Definir el concepto de microhemorragia cerebral y revisar las secuencias de resonancia magnética (RM) utilizadas para su valoración.
Revisar cuáles son las patologías que presentan microhemorragias y que pueden beneficiarse del uso de secuencias de susceptibilidad magnética (SWI).
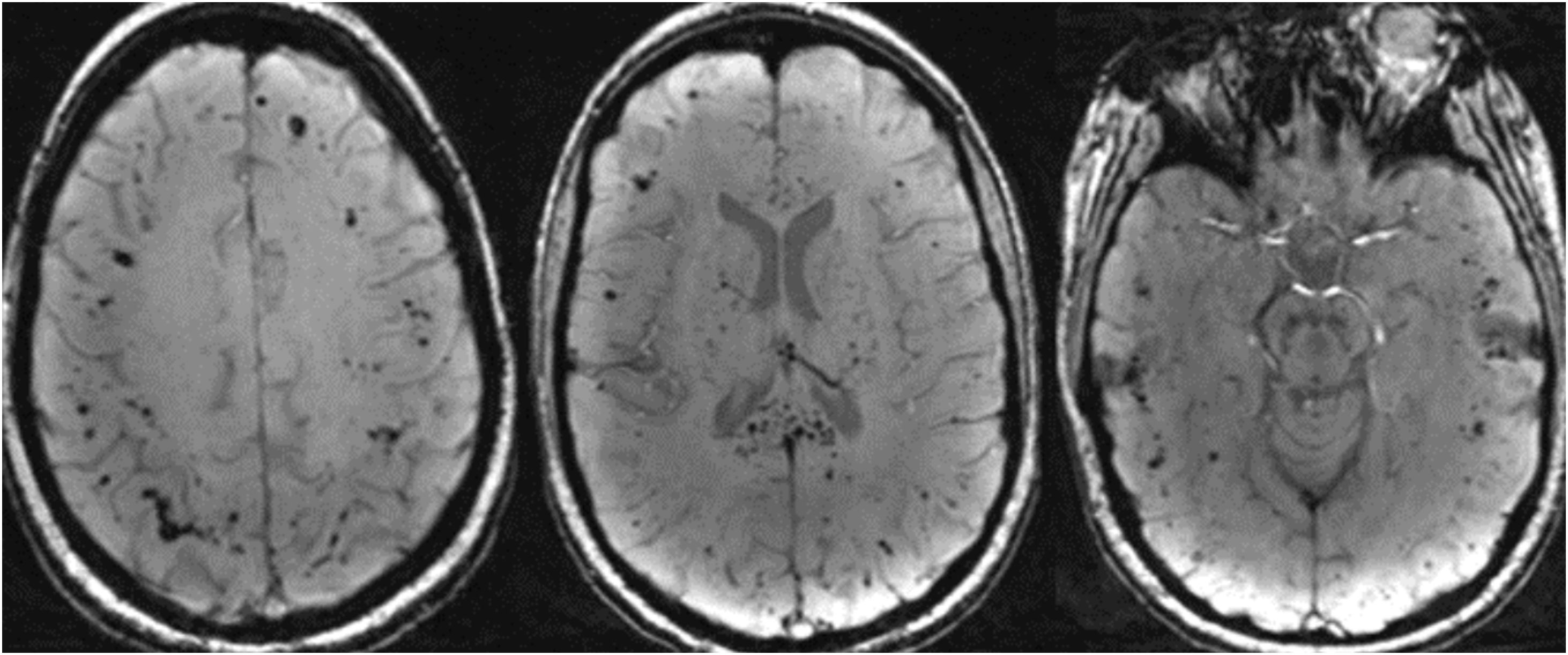
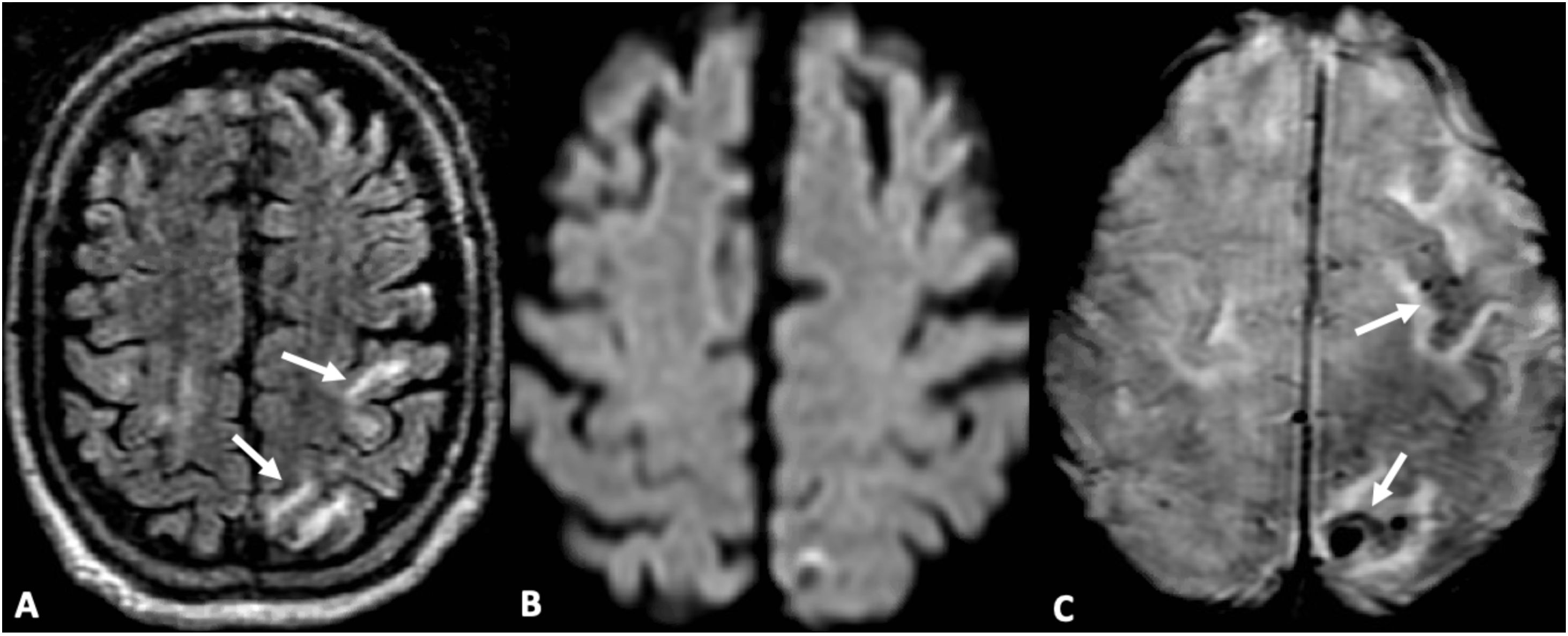
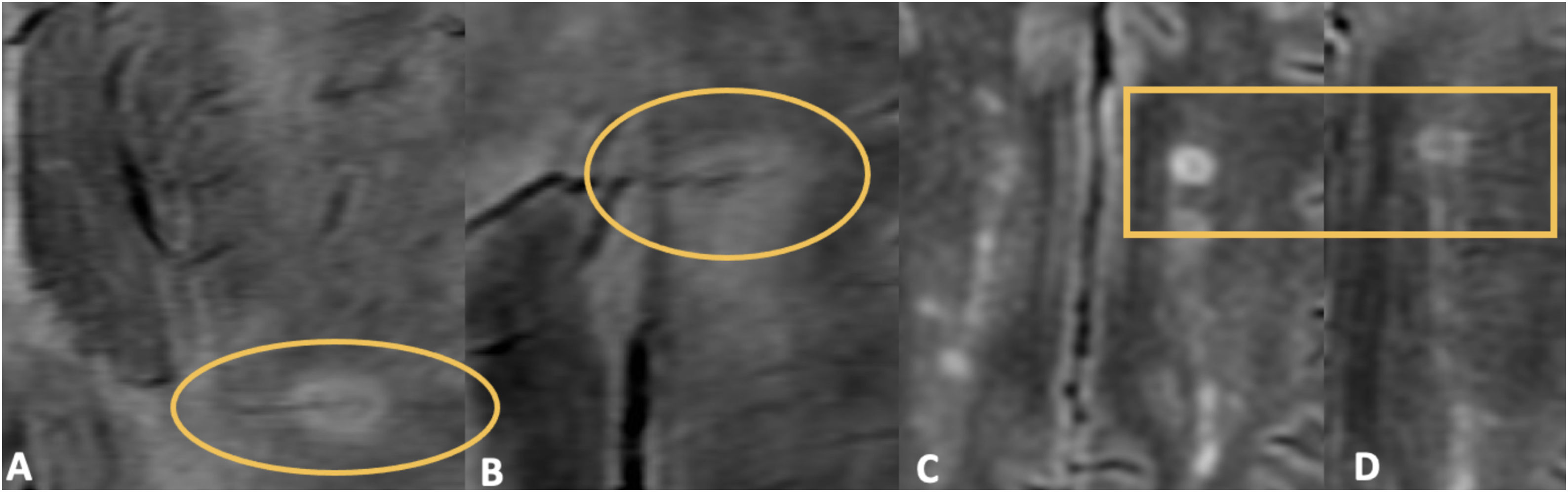
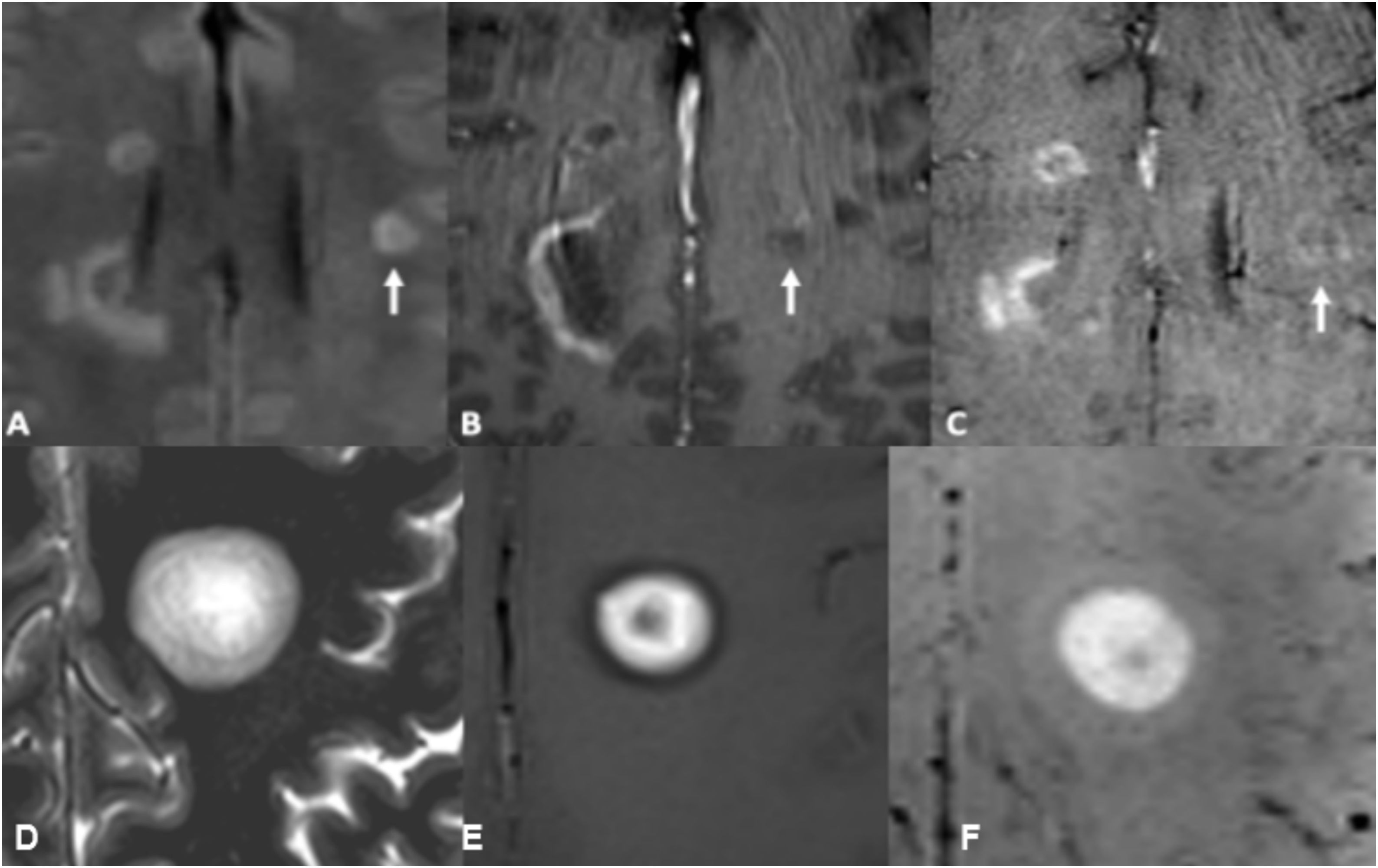
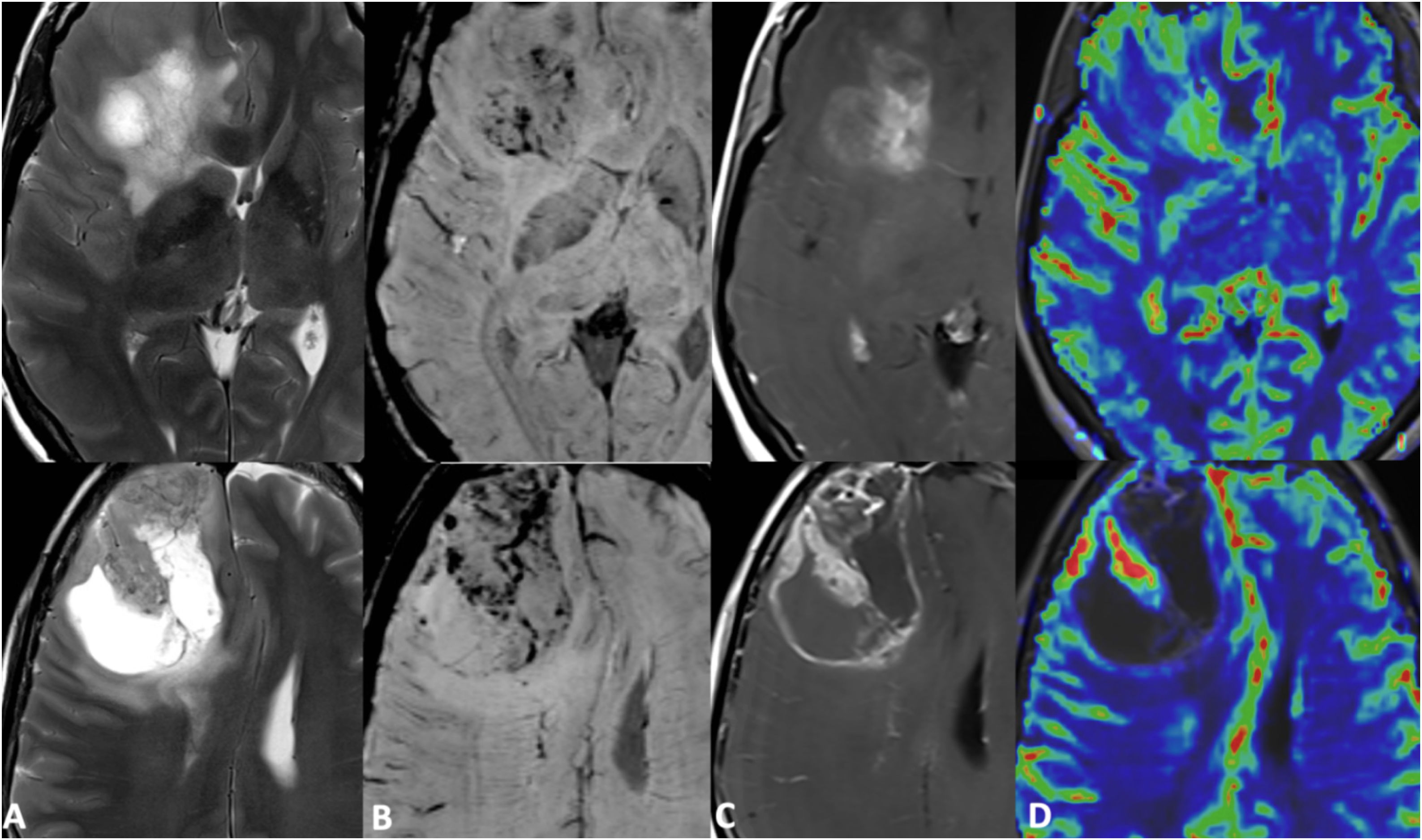
ConclusiónLas SWI son útiles en la detección y caracterización de microhemorragias, venas y otras fuentes de susceptibilidad.
La secuencia SWI mejora la sensibilidad diagnóstica con respecto a las secuencias convencionales potenciadas en T2* (eco de gradiente T2* [2D-GRE]).
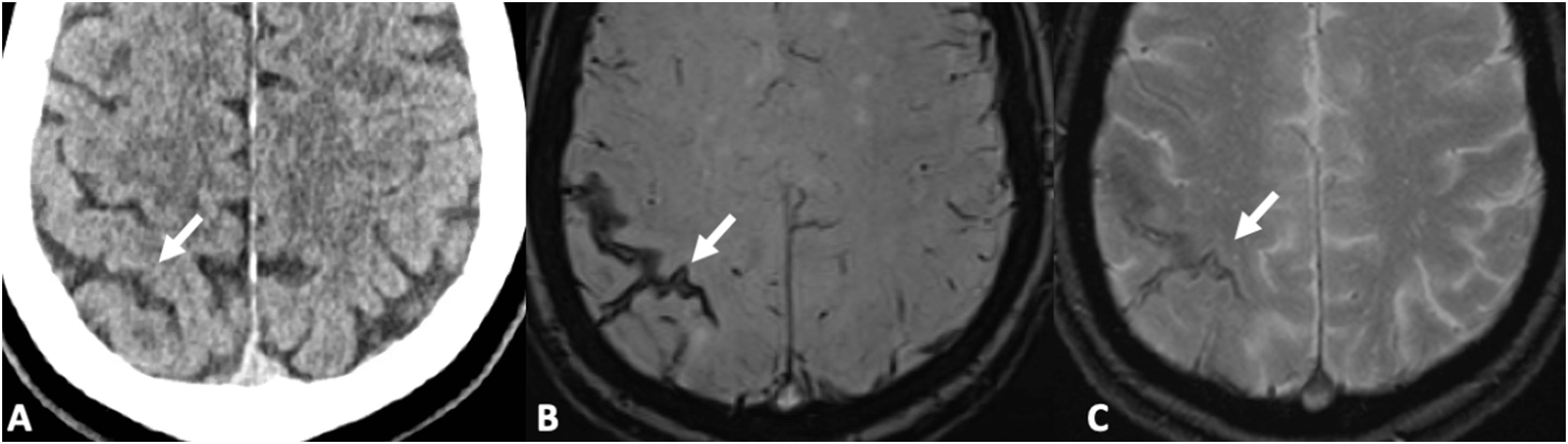
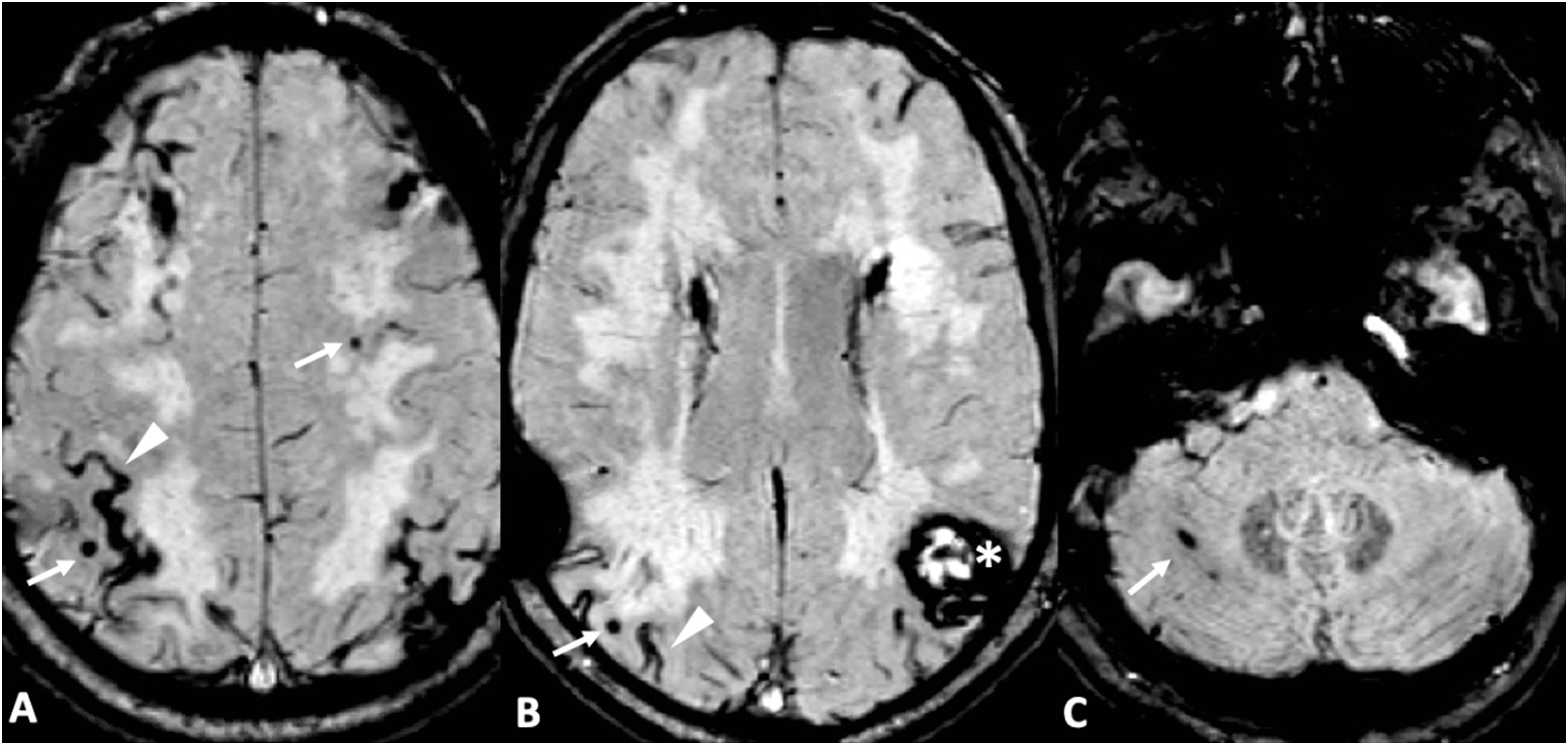
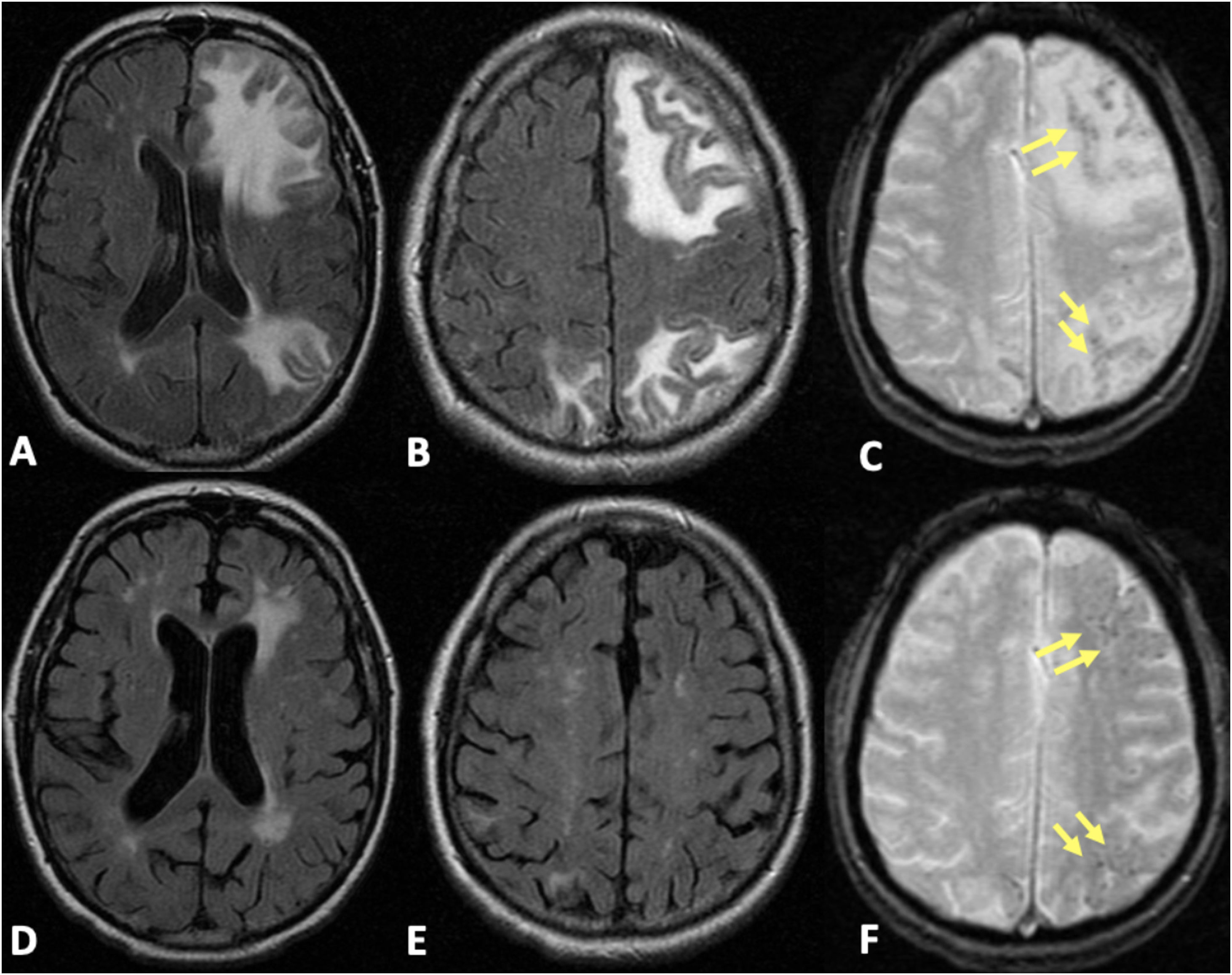
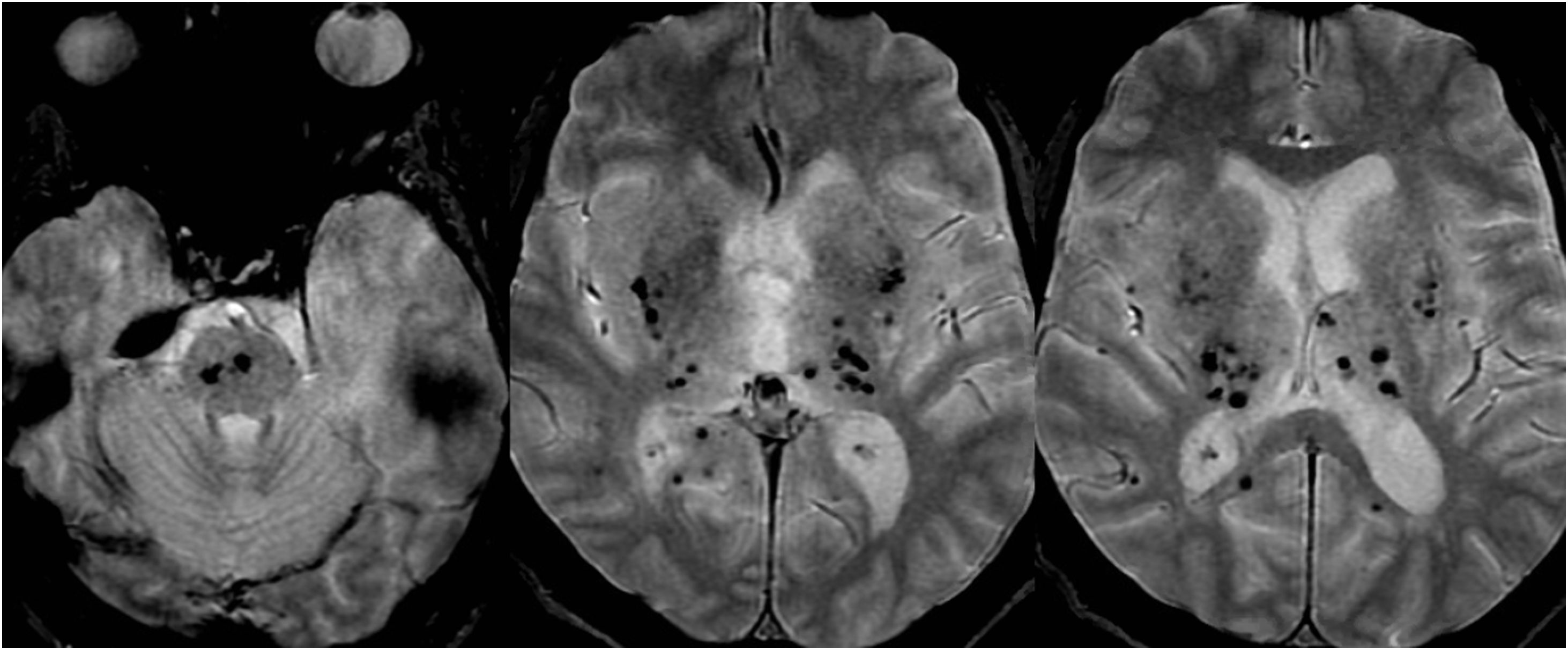
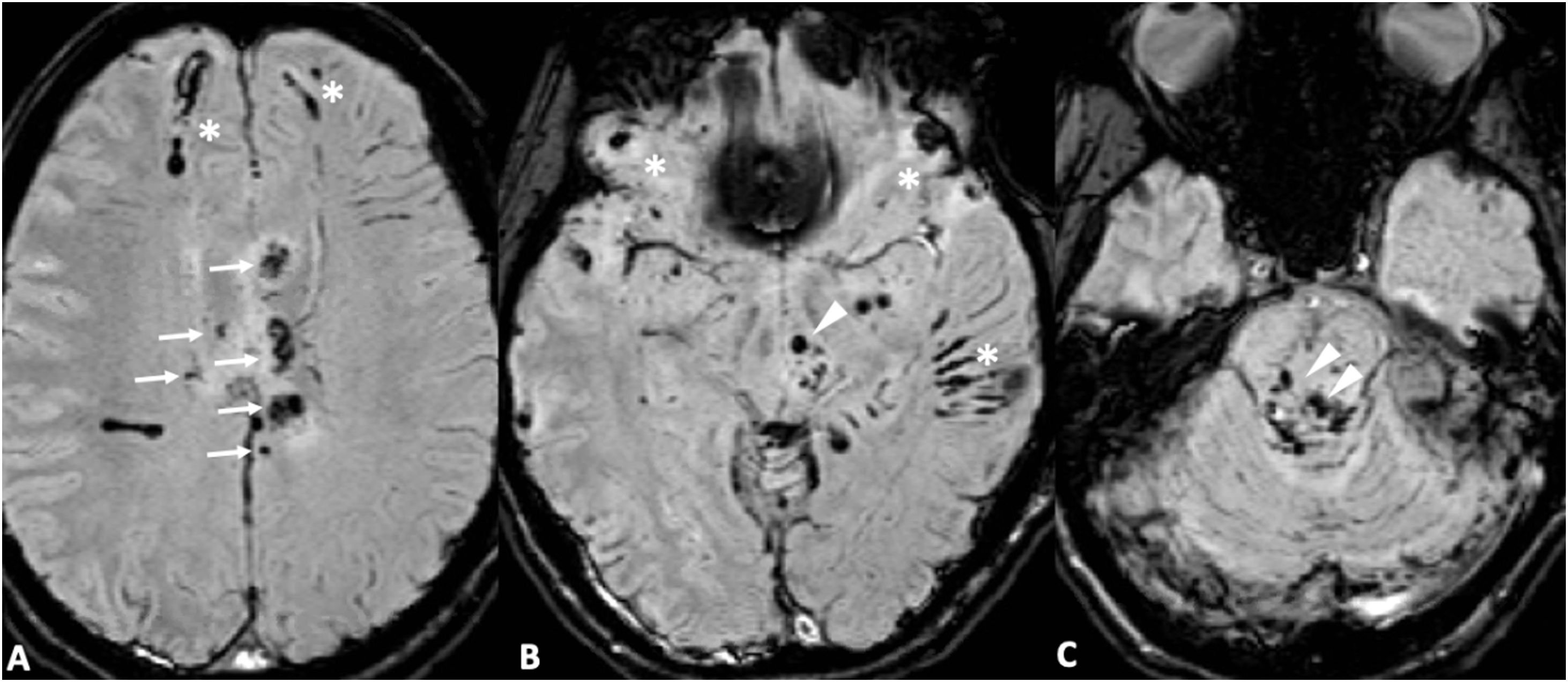
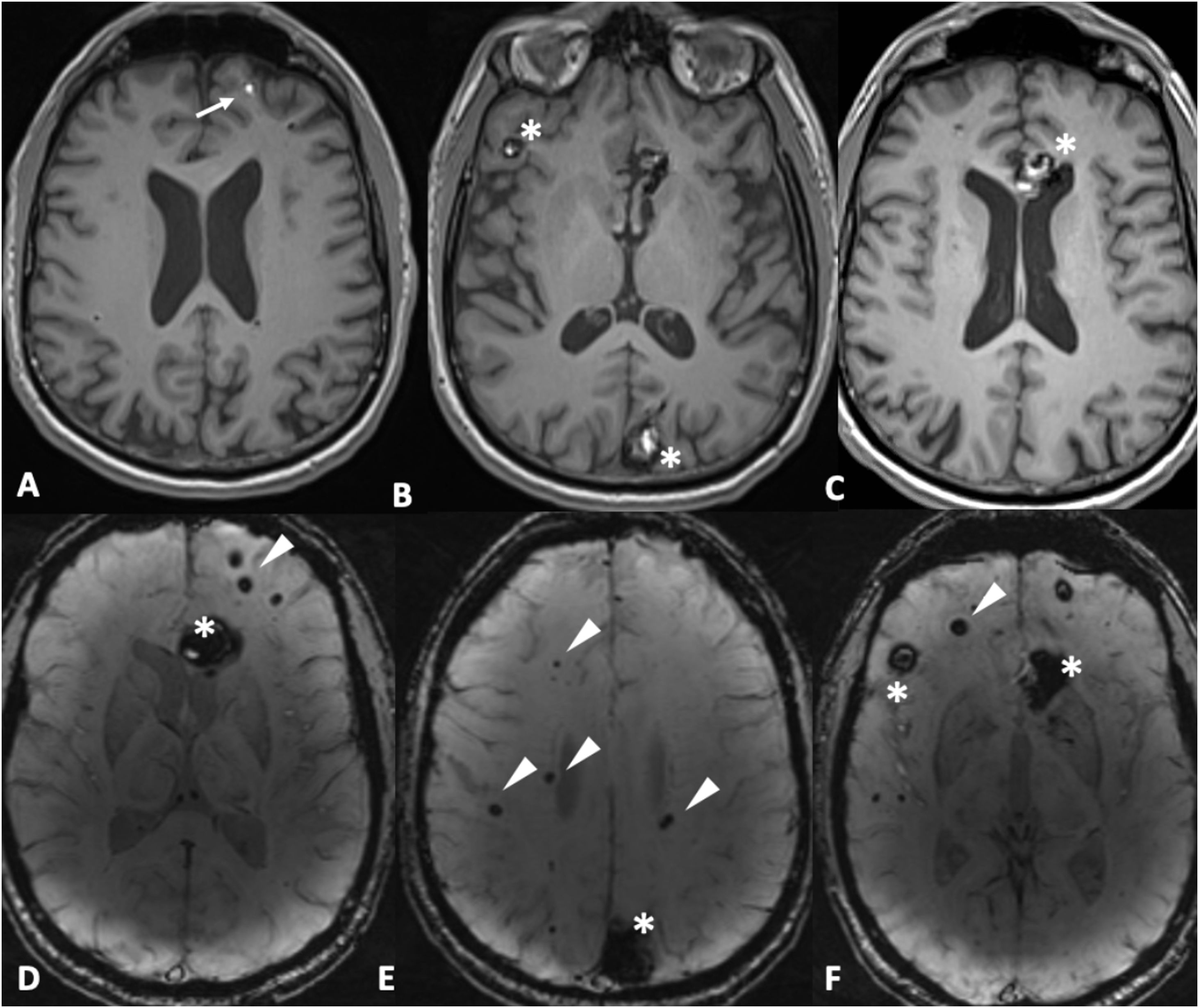
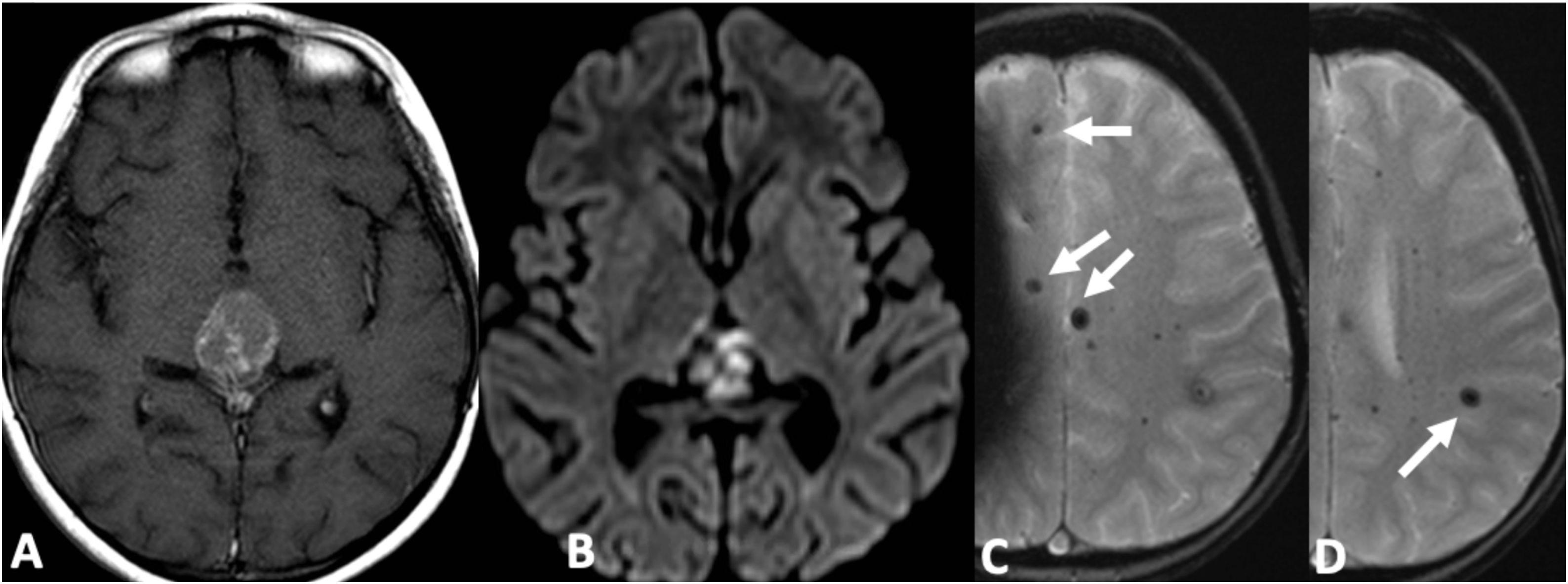
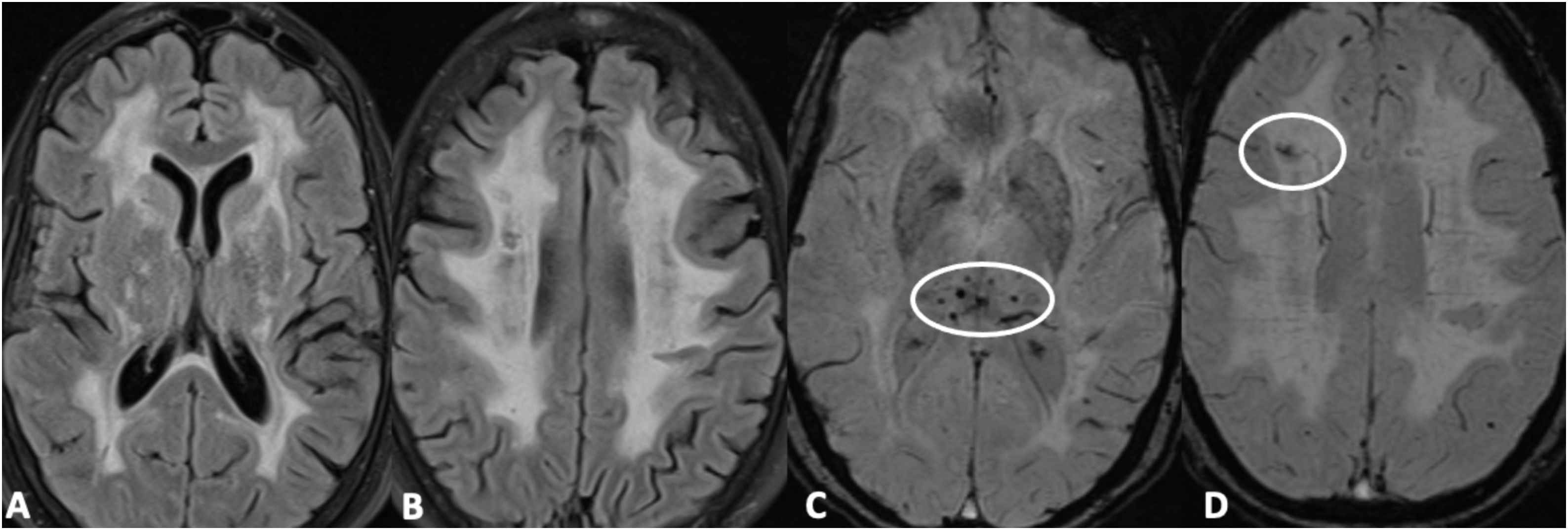
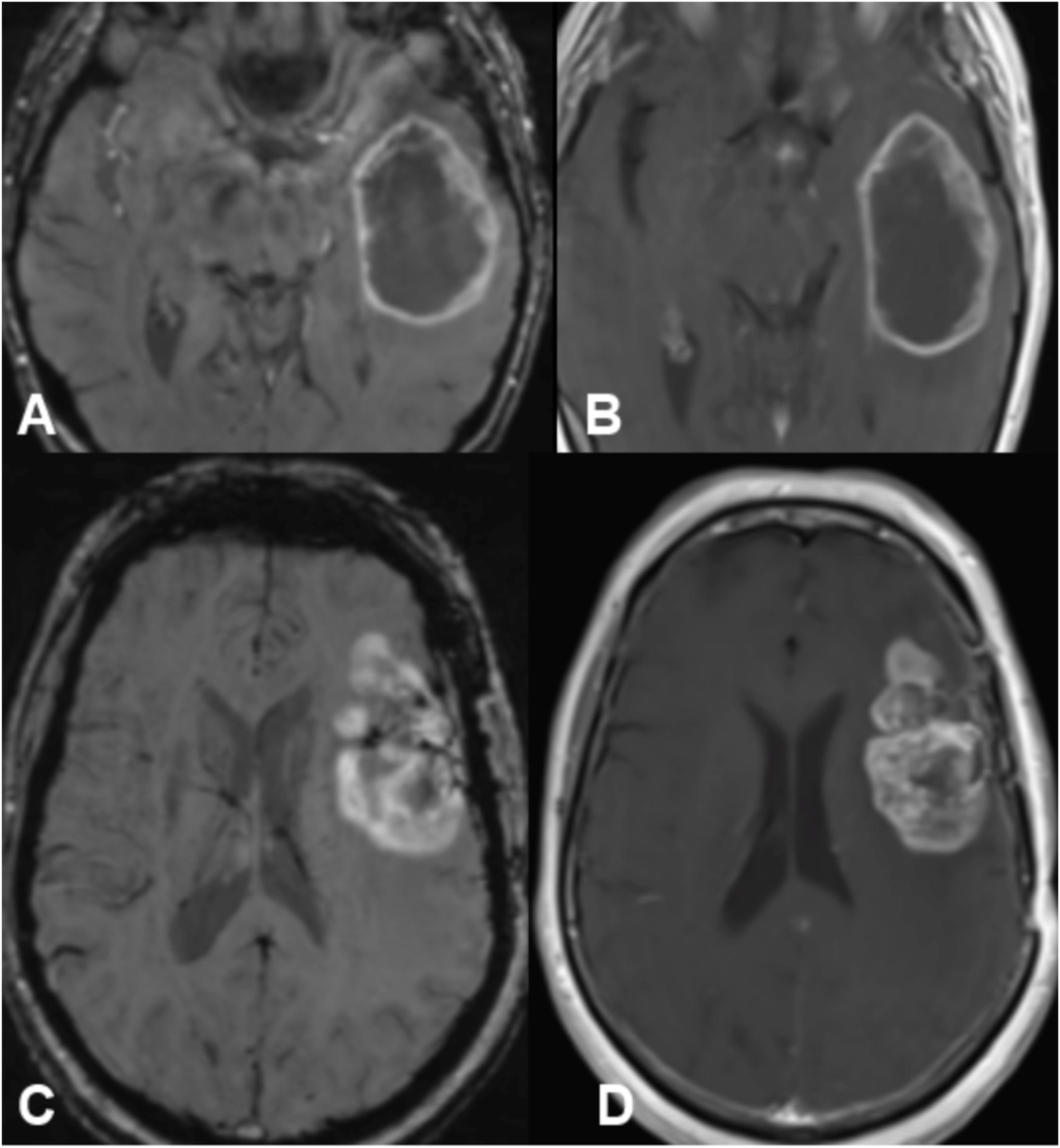
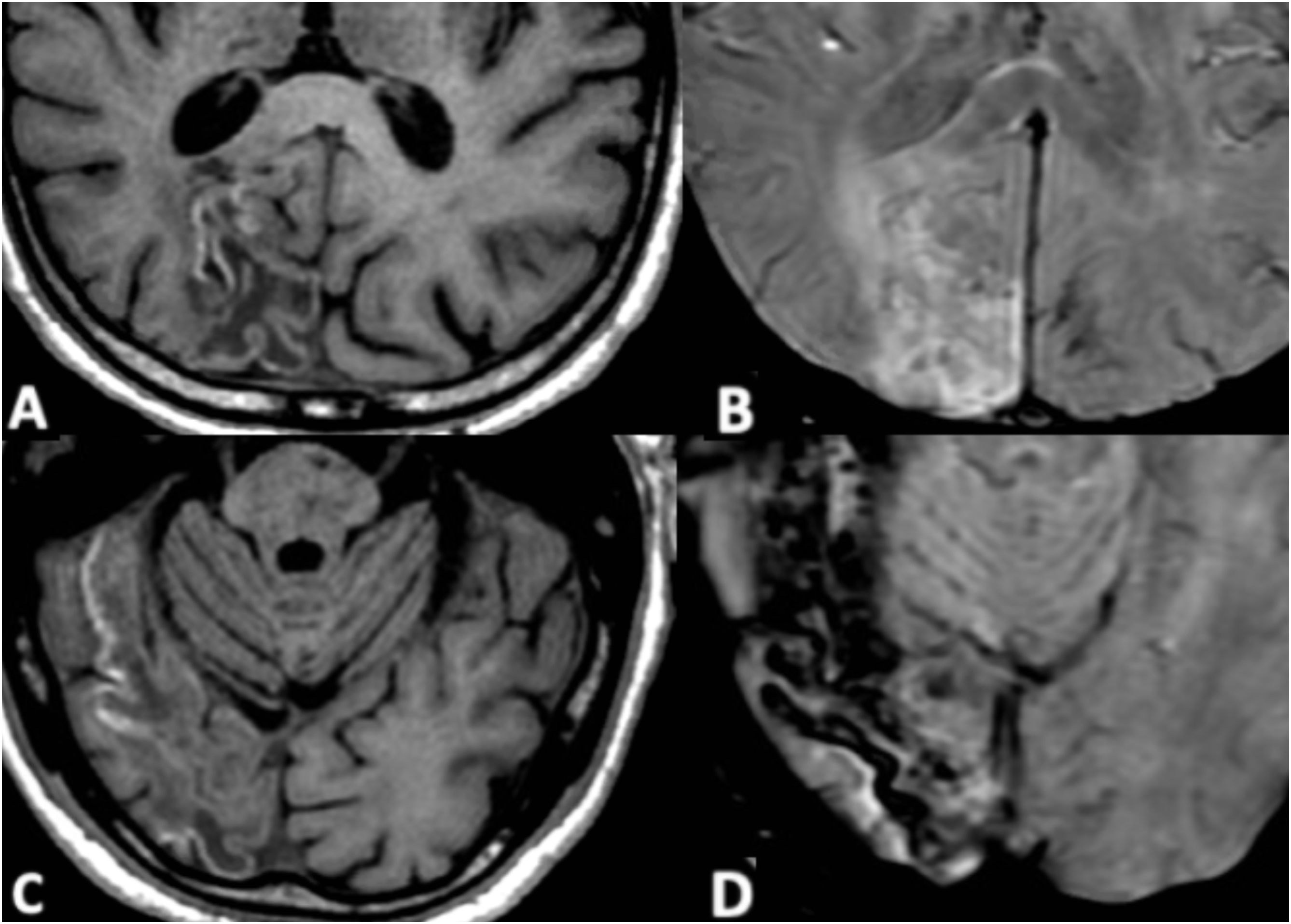
Las microhemorragias cerebrales pueden asociarse a diversas enfermedades, aparecer en contextos clínicos menos conocidos o servir como biomarcador tumoral en gliomas (ITTS) y como marcador de actividad inflamatoria en las placas de esclerosis múltiple (EM).
Define the concept of cerebral microbleeds (CMB) and describe the most useful MRI sequences for detecting this finding.
Review the entities that most frequently present with CMB and that may benefit from the use of susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) sequences.
ConclusionsSWI is a useful MRI sequence for the detection and characterization of microhemorrhages, venous structures and other sources of susceptibility in imaging.
SWI is particularly sensitive to local magnetic field inhomogeneities generated by certain substances and is superior to T2* GRE sequences for this assessment.
CMB may be seen in different neurologic conditions, in certain infrequent clinical contexts and have a key role as a biomarker status in gliomas (ITTS) and as a marker of inflammatory activity in multiple sclerosis.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora