La artrosis erosiva es una patología infrecuente con tratamiento de escasa eficacia. A pesar de tratarse con magnetoterapia, no existe evidencia para su uso. Los objetivos son evaluar la eficacia de la magnetoterapia en pacientes con artrosis erosiva de manos en cuanto a dolor, comparándola con placebo, y determinar su seguridad.
MétodoEstudio experimental prospectivo, aleatorizado, doble ciego formado por grupo experimental (GI: tratamiento con magnetoterapia, 15 sesiones de 20min 5días/semana consecutivos) y grupo control (GC: placebo). Previo al tratamiento, al final y a los 3meses se evaluó el dolor con Escala Visual Analógica (EVA). Secundariamente, funcionalidad (escala Disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand [DASH]), rigidez (Índice Kapandji modificado), fuerza de prensión (dinamometría) y calidad de vida (cuestionario SF-36).
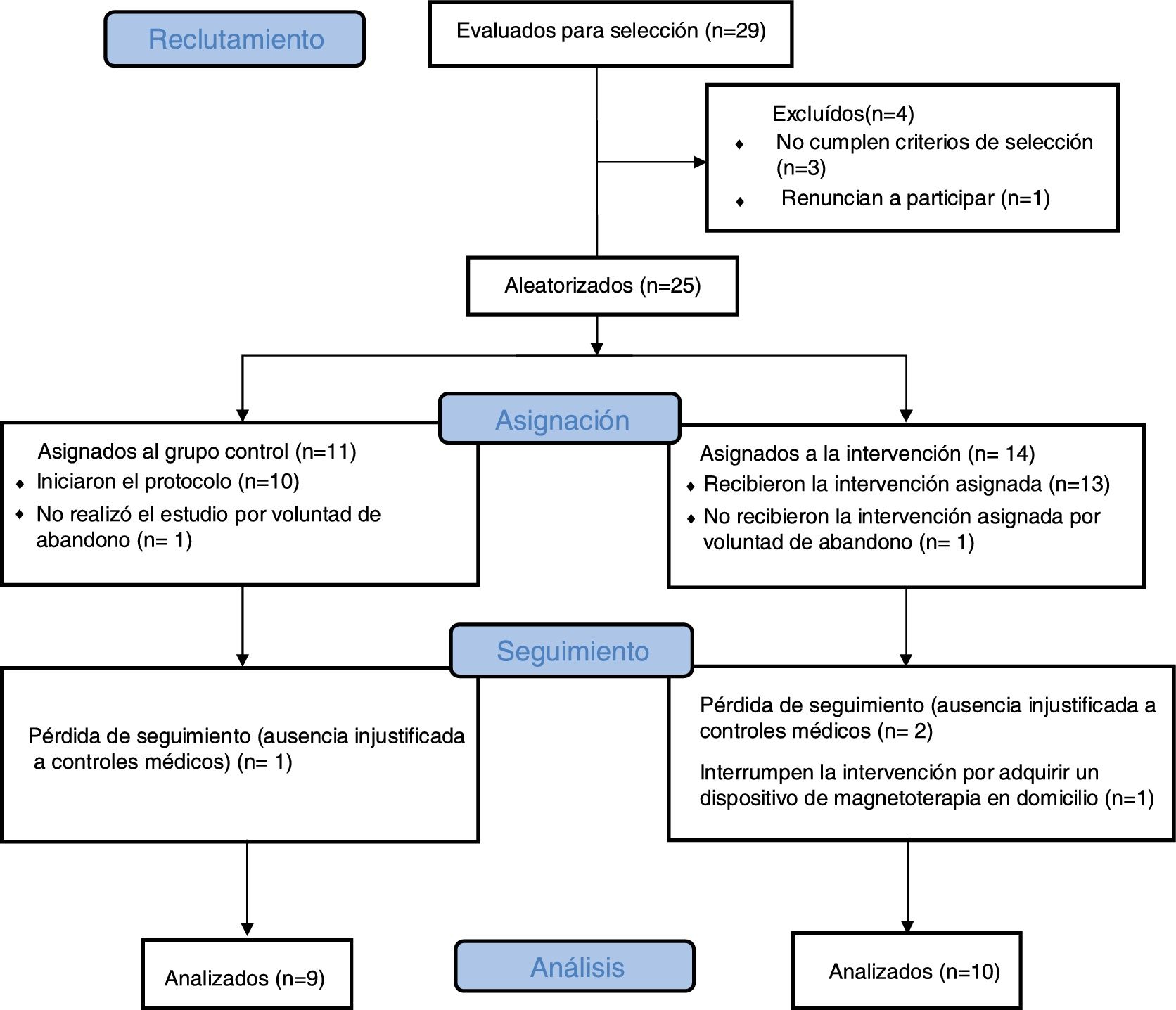
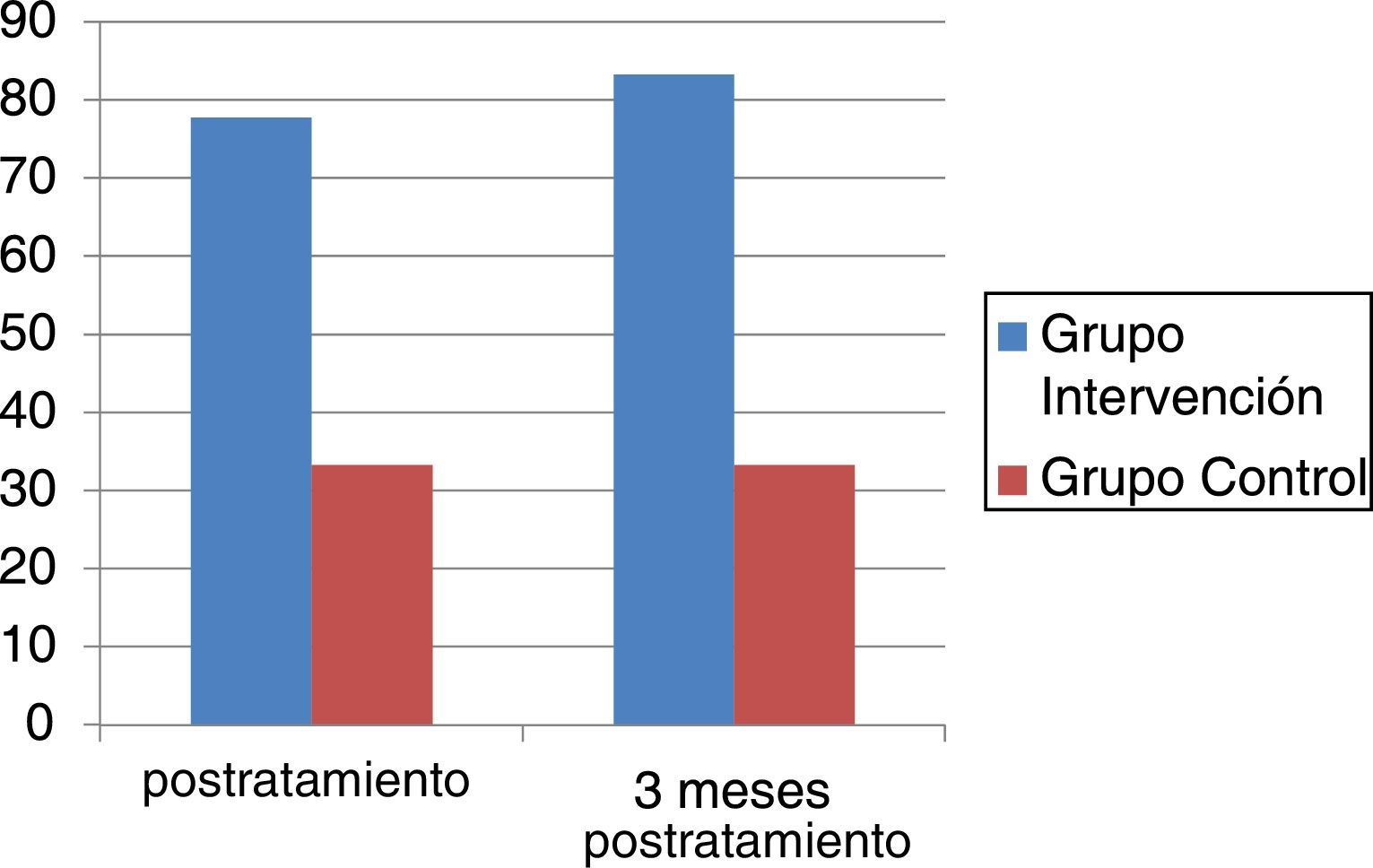
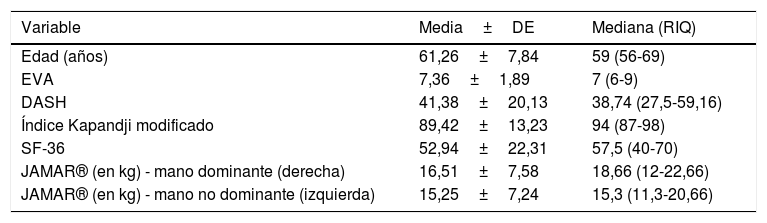
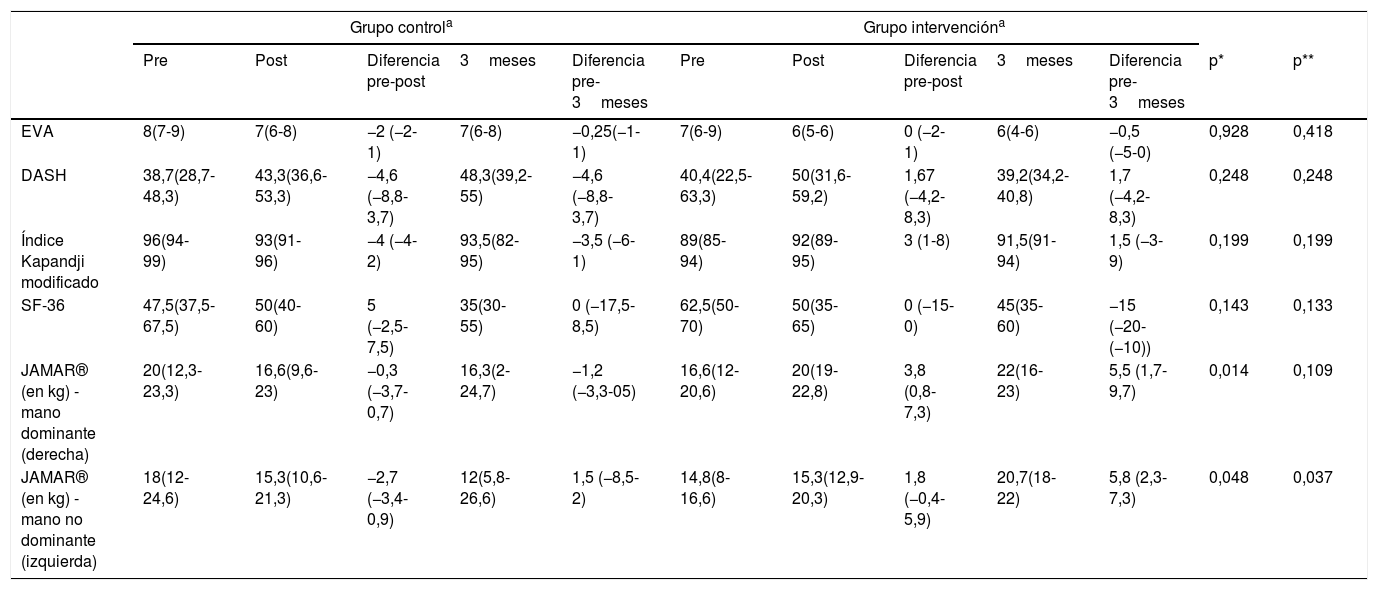
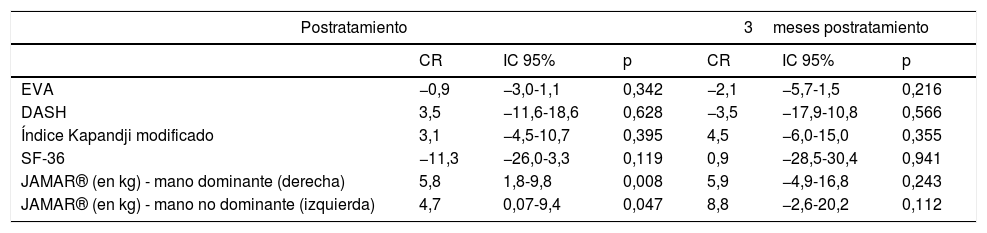
ResultadosDe 29 pacientes valorados se excluyeron 10, quedando 19, todas mujeres con una edad media de 59años. Se aleatorizaron 10 al GI y 9 al GC, siendo comparables. Se observó un mayor porcentaje de pacientes en el GI en relación con el GC con control del dolor (EVA<6) postratamiento y a los 3meses (77,8% vs. 33,3%, p=0,1 y 83,3% vs. 33,3%, p=0,2, respectivamente) y una tendencia a disminuir el dolor en el GI a los 3meses (coeficiente de regresión: −2,1 (IC 95%: −5,7-1,5; p=0,2). No hubo más diferencias excepto mayor fuerza de prensión en GI tanto en mano dominante como no dominante (p=0,01 y p<0,05, respectivamente). No se presentaron eventos adversos ni efectos secundarios.
ConclusiónEl tratamiento con magnetoterapia en pacientes con artrosis erosiva de manos es seguro y parece contribuir a una mejora clínica.
Erosive arthritis is an unusual pathology. Despite using magnetotherapy as a treatment, there is no evidence supporting its use.
The aim of the study is to evaluate magnetotherapy efficacy in patients suffering from hand erosive arthritis, compared to placebo, in terms of pain. Treatment safety will be also evaluated.
MethodProspective experimental double-blind randomized study consisting of an intervention group (IG: treatment with magnetotherapy: 15 20-minute-sesions 5 consecutive days per week) and a control group (CG: placebo). Treatment efficacy was evaluated at the end and 3 months after. We used Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for assess pain. Secondarily, functionality (The Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score), rigidity (Modified Kapandji Index), grip strength (dynamometry) and quality of life (SF-36 questionnaire) were assessed.
Results29 patients were evaluated. Due to exclusion criteria, there were 19 patients left, all women with an average age of 59. After randomization, 10 were awarded to IG and 9 to CG, being both comparable groups. A higher percentage of patients with pain controlled (VAS<6) was found in IG post treatment and after 3-months (77.8% vs 33.3%, p=0.1 y 83.3% vs 33.3%, p=0.2; respectively). A tendency to decrease VAS for IG at 3-months (regression coefficient: −2.1 (95% CI: −5.7-1.5; p=0.2) was showed. There were no other statistically significant differences, except a higher dynamometry results in IG, in both hands (p<0.01 and p<0.04 respectively). There were neither adverse effects nor secondary effects.
ConclusionMagnetotherapy treatment for hand erosive arthritis patients is safe and probably leads to clinical improvement.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora