To compare the image quality and dose of radiation in two groups of patients undergoing CT angiography of the lower limbs, one with tube voltage of 80kV and the other with tube voltage of 100kV.
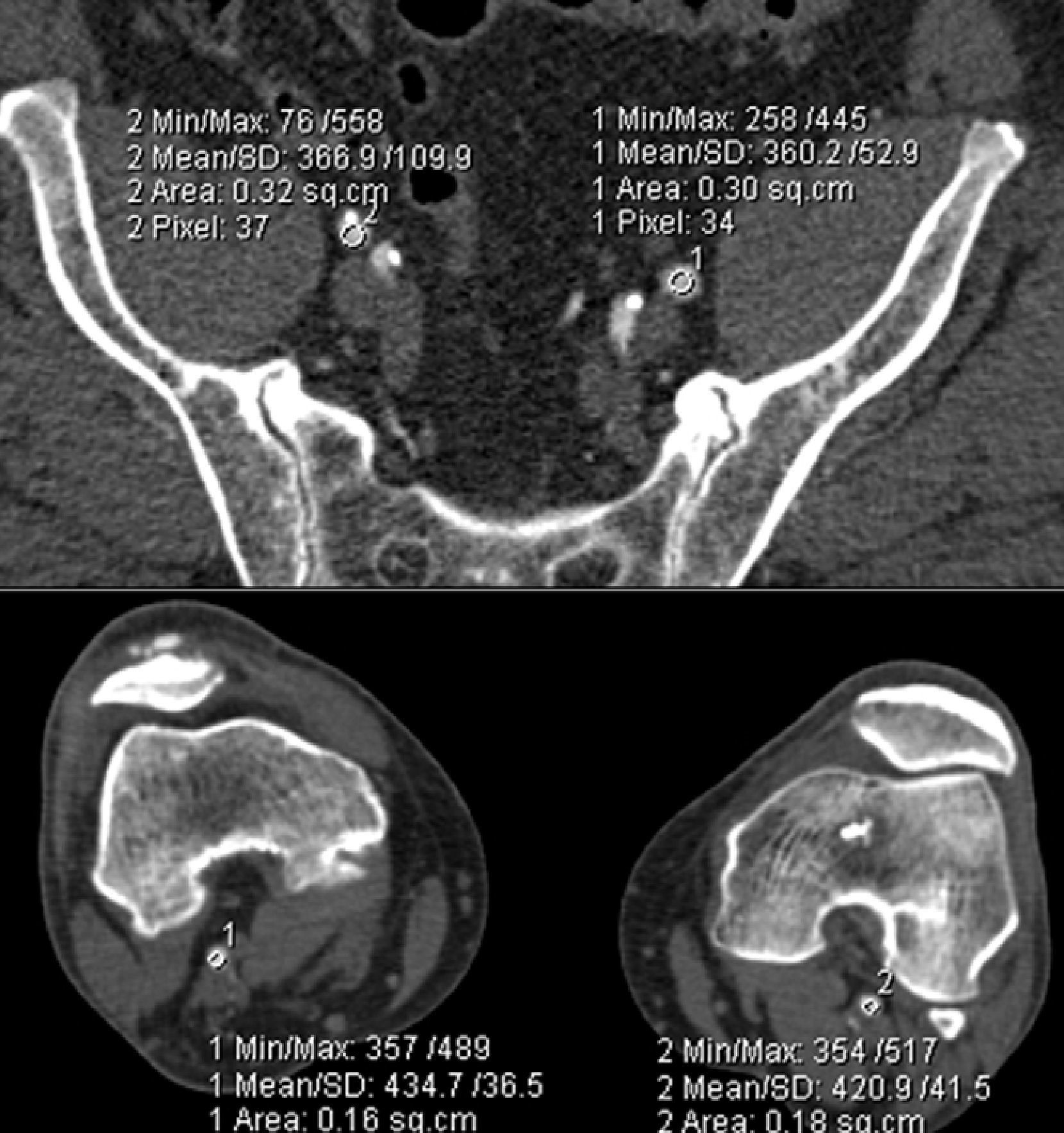
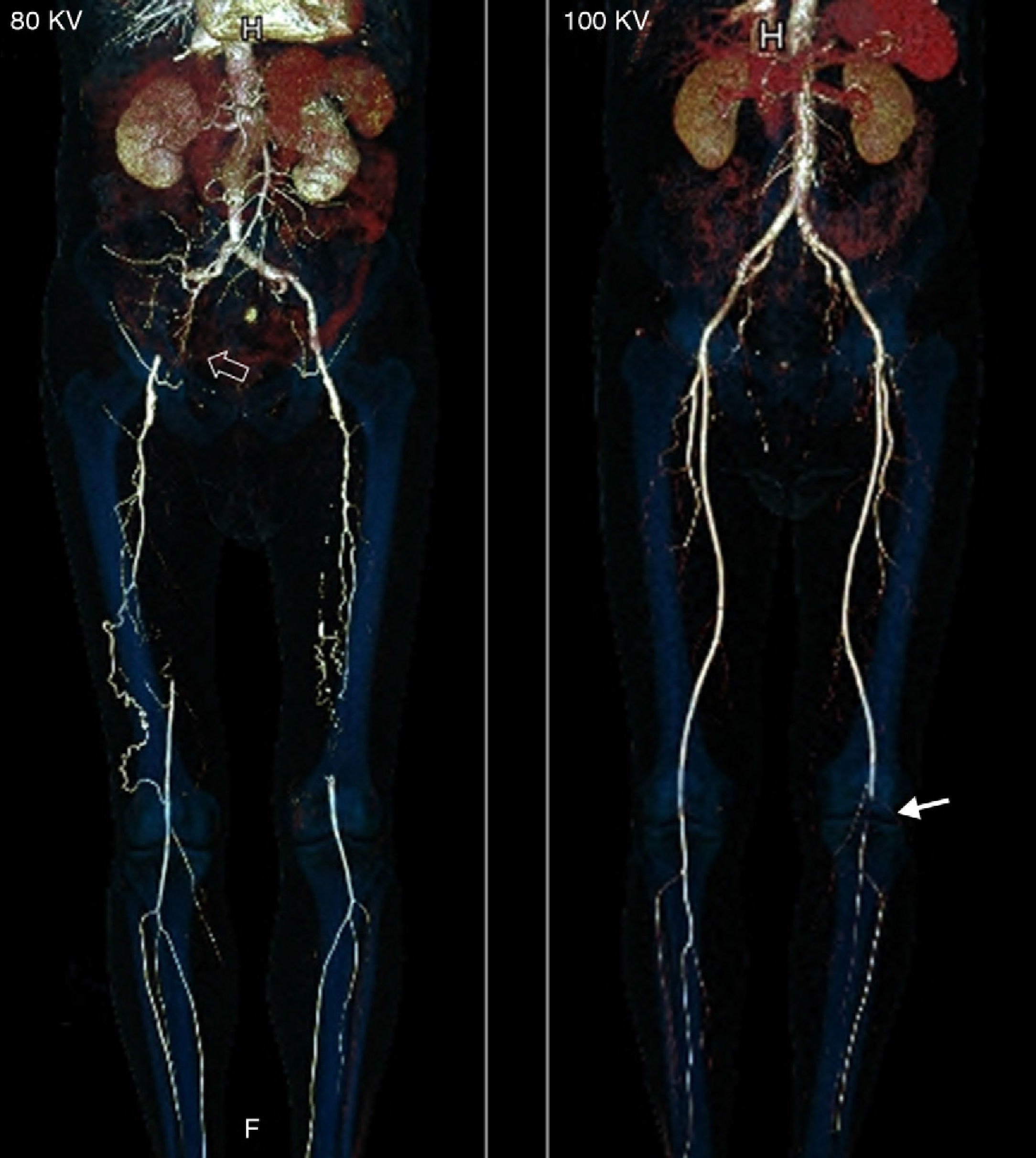
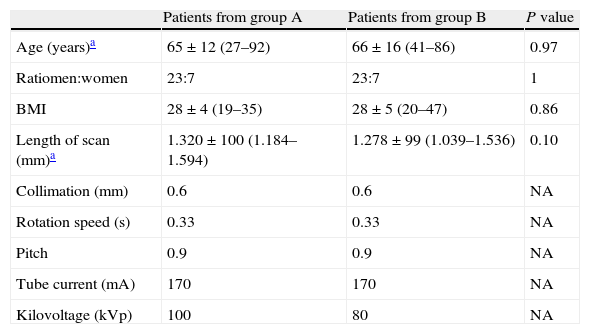
Materials and methodsWe performed CT angiography of the lower limbs in 60 patients with suspected peripheral arterial disease. Patients were randomly assigned to one of the two groups; in one group, CT angiography was performed using a tube voltage of 80kV, whereas in the other it was performed using 100kV. The remaining acquisition parameters were the same in both groups. The images were analyzed by quantifying vascular density (VD) and noise (N) and by calculating the quotients density/noise (QVDN) and contrast/noise (QCN). Two radiologists working independently evaluated the subjective quality of the images. We calculated the estimated effective dose (EED) based on the dose-length product (DLP).
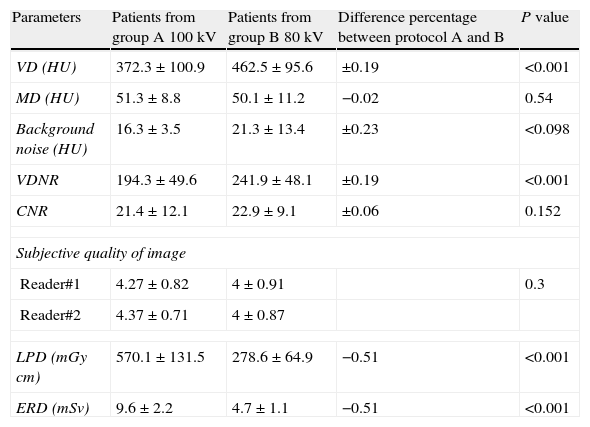
ResultsIn the group studied at 80kV, VD was significantly higher (462.5UH±95.6 vs 372UH±100.9; P<.001), QVDN was significantly higher (241.9±48.1 vs 194.3±49.6; P<.001), and there were trends toward higher N (21.3UH±13 vs 16.3UH±3.5; P=.098) and toward higher QCN (21.4±12.1 vs 22.9±9.1; P=.15). No significant differences were found in the subjective quality of the images. The EED was significantly lower in the group studied at 80kV (4.73mSv±1.1 vs 9.6mSv±2.2; P<.001).
ConclusionUsing 80kV instead of 100kV for CT angiography of the lower limbs reduces the dose of radiation without affecting the diagnostic efficacy of the study.
Comparar la calidad de imagen y la dosis de radiación en 2 grupos de pacientes a los que se realiza angio-TC de extremidades inferiores con 80 y 100kV.
Material y métodosSe realizó angio-TC de miembros inferiores a 60 pacientes con sospecha de enfermedad arterial periférica aleatorizados en 2 grupos, en uno la TC se realizó con 80kV y en el otro con 100kV. Los demás parámetros de adquisición se mantuvieron constantes. Se analizaron las imágenes cuantificando la densidad vascular (DV) y el ruido (R), y se calcularon los cocientes densidad vascular/ruido (CDVR) y contraste/ruido (CCR). Dos radiólogos evaluaron independientemente la calidad subjetiva de las imágenes. Se calculó la dosis efectiva estimada (DEE) basada en el producto dosis-longitud (DLP).
ResultadosEl grupo de 80kV presentó valores significativamente más elevados de la DV (462,5UH±95,6 vs. 372UH±100,9; p<0,001) y del CDVR (241,9±48,1 vs. 194,3±49,6; p<0,001) y diferencias no significativas del R (21,3UH±13 vs. 16,3UH±3,5; p=0,098) y el CCR (21,4±12,1 vs. 22,9±9,1; p=0,15). No hubo diferencias significativas en la calidad subjetiva de la imagen y la dosis efectiva fue significativamente menor en el grupo de 80kV (4,73mSv±1,1 vs. 9,6mSv±2,2; p<0,001).
ConclusiónLa utilización de 80kV en el estudio de angio-TC de miembros inferiores disminuye la dosis de radiación sin afectar a la eficacia diagnóstica del estudio respecto a la utilización de 100kV.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora