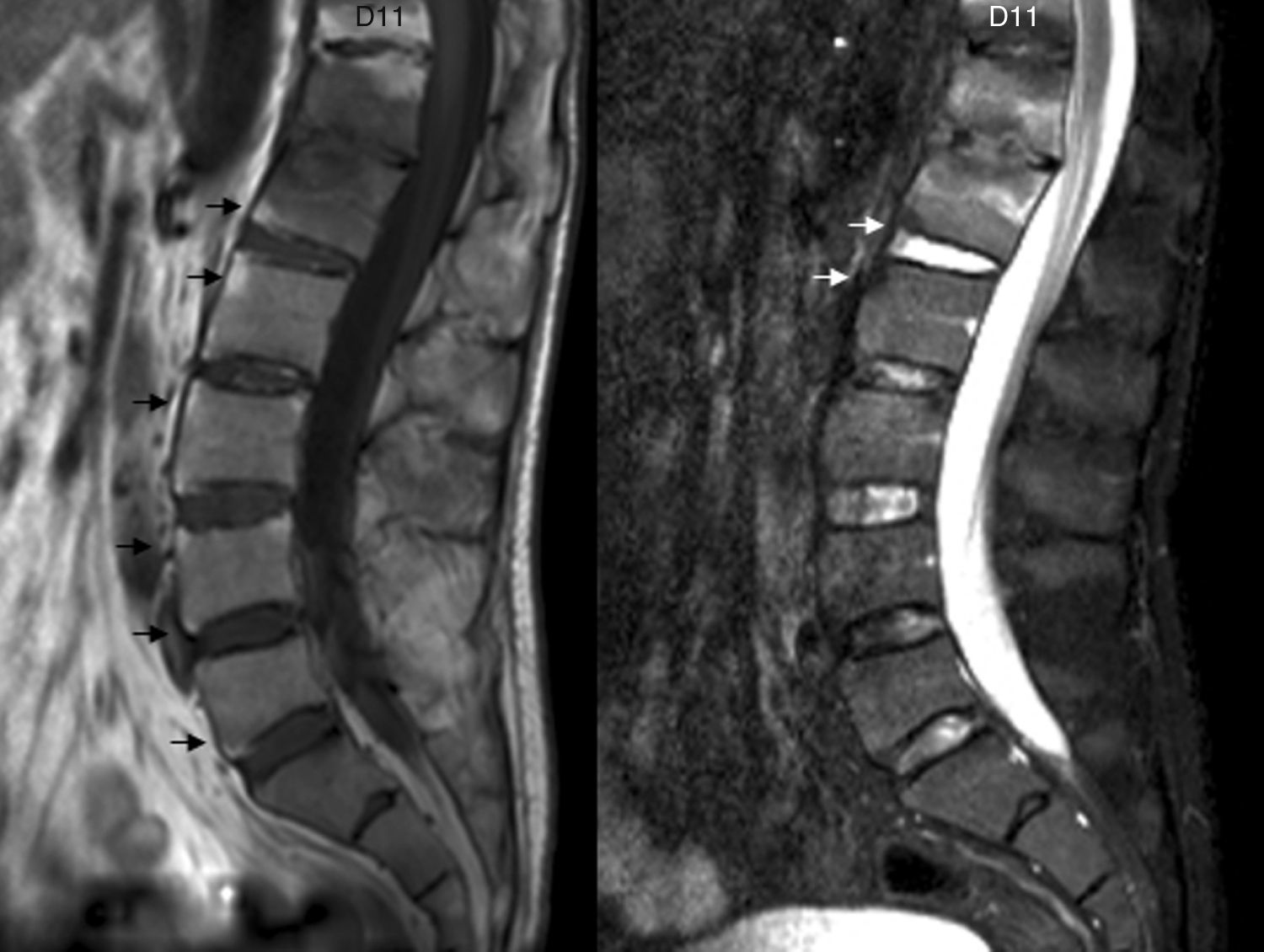
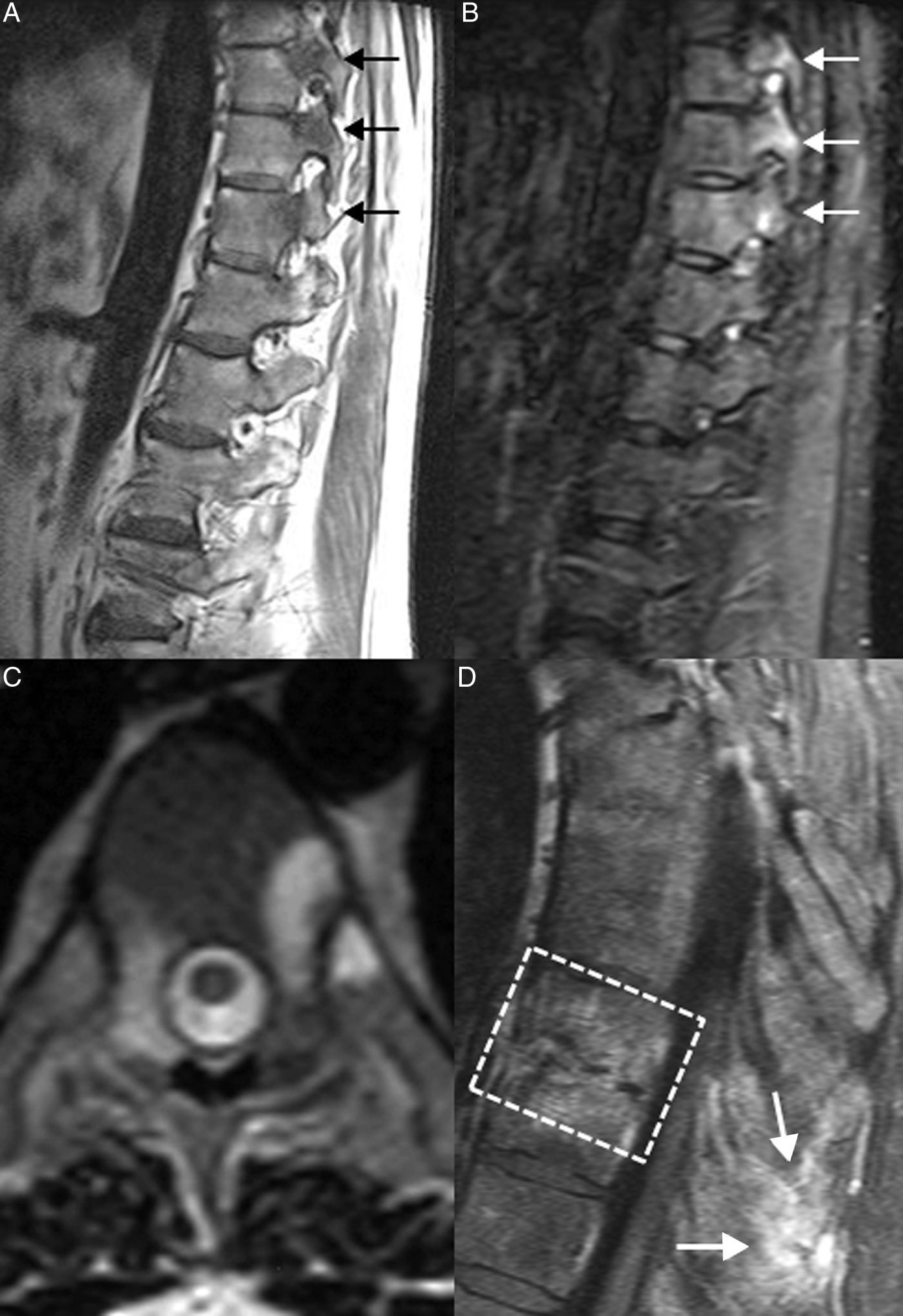
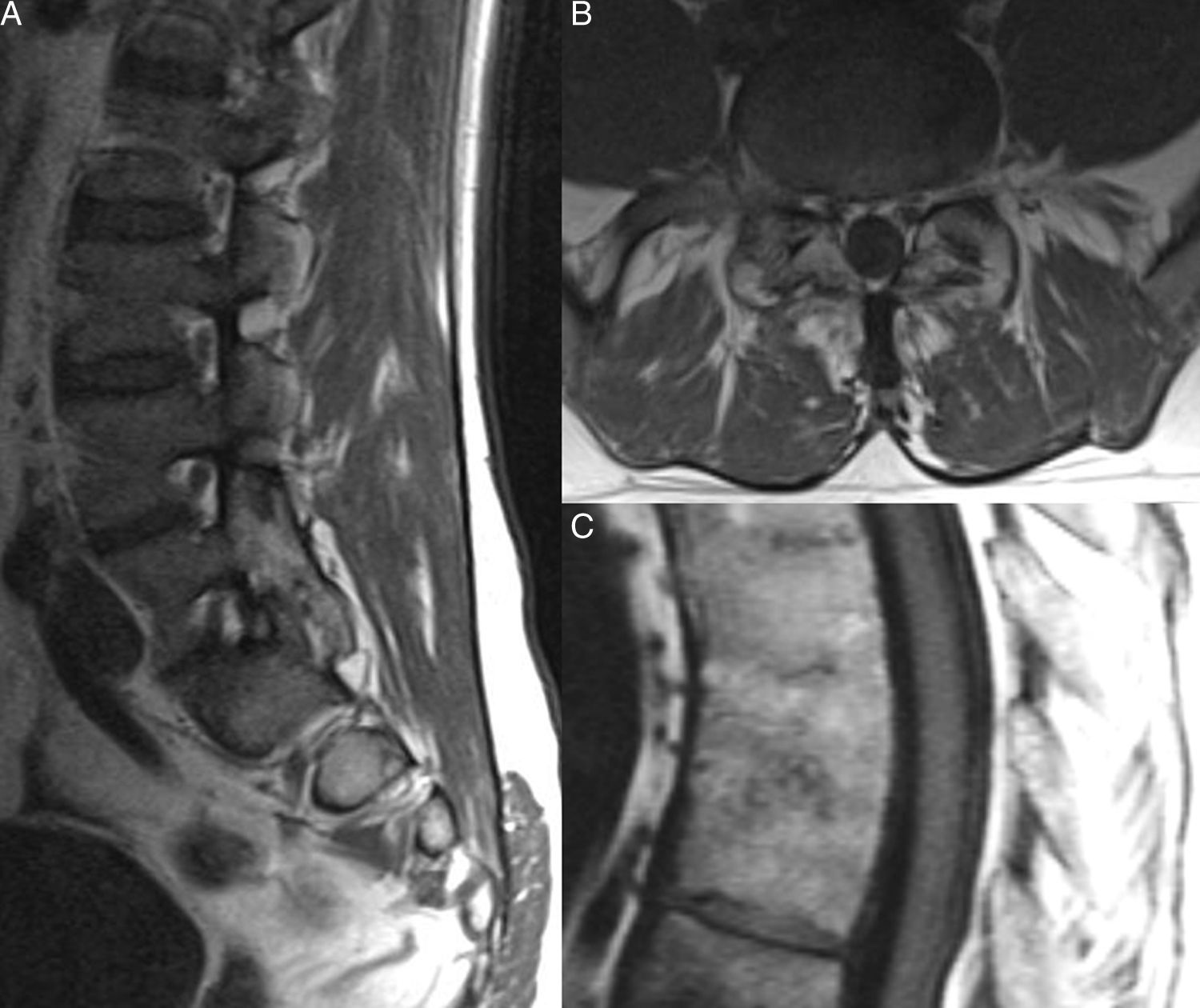
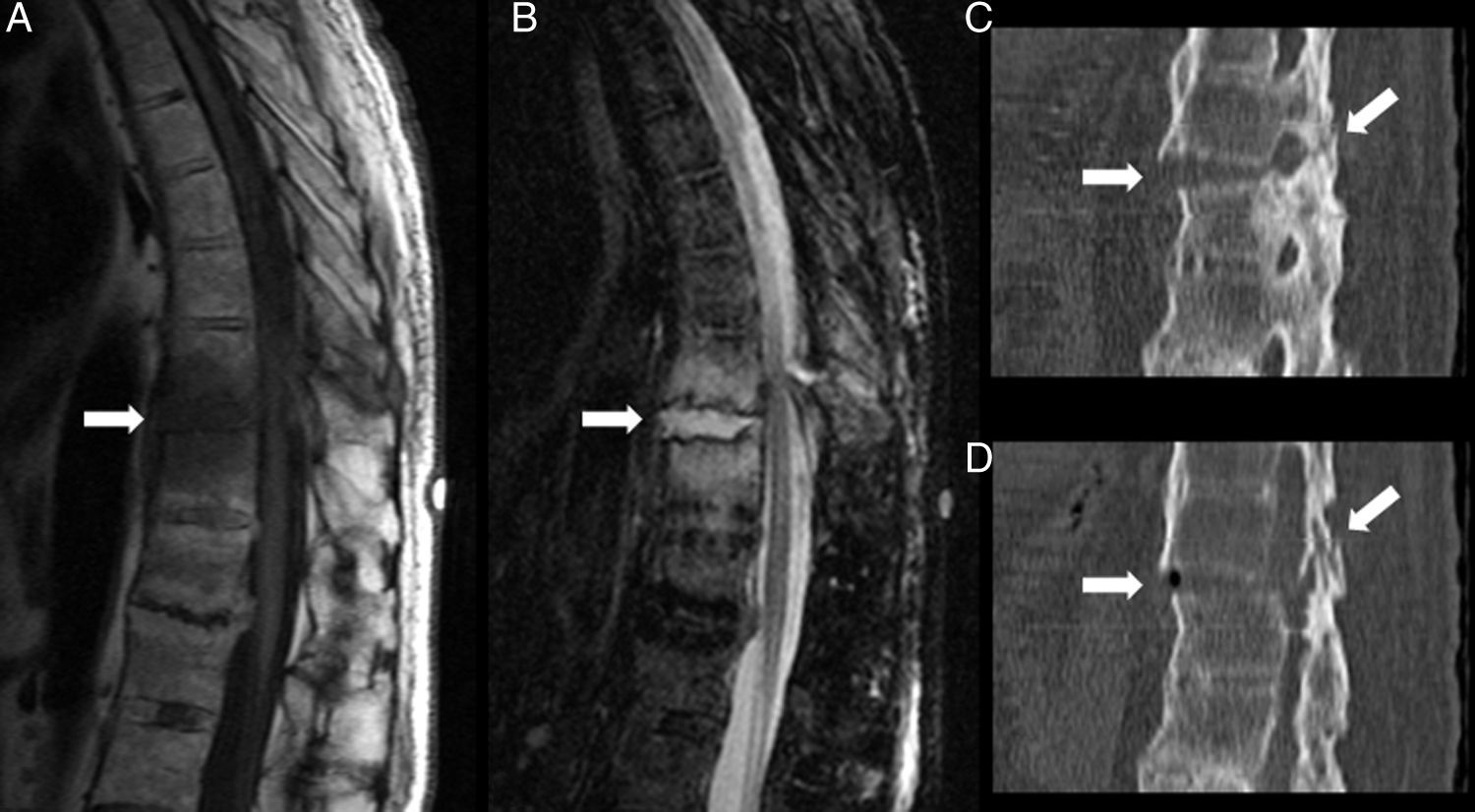
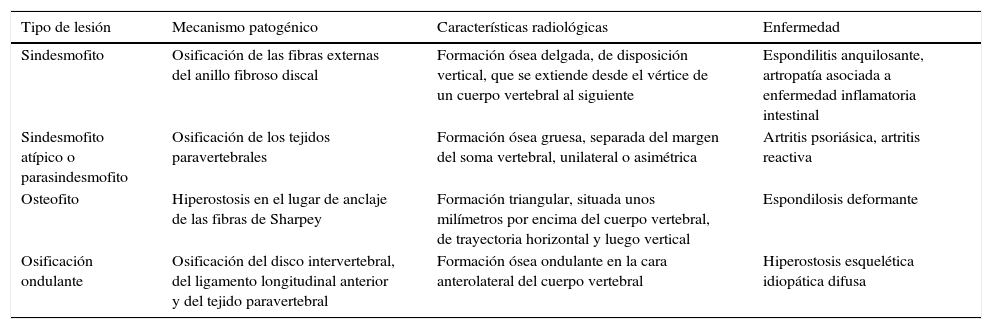
La afectación raquídea es frecuente tanto en las espondiloartritis como en la artritis reumatoide, la cual afecta selectivamente al segmento cervical. La afectación reumatoide de la columna cervical presenta unas manifestaciones radiológicas típicas, fundamentalmente en forma de varios tipos de patrones de inestabilidad articular atloaxoidea. La resonancia magnética (RM) es la técnica de elección para evaluar la posible repercusión mielorradicular de la inestabilidad atloaxoidea en los pacientes con artritis reumatoide, así como para evaluar parámetros indicativos de inflamación activa, como el edema óseo y la sinovitis. La afectación axial es característica en las espondiloartritis y presenta unas manifestaciones radiográficas distintivas, que reflejan fenómenos destructivos y reparativos. El uso de la RM ha cambiado la concepción de la espondiloartritis al conseguir detectar de manera directa los cambios inflamatorios propios de la enfermedad, permitiendo establecer un diagnóstico precoz cuando las radiografías son normales (espondiloartritis axial no radiográfica), evaluar el pronóstico de la enfermedad y contribuir a la planificación del tratamiento.
Spinal involvement is common both in the spondyloarthritides and in rheumatoid arthritis, in which the cervical segment is selectively affected. Rheumatoid involvement of the cervical spine has characteristic radiologic manifestations, fundamentally different patterns of atlantoaxial instability. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the technique of choice for evaluating the possible repercussions of atlantoaxial instability on the spinal cord and/or nerve roots in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as well as for evaluating parameters indicative of active inflammation, such as bone edema and synovitis. Axial involvement is characteristic in the spondyloarthritides and has distinctive manifestations on plain-film X-rays, which reflect destructive and reparative phenomena. The use of MRI has changed the conception of spondyloarthritis because it is able to directly detect the inflammatory changes that form part of the disease, making it possible to establish the diagnosis early in the disease process, when plain-film X-ray findings are normal (non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis), to assess the prognosis of the disease, and to contribute to treatment planning.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora