To determine the rate of recanalization, functional outcome at three months, and independent prognostic factors in patients with posterior circulation strokes treated with stent-retrievers and to compare these results with those of patients in an earlier series treated with “classical methods”.
Material and methodsThis was a retrospective study of consecutive patients with posterior circulation strokes treated with stent-retrievers at our center between December 1, 2011 and May 1, 2018. The main outcome variables were the rate of recanalization according to the Thrombosis in Cerebral Infarction (TICI) scale and functional independence score 90 days after treatment according to the modified Rankin Scale (mRS). We analyzed demographics, cerebrovascular risk factors, clinical findings, and probable origin. Descriptive statistics and a binary logistic regression model were used to analyze the data.
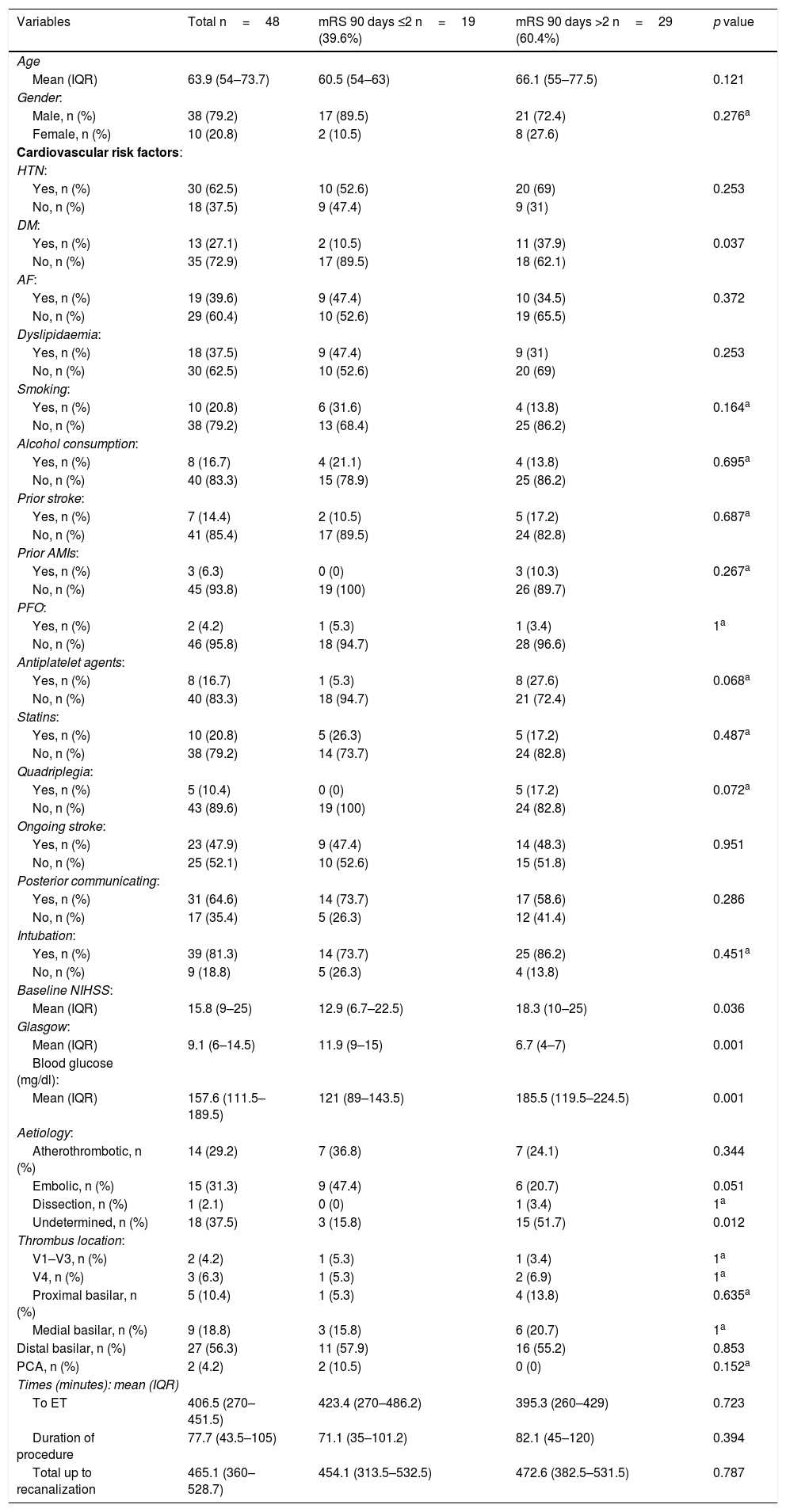
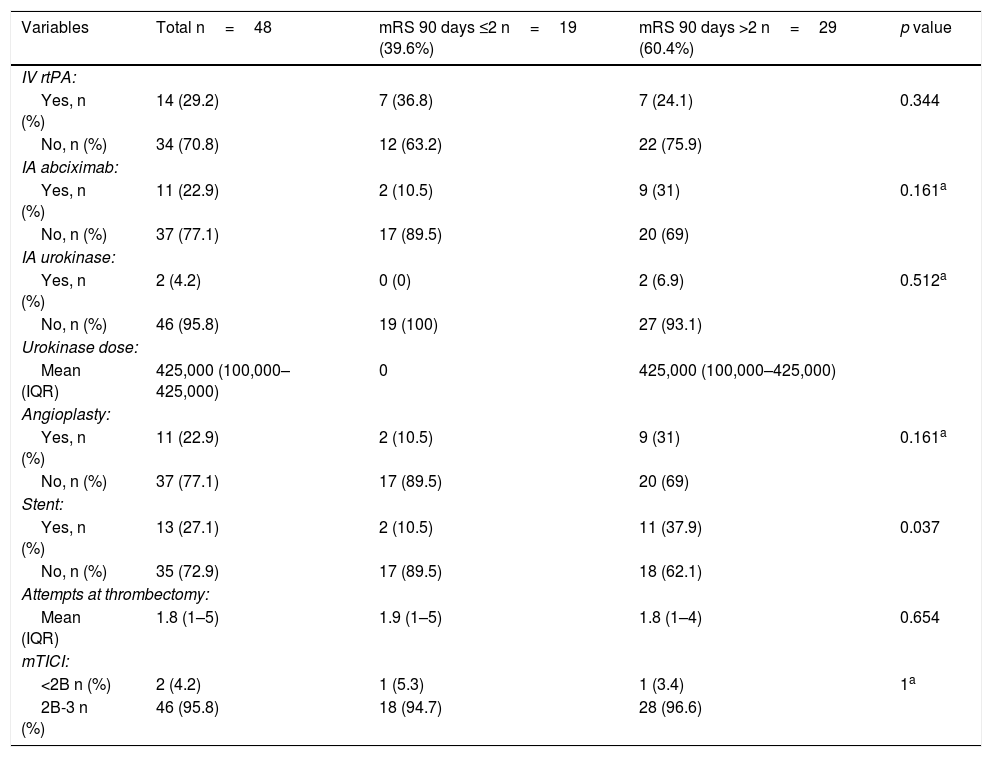
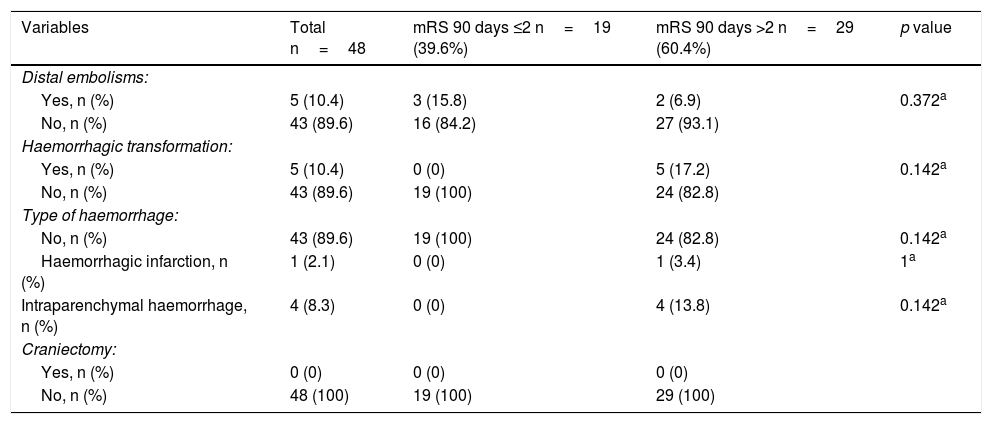
ResultsWe included 75 patients: 27 treated with “classical methods” and 48 treated with stent-retrievers (10 women; mean age, 63.9 years; median National Institute of Health Stroke Score, 15.8 (IQR 9–25); median Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), 9.1 (IQR 6–14,5). TICI 2b-3 recanalization was achieved in 46 (95.8%) patients treated with stent-retrievers and in 15 (55.6%) patients treated with “classical methods” (p<0.0001). No significant differences were observed in the rate of patients achieving mRS 0–2at 90 days (19 (39.6%) of those treated with stent-retrievers vs. 6 (22.2%) of those treated with “classical methods”). Mortality was lower among patients treated with stent-retrievers (14 (29.2% vs. 15 (55.6%) in those treated with “classical methods”, p=0.024). GCS score was independently associated with mRS at 90 days (OR:0.67; 95%CI:0.5–0.91; p=0.01).
ConclusionsIn patients with posterior circulation infarcts, treatment with stent-retrievers achieved high rates of recanalization and functional independence at 90 days. The rate of complications was similar to those reported in other studies. GCS is an independent predictor of functional independence at 90 days.
Valorar la tasa de recanalización, resultado funcional a 3 meses y factores pronósticos independientes de pacientes con ictus de circulación posterior (ICP) tratados mediante stent-retriever, comparándolos con una serie anterior tratada con “métodos clásicos”.
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo monocéntrico de pacientes consecutivos con ICP tratados con stent-retriever entre el 1 de diciembre de 2011 y el 1 de mayo de 2018. Las variables principales estudiadas son tasa de recanalización y escala mRS (Modified Rankin Scale) a 90 días. Se valoran datos demográficos, factores de riesgo cerebrovasculares, datos clínicos y origen probable. Se ha realizado un análisis estadístico descriptivo y un modelo de regresión logística binaria.
ResultadosGrupo stent-retriever (n=48), grupo “métodos clásicos” (n=27). Edad media de la serie actual 63,9 años (20,8% mujeres) con una puntuación media en el NIHSS (National Institute of Health Stroke Score) de 15,8 (rango intercuartílico [RIQ] 9–25) y una media en la escala de Coma de Glasgow (GCS) de 9,1 (RIQ 6–14,5). Se consiguió el 95,8% de recanalizaciones TICI 2b-3 (46/48) en el grupo actual frente al 55,6% (15/27) con “métodos clásicos” (p<0,0001). No existe diferencia significativa en la escala mRS 0–2 a 90 días [serie actual, 39,6% (19/48); serie previa, 22,2% (6/27)]. Hay diferencia significativa (p=0,024) en la mortalidad: serie actual, 29,2% (14/48); serie previa, 55,6% (15/27).
La GCS se relacionó de forma independiente con la mRS a 90 días (odds ratio, 0,67; intervalo de confianza, 0,5-0,91; p=0,01).
ConclusionesLos stent-retrievers logran elevadas tasas de recanalización en el ICP, con independencia funcional a los 3 meses y complicaciones similares a las de otros estudios. La GCS es un factor pronóstico independiente del resultado funcional a 90 días.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora