To determine the cost effectiveness of breast biopsy by 9G vacuum-assisted guided by vertical stereotaxy or ultrasonography in comparison with breast biopsy by 14G core-needle biopsy and surgical biopsy.
Material and methodsWe analyzed a total of 997 biopsies (181 vacuum-assisted, 626 core, and 190 surgical biopsies). We calculated the total costs (indirect and direct) of the three types of biopsy. We did not calculate intangible costs. We measured the percentage of correct diagnoses obtained with each technique. To identify the most cost-effective option, we calculated the mean ratios for the three types of biopsies.
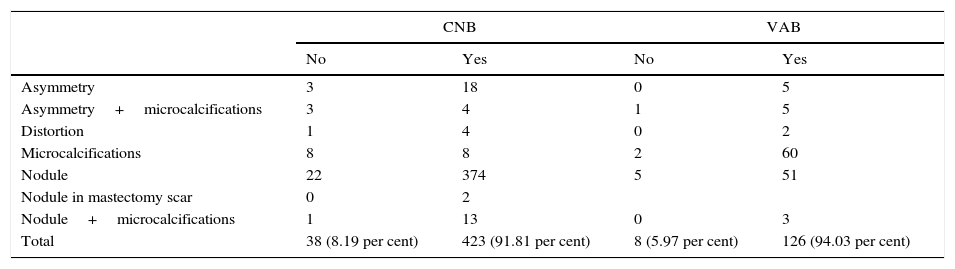
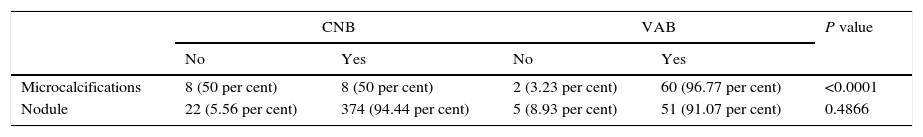
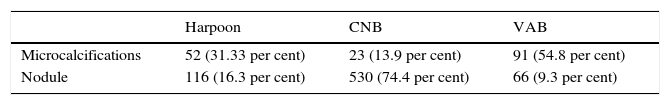
ResultsTotal costs amounted to €225.09 for core biopsy, €638.90 for vacuum-assisted biopsy, and €1780.01 for surgical biopsy. The overall percentage of correct diagnoses was 91.81 per cent for core biopsy, 94.03 per cent for vacuum-assisted biopsy, and 100 per cent for surgical biopsy; however, these differences did not reach statistical significance (P=0.3485). For microcalcifications, the percentage of correct diagnoses was 50 per cent for core biopsy and 96.77 per cent for vacuum-assisted biopsy (P<0.0001). For nodules, there were no significant differences among techniques. The mean cost-effectiveness ratio considering all lesions was 2.45 for core biopsy, 6.79 for vacuum-assisted biopsy, and 17.80 for surgical biopsy.
ConclusionCore biopsy was the dominant option for the diagnosis of suspicious breast lesions in general. However, in cases with microcalcifications, the low percentage of correct diagnoses achieved by core biopsy (50 per cent) advises against its use in this context, where vacuum-assisted biopsy would be the technique of choice because it is more cost-effective than surgical biopsy, the other technique indicated for biopsying microcalcifications.
Realizar estudio de costo-efectividad de la biopsia por aspiración al vacío (BAV) (9G) guiada por estereotaxia vertical o ecografía comparada con biopsia con aguja gruesa (BAG) (14G) y biopsia con arpón.
Material y métodosAnalizamos 997 biopsias mamarias (181 BAV, 626 BAG y 190 arpones). Calculamos costes totales (directos e indirectos) de los tres tipos de biopsia. No calculamos costes intangibles. El efecto a medir fue el “porcentaje de diagnósticos correctos” obtenidos con cada una de las técnicas. Calculamos los ratios medios de los tres tipos de biopsias e identificamos la opción dominante más costo-efectiva.
ResultadosCostes totales de BAG 225,09€, de BAV 638,90€ y de biopsia con arpón 1780,01€. Porcentaje de diagnósticos correctos globales con BAG 91,81%, BAV 94,03% y biopsia con arpón 100%, sin diferencias significativas (p=0,3485). En microcalcificaciones, los porcentajes de diagnósticos correctos fueron con BAG 50% y con BAV 96,77%, p<0,0001. En nódulos tampoco hubo diferencias significativas. El ratio medio costo-efectividad considerando todas las lesiones en conjunto, fue para BAG 2,45, BAV 6,79 y arpón 17,80.
ConclusiónLa BAG fue la opción dominante para el diagnóstico de lesiones mamarias sospechosas de malignidad en general. En el caso de las microcalcificaciones, el bajo porcentaje de diagnósticos de la BAG (50%) desaconsejan su uso y colocan a la BAV como técnica de elección; la BAV es, además, más costo-efectiva que el arpón, que es la otra técnica indicada para biopsiar microcalcificaciones.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora