We used an animal model to analyze the reproducibility and accuracy of certain biomarkers of bone image quality in comparison to a gold standard of computed microtomography (μCT).
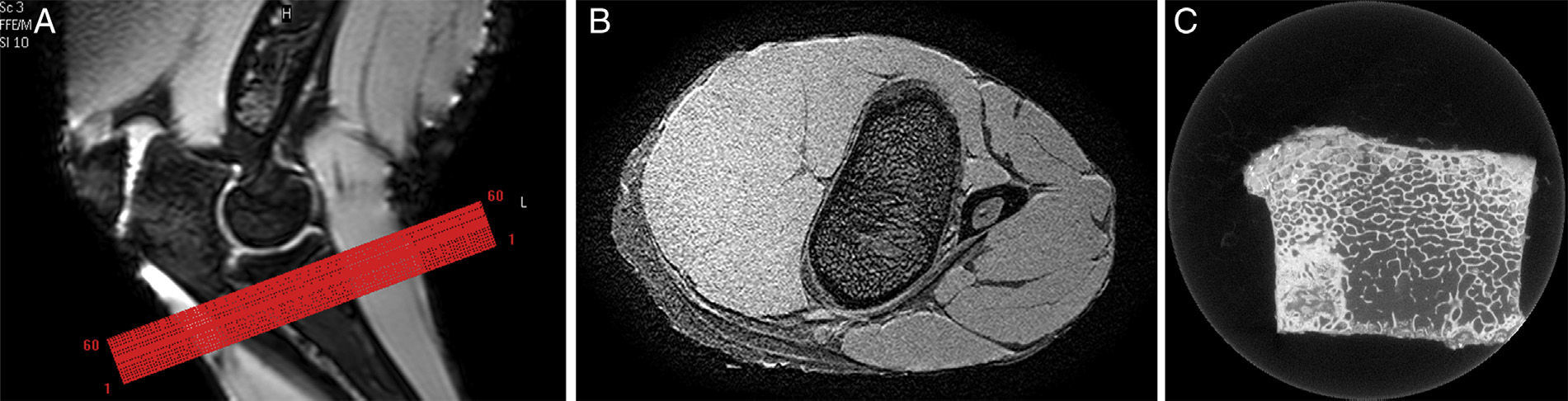
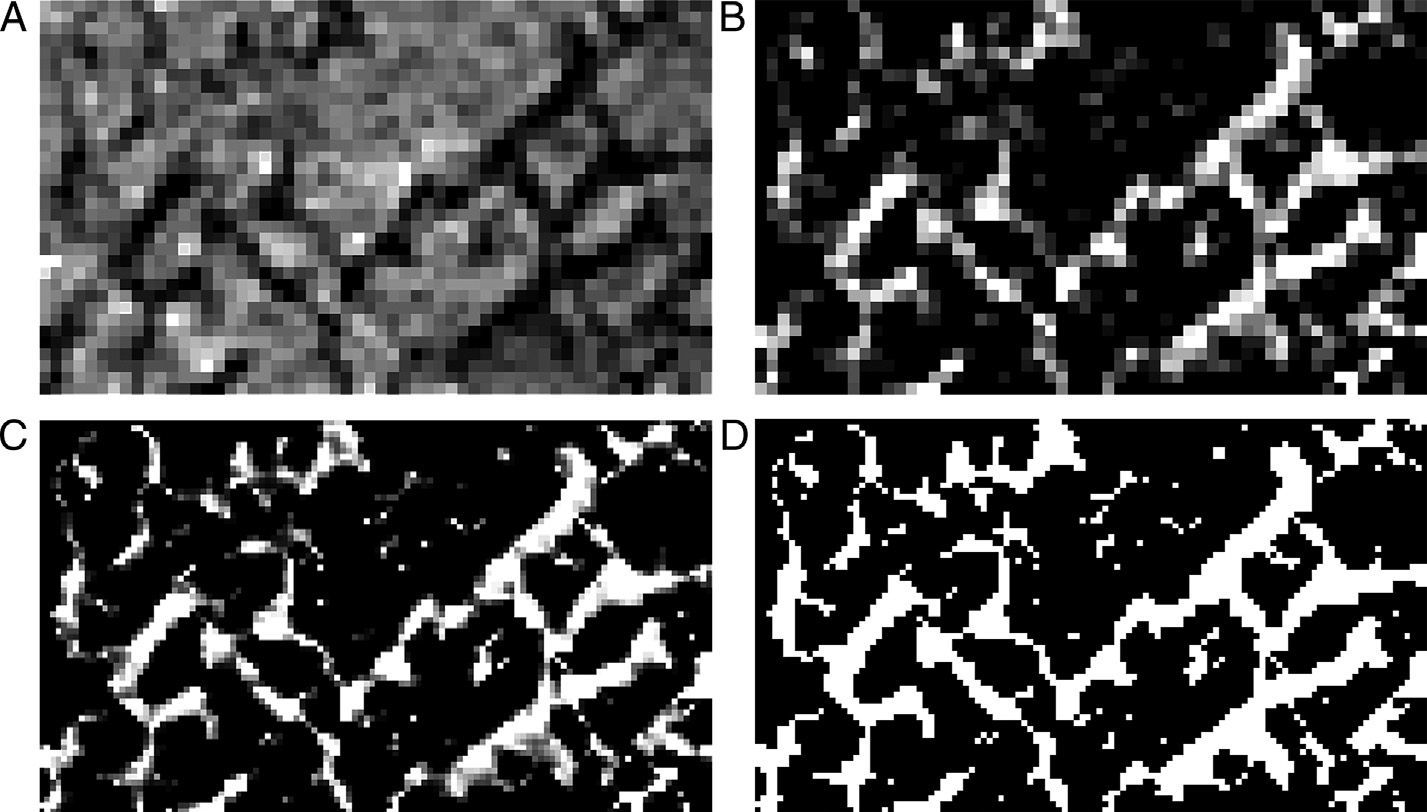
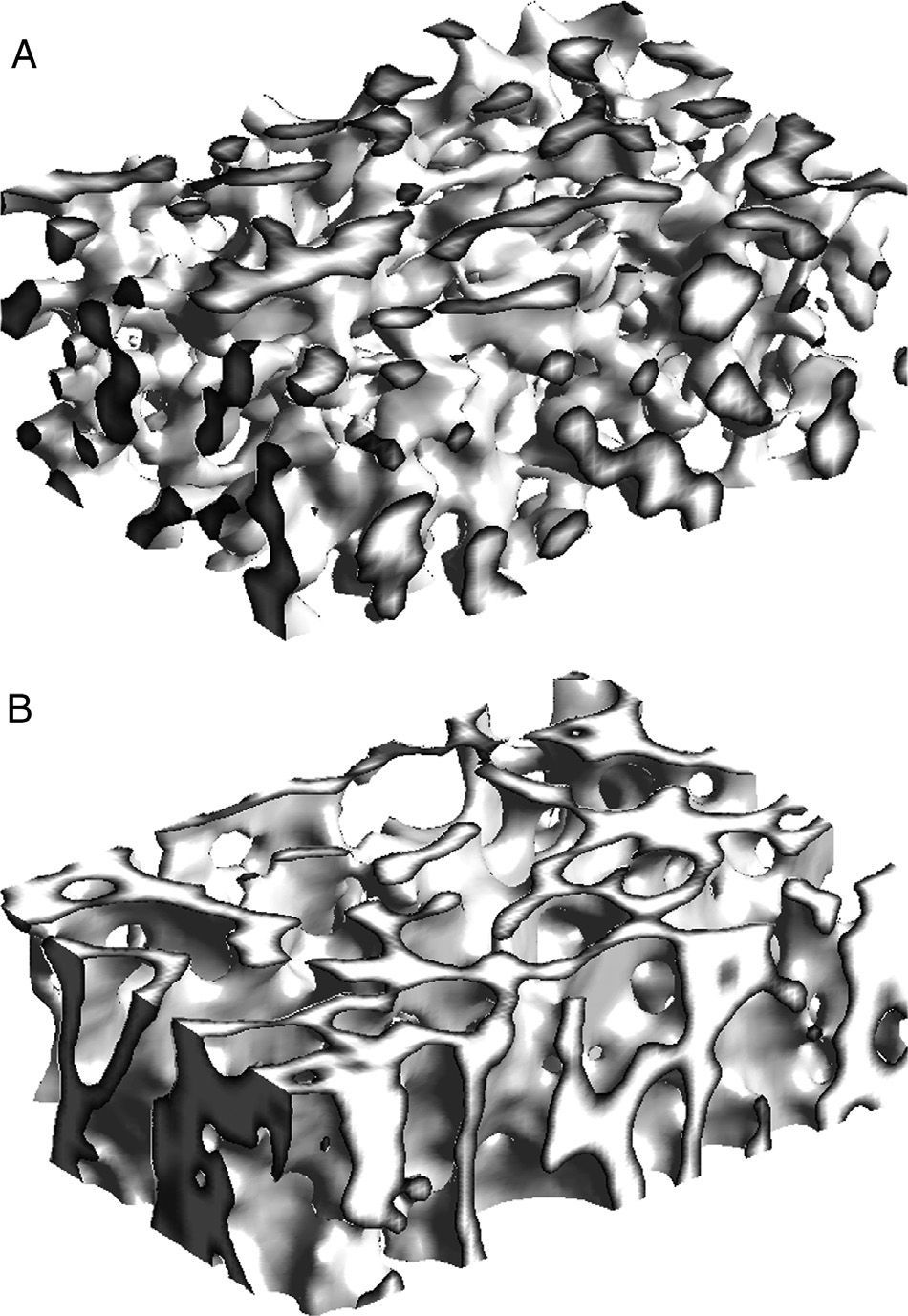
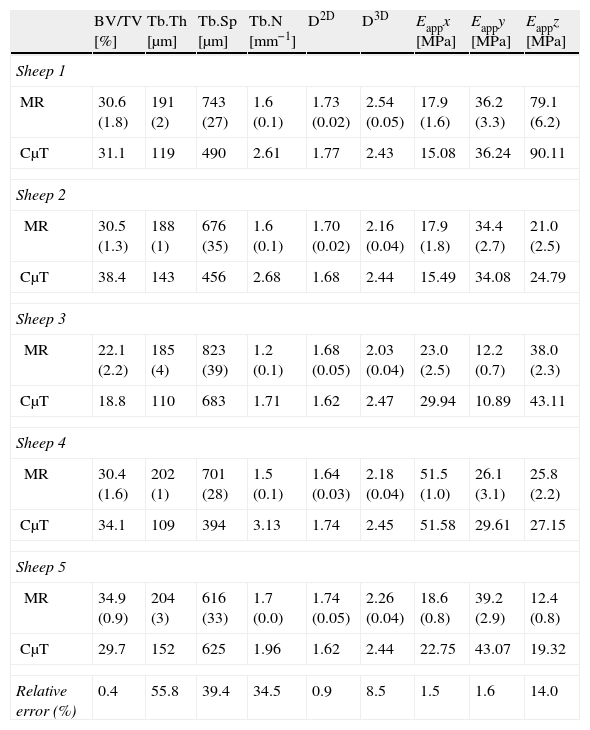
Materials and methodsWe used magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and μCT to study the metaphyses of 5 sheep tibiae. The MR images (3T) were acquired with a T1-weighted gradient echo sequence and an isotropic spatial resolution of 180μm. The μCT images were acquired using a scanner with a spatial resolution of 7.5μm isotropic voxels. In the preparation of the images, we applied equalization, interpolation, and thresholding algorithms. In the quantitative analysis, we calculated the percentage of bone volume (BV/TV), the trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), the trabecular separation (Tb.Sp), the trabecular index (Tb.N), the 2D fractal dimension (D2D), the 3D fractal dimension (D3D), and the elastic module in the three spatial directions (Ex, Ey and Ez).
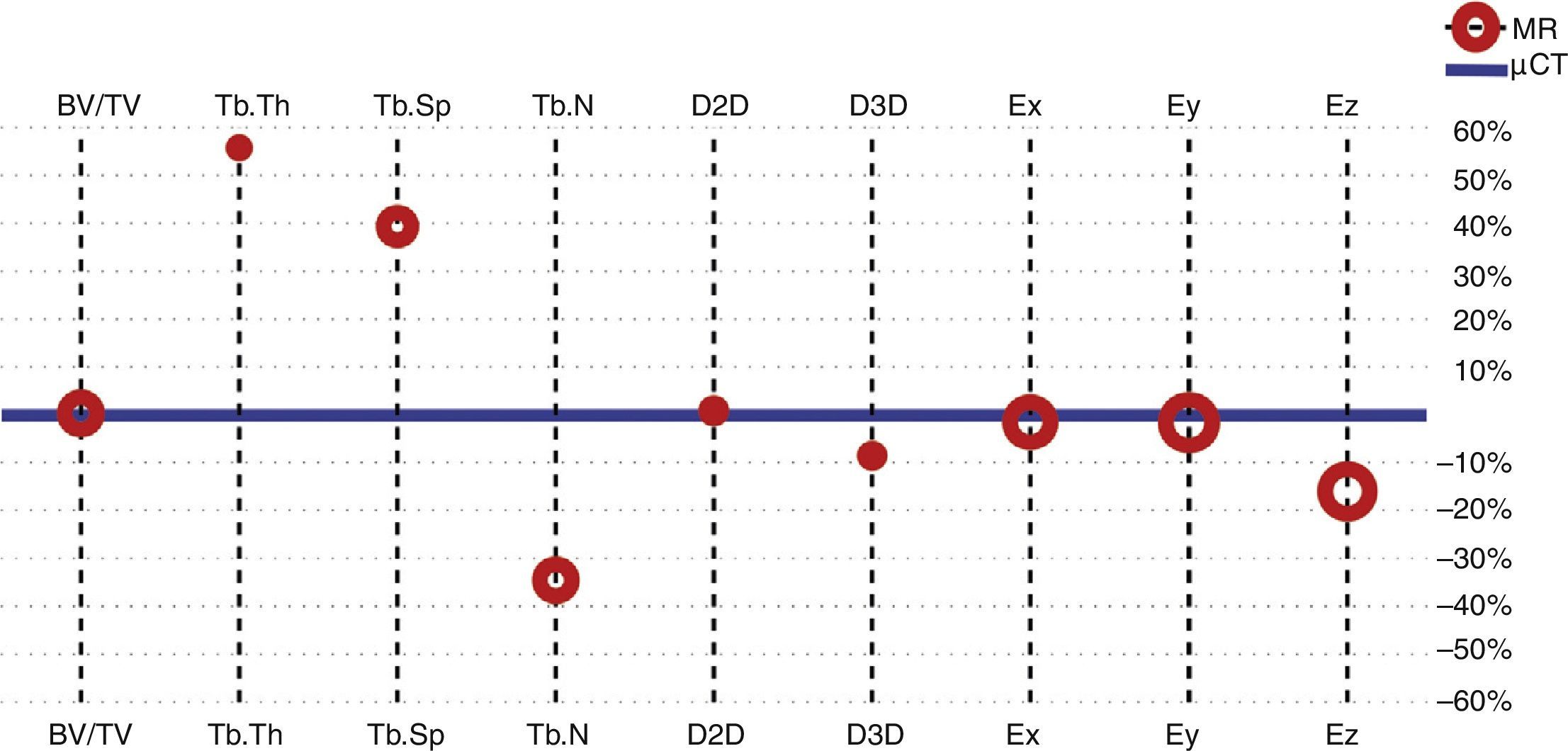
ResultsThe morphometric and mechanical quantification of trabecular bone by MR was very reproducible, with percentages of variation below 9% for all the parameters. Its accuracy compared to the gold standard (μCT) was high, with errors less than 15% for BV/TV, D2D, D3D, and Eappx, Eappy and Eappz.
ConclusionsOur experimental results in animals confirm that the parameters of BV/TV, D2D, D3D, and Eappx, Eappy and Eappz obtained by MR have excellent reproducibility and accuracy and can be used as imaging biomarkers for the quality of trabecular bone.
En este trabajo se analizan en un modelo animal la reproducibilidad y la exactitud de ciertos biomarcadores de imagen de calidad ósea utilizando como patrón de referencia la microtomografía computarizada (μTC).
Material y métodosSe estudiaron con RM y μTC 5 metáfisis tibiales de oveja. Las imágenes de RM (3 Tesla) se adquirieron con una secuencia eco de gradiente potenciada en T1 y una resolución espacial isotrópica de 180μm. Las imágenes de μTC se adquirieron en un escáner con una resolución espacial de 7,5μm en vóxeles isotrópicos. En la preparación de las imágenes se aplicaron algoritmos de ecualización, interpolación y umbralización. En el análisis cuantitativo se calculó el porcentaje de volumen de hueso (BV/TV), el grosor trabecular (Tb.Th), la separación trabecular (Tb.Sp), el índice trabecular (Tb.N), la dimensión fractal en 2D (D2D) y 3D (D3D) y el módulo elástico en las 3 direcciones del espacio (Ex, Ey y Ez).
ResultadosLa cuantificación morfométrica y mecánica del hueso esponjoso con la RM fue muy reproducible, con porcentajes de variación por debajo del 9% para todos los parámetros. Su exactitud con respecto a la μTC fue alta, con errores inferiores al 15% para BV/TV, D2D, D3D y Eappx, Eappy y Eappz.
ConclusionesLos resultados experimentales en animales confirman que los parámetros de BV/TV, D2D, D3D y Eappx, Eappy y Eappz obtenidos a partir de RM tienen una excelente reproducibilidad y precisión, y pueden emplearse como biomarcadores de imagen de la calidad del hueso trabecular.