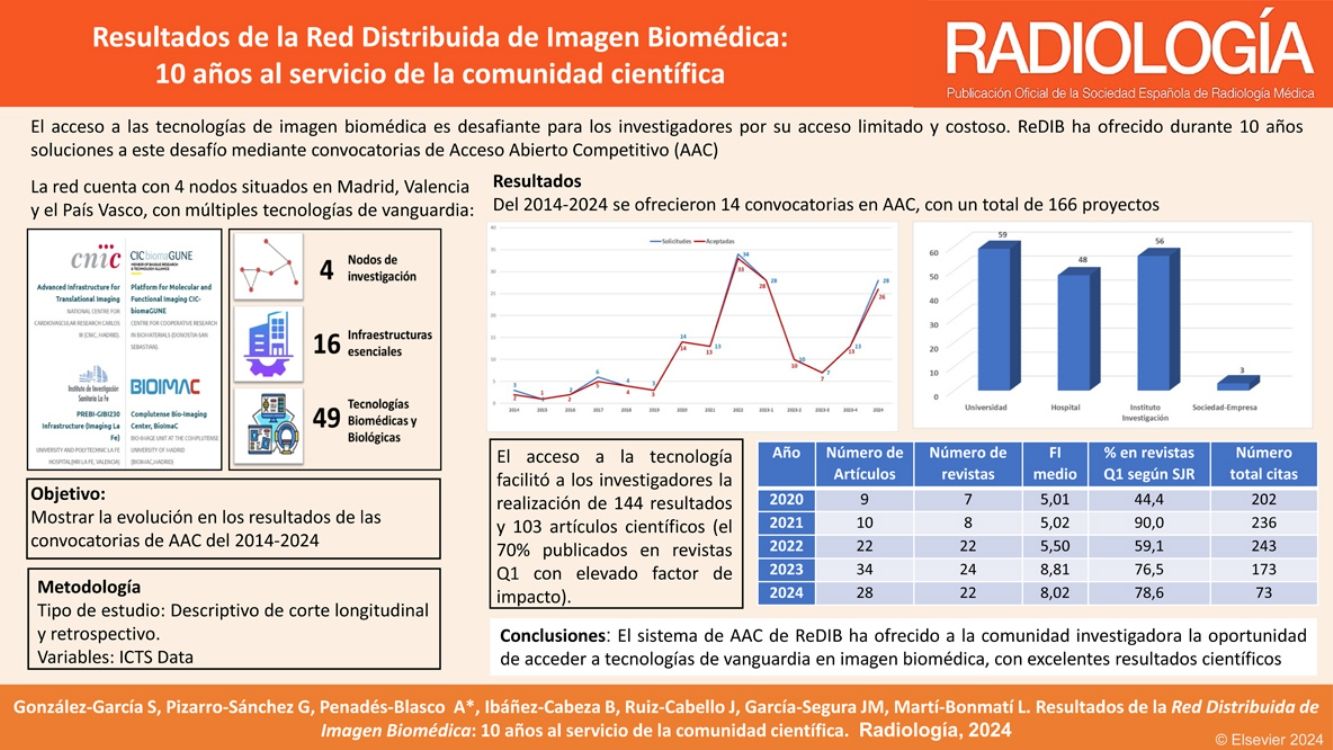
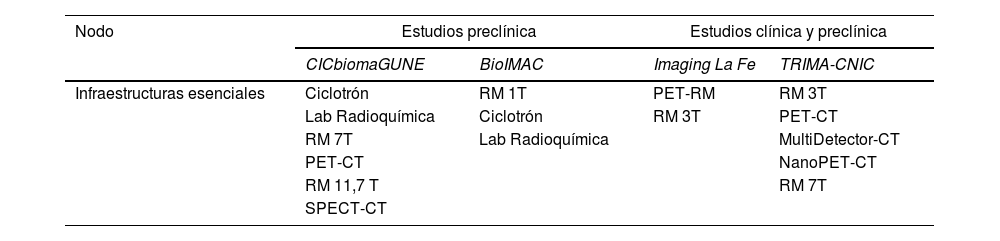
La Red Distribuida de Imagen Biomédica (ReDIB) es una infraestructura científica y técnica singular distribuida en 4 nodos que, desde hace 10 años, ofrece sus servicios a la comunidad científica nacional e internacional. A través de sus convocatorias de acceso abierto competitivo (AAC), los usuarios han tenido acceso a técnicas de imagen biomédica avanzadas tanto para la investigación básica como clínica. El objetivo es mostrar la actividad y los resultados de las convocatorias de AAC de ReDIB.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio descriptivo de corte longitudinal retrospectivo. Se incluyó: número de convocatorias, solicitudes presentadas, sector de procedencia, países de origen, porcentaje de uso del equipamiento esencial y los resultados científicos obtenidos a partir de la concesión del acceso.
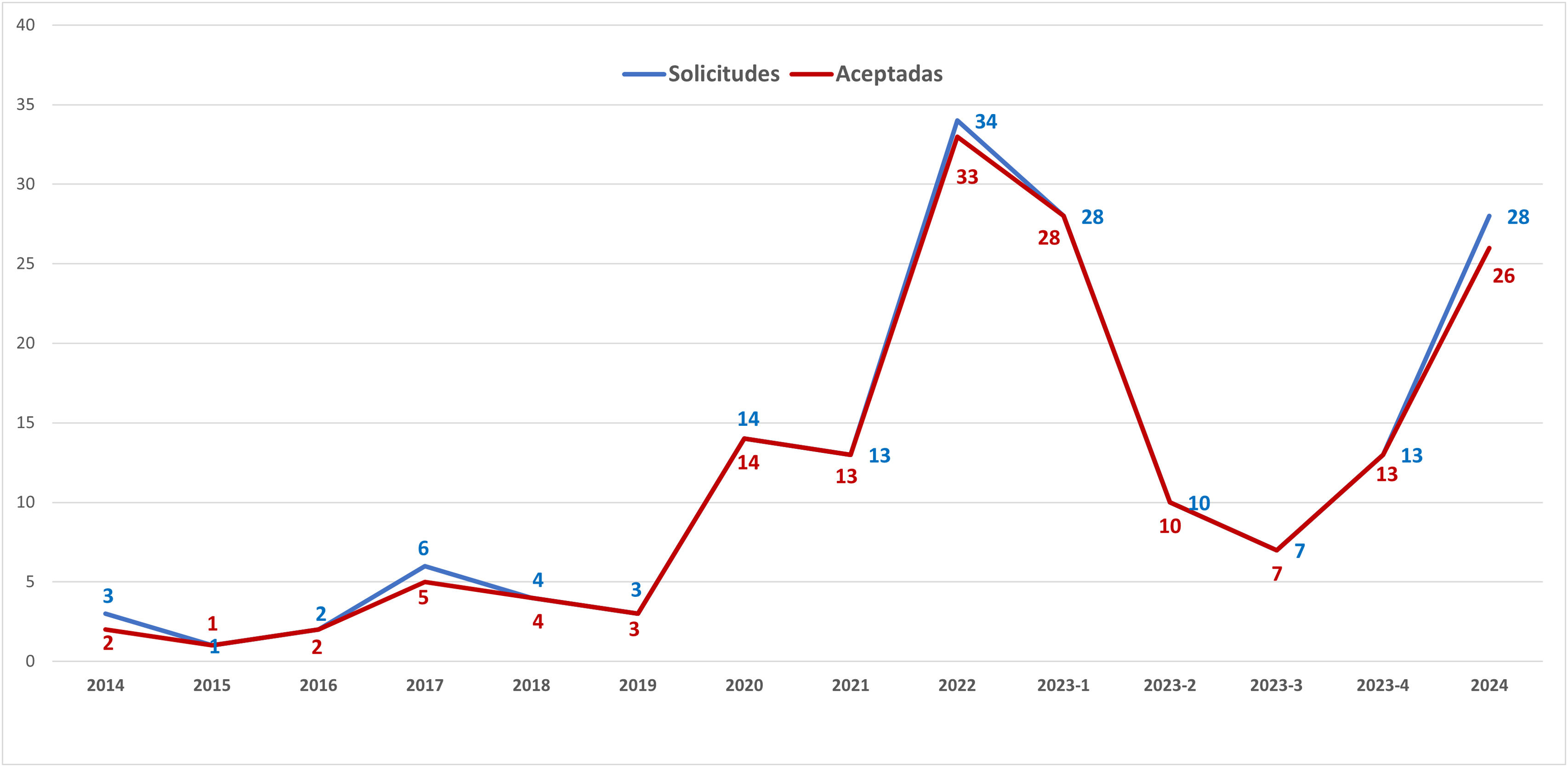
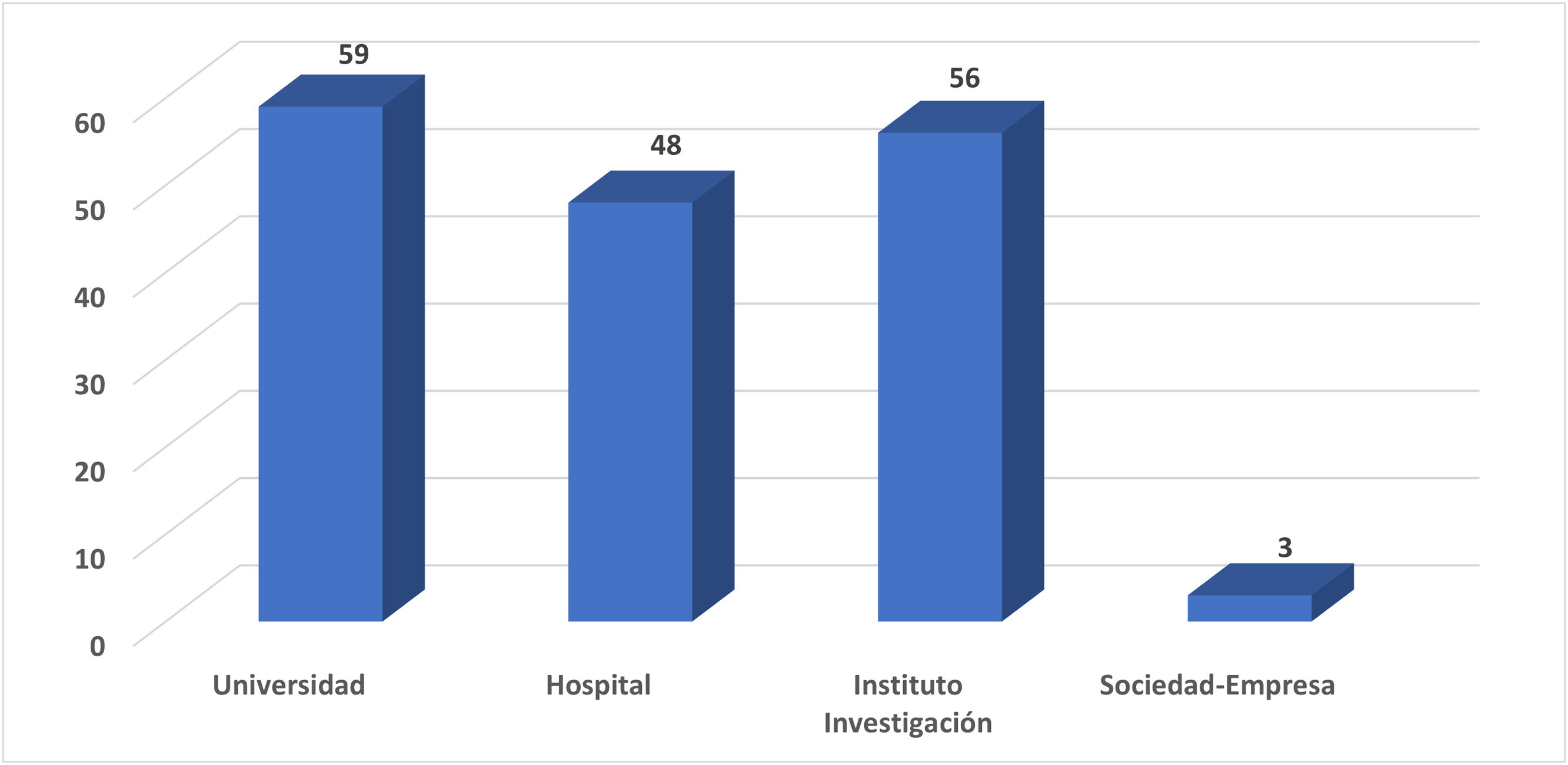
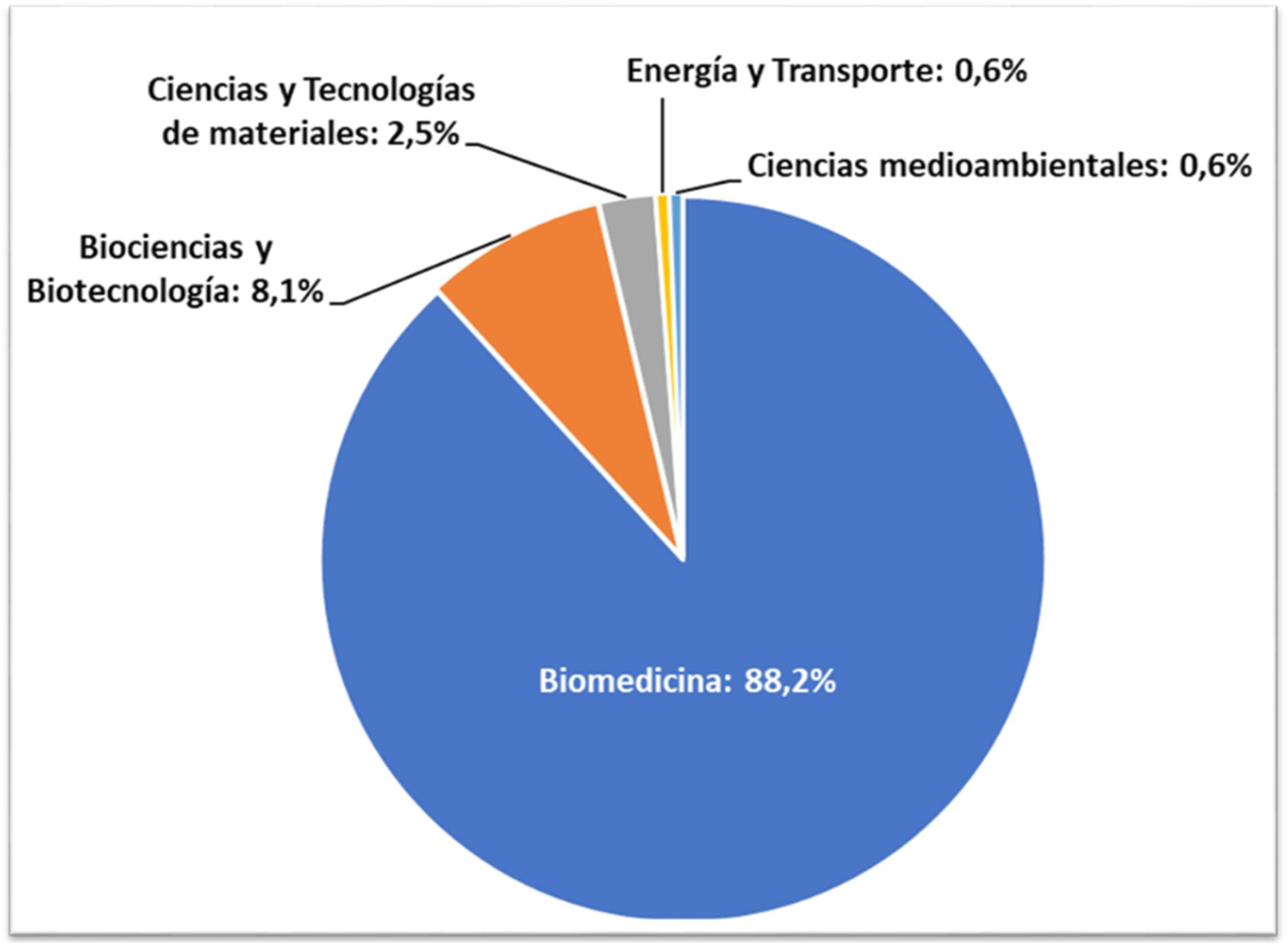
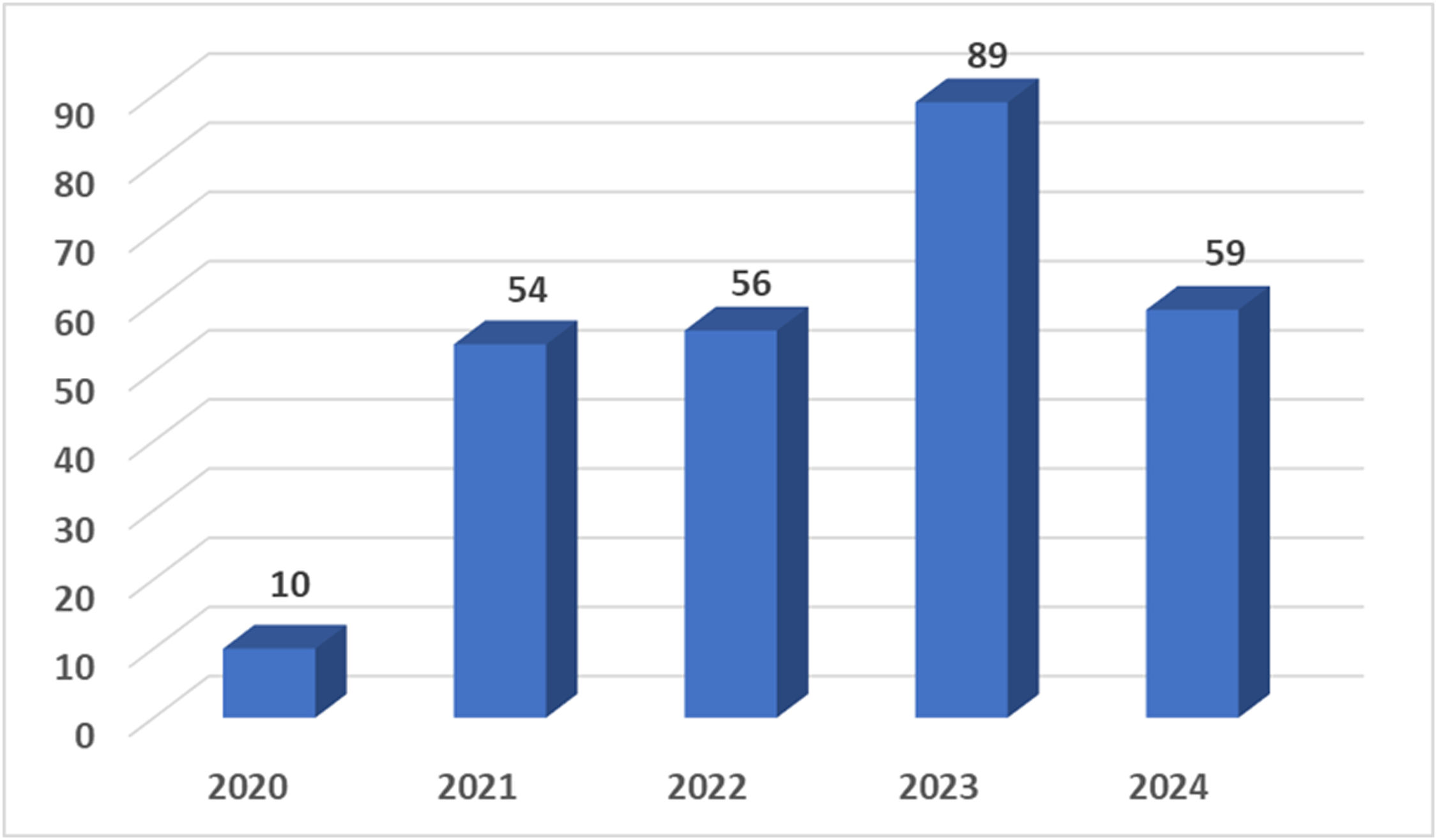
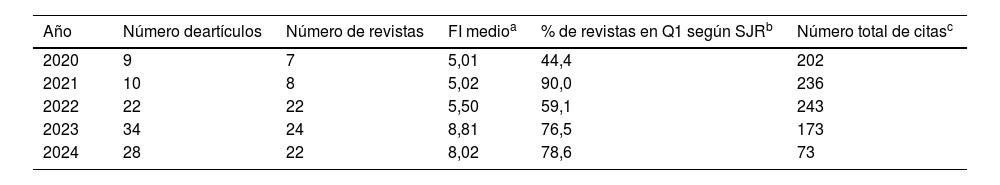
ResultadosEn 14 convocatorias se presentaron 166 propuestas, 144 de ellas en los últimos 4 años, con un alto índice de aceptación (97%). El 88,2% de las solicitudes pertenecieron al área temática de biomedicina, proviniendo el 69,3% de universidades e institutos de investigación. Entre 2020 y 2024 se concedieron 144 solicitudes, el uso medio de las infraestructuras fue del 69%, con una media de 0,99 resultados científicos por acceso concedido.
DiscusiónEl sistema de AAC ha ofrecido a la comunidad investigadora la oportunidad de acceder a tecnologías de vanguardia en la imagen biomédica, con un excelente resultado científico. La constante modernización e incorporación de nuevas infraestructuras tecnológicas ha incrementado la capacidad del servicio brindado, con un uso que ha aumentado el número de artículos científicos publicados por acceso concedido.
The Distributed Biomedical Imaging Network (ReDIB) is a Scientific and Technical Infrastructure that is distributed across four hubs and has been offering its services to the national and international scientific community for 10 years. Through its competitive open access calls (OACs), ReDIB users have had access to the most advanced biomedical imaging techniques in both basic and clinical research. This article describes the activity and results of the ReDIB OACs between 2014 and 2024.
Material and methodsA retrospective longitudinal descriptive study was carried out. The following information was included: number of OACs, the applications submitted, the sector, countries of origin, percentage of use of essential equipment and the scientific results obtained from granting access.
ResultsIn 14 OACs, 166 proposals were submitted, of which 144 were within the last four years. The acceptance rate was high (97%). 88.2% of the applications were related to biomedicine, with 69.3% coming from universities and research institutes. Between 2020 and 2024, 144 applications were granted, of which 69% used the infrastructures, with an average of 0.99 of scientific results per access granted.
DiscussionThe ReDIB OAC system has offered the research community the opportunity to access cutting-edge technologies in biomedical imaging, with excellent scientific results. The continuous technological modernisation and the incorporation of new infrastructures have increased the capacity of the service, resulting in a significant increase in the number of scientific publications per access granted.